Welcome to our comprehensive guide on resolving the pesky issue of broken registry items.
If you’ve ever encountered computer slowdowns, frequent errors, or unexplained crashes, these troublesome culprits may lurk within your system, impeding its optimal performance.
Fortunately, armed with the right knowledge and a systematic approach, you can swiftly identify and repair these broken registry items, rejuvenating your computer’s efficiency and stability.
In this article, we’ll dive into the world of registry items, shed light on their significance, and equip you with a proven method for resolving notoriously broken entries.
From understanding the basics to implementing effective solutions, we’ve got you covered every step of the way.
Before we embark on our journey toward a smoother computing experience, let’s start by unraveling the mysteries of broken registry items and their impact on your system’s performance.
Are you ready to regain control over your computer’s speed and reliability?💁
Let’s get started!
What Is Windows Registry? 🤔
Most Windows users never hear about Windows Registry—and are oblivious of its existence—until they experience broken Registry items.
This is because the registry does its work in the background. It is automatically enabled when you turn on your computer.
Windows Registry is the total of all databases containing options, settings, all the vital information, and values for hardware and software installed in the computer. Regardless of what version of Windows you are using, there is a Registry.
When you want to change, update, or upgrade software, the computer refers to the Registry to obtain relevant keys and values.
As you work with the software and make changes with it it, the Registry updates itself. The same applies to hardware installation and usage.
There are two important elements contained in the Registry: keys and values.
Keys and Values
Keys and values stored in the Registry contain all important computer software and hardware information. The keys and values are always obtained for changes to be made on the computer.
When you install software or hardware, the initial configuration settings are stored as keys and values. These settings include program location, version, and how to start the program.
Changes made to the configuration will be updated while the hardware or software is being used.
Regedit
Since most of the operation of the Registry is done automatically, you may be wondering if there is a way for you to manually make changes in the Registry or even view the entries in the Registry. This is why Regedit is important.
Regedit is a free utility included by default in every version of Windows. It is an editor for Windows Registry. It allows you to access and configure the Registry.
In reality, RegEdit is a component of the Registry. That part of the registry makes it possible for you to not only view but make changes in the Registry itself.
You access the Registry editor by executing the RegEdit from the command prompt or by using the search box in the start menu.
What Are Broken Registry Items?
By now, you’ll have seen how integral the Registry is to the everyday operation of your computer. It is a vital component in ensuring the computer’s stability, reliability, and high performance.
When there are problems with the Registry, it can have terrible effects on the general operation of the computer. Some of these problems in the registry are:
- Fragmentation and corruption. If some entries in the Registry are corrupted or invalid duplicates are made, it can cause errors in the computer.
- Garbage entries. Invalid entries in the Registry take up memory and storage space unnecessarily.
- Traces of programs improperly uninstalled.
- Traces of programs are improperly duplicated during updates or upgrades.
All these are what are referred to as broken Registry items.
The side effects of broken Registry items are reduced performance, reliability, stability, and system crash.
1. Reduced Performance
Broken Registry items make it take longer for each active process to reference the registry and receive or change registry entries. This means the software will run much slower on the computer, and all-around performance will be reduced.
2. Reduced Reliability
Due to duplicates and fragments, the Registry is larger than it should be. This increased size means the possibility of programs being unable to access their Registry entries is greater. Hence, programs will stop unexpectedly, and you will lose unsaved data.
3. Reduced Stability
As programs take longer to access their Registry entries, program freezes, and restarts become more frequent.
4. System Crash
If the damage in the Registry is excessive, it may even lead to a system crash. It is, therefore, important that you try to fix all problems as early as possible.
Causes of Broken Registry Items:-
Many things can cause broken Registry items. A few of them will be explained briefly.
1. Malware and Viruses
Whenever there is a problem with your computer, malware and viruses are usually among the suspects. That trend also continues with the problem of broken Registry items.
Some viruses attack and modify the Registry. Even when removed, remnants of the malware may remain. Clean up the registry to remove all traces of the virus.
2. Fragmented Registry
When you update or upgrade software, sometimes there are invalid duplicates of the software in the Registry. This makes the Registry size bigger than it should be and consumes the computer’s resources even more than is needed.
It is usually not a serious problem unless there are many fragments in the Registry.
3. System Shutdown Error
Every time you shut down the computer saves a copy of the Registry. If the system shuts down unexpectedly or experiences a crash, it can lead to serious broken Registry problems.
Methods To Fix Broken Registry Items
There are multiple possible fixes you can try to resolve all issues. You can try any of them, or a combination since only one method may not effectively resolve all problems.
These fixes aim to delete those fragments duplicates, and uninstall the remains; and resolve any other underlying issues. Here are some of these possible fixes explained.
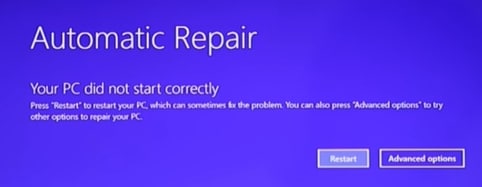
1. Use Automatic Repair
The feature that allows you to make automatic repairs is present in the newer versions of Windows. It attempts to fix broken Registry items by repairing any corrupt or invalid keys. Here are the steps involved in doing this.
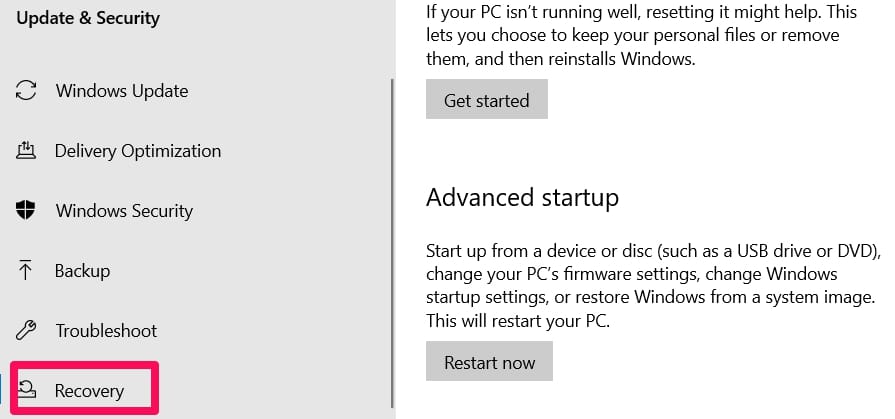
Open Settings. You can search for Settings using the search feature of the Start menu. Open the Settings panel, then enter its interface.
Click on Update and Security. Click on Recovery.
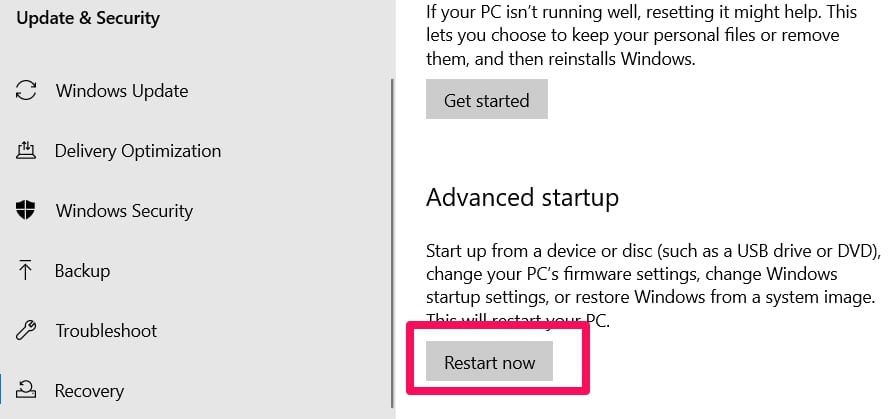
Under Recovery, go to the Advanced Startup and click Restart now.
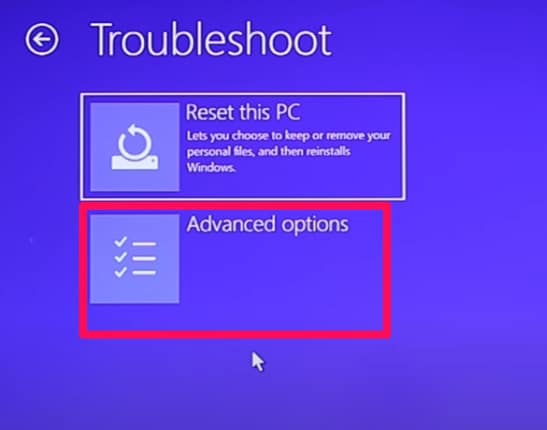
Wait for a little, when options appear, click Troubleshoot. Next, click Advanced options.
Click Automatic Repair/Startup repair.
- When asked to enter a recovery key in the automatic repair mode, do so, then click Continue.
- Wait while the Automatic repair diagnoses and does repairs. The computer may restart the process.
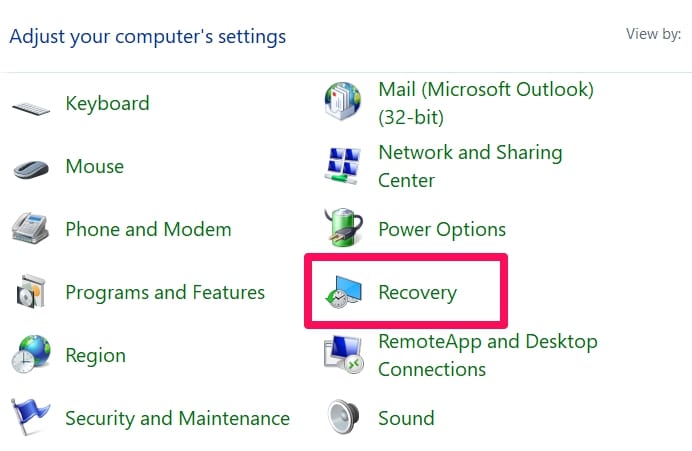
2. Use System Restore
System Restore helps to restore the system to a state it was before it began experiencing problems. This is particularly true if the problems are recent, or if they began after a recent installation or update.
If you enable System Restore, Windows will automatically create restore points whenever you make major changes such as installing software or drivers or making an upgrade. Restore points can be created manually also.
To try this method follow these steps:
Go to the Control panel. Select Recovery.
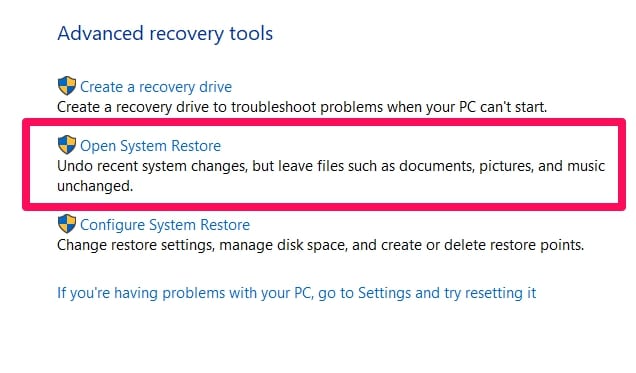
Under Advanced Recovery tools, choose Open System Restore.
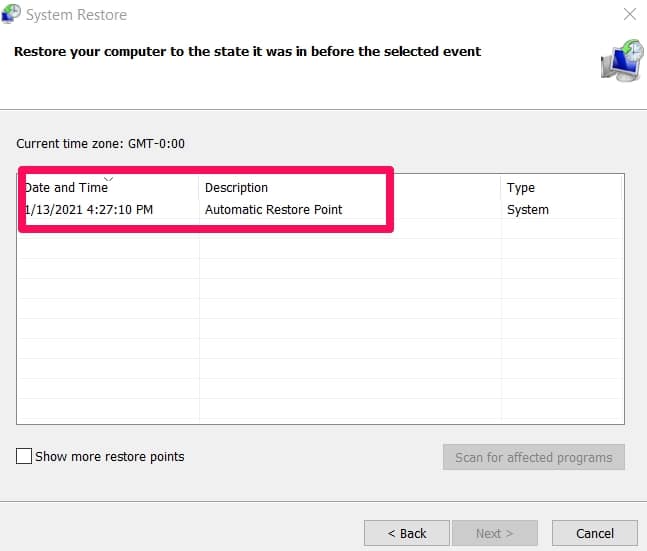
In the Restore system files and settings, click next. Select the restore point you want to use. Scan for affected programs and drivers. Click OK to proceed.
Click Next, then click Finish. Wait while system restore takes place. Restart the computer once it is completed.
3. Use System File Checker
This performs the repair in command prompt. File checker is a built-in tool in Windows to look for missing or corrupted files and make repairs. The steps involved are given below.
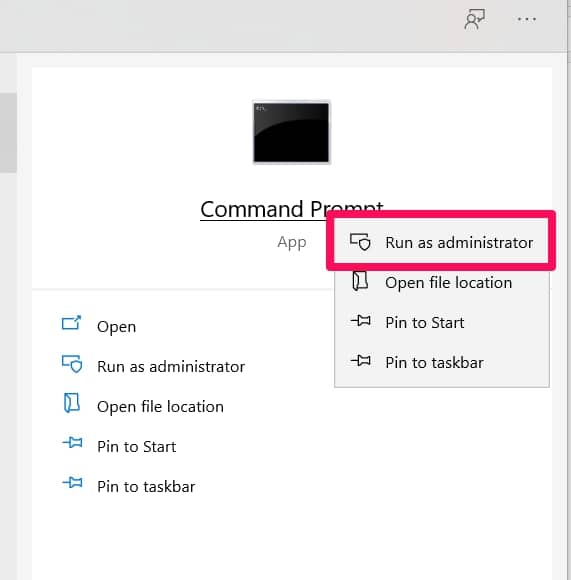
Type cmd or command prompt in the search bar
Right-click on the Command prompt and select Run as administrator to enter the command prompt interface.
Type the command: “sfc/scannow” without the quotes, then press Enter. This will help scan the protected system files. All damaged files will be replaced with cached copies.
Wait for the scan to be completed. Restart the computer after a scan.
4. Use DISM Command
This method can be used as a stand-alone solution or in combination with other methods. Here are the steps:
Run command prompt with administrator rights.
Use command: “DISM/Online/Cleanup-Image/ScanHealth” and press Enter.
Wait for the scan to be complete then restart your computer.
5. Resetting Windows System
Windows has a reset function. This reinstalls Windows. Follow these steps for the reset.
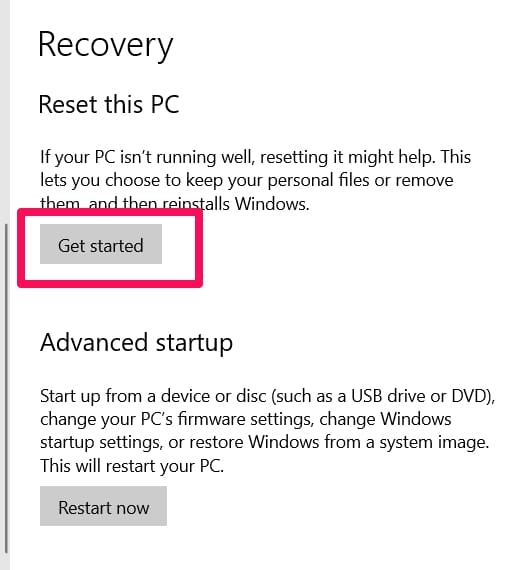
Go to Settings, click Update and Security, then click Recovery.
Under Reset, this PC, click Get started.
If you choose “Keep my files”, apps will be removed, but your files won’t. If you choose to Remove everything, then everything will be removed. Make sure to backup.
Choose either remove my files or Remove files and a clean drive.
Click Reset to begin. Make sure you read the reset information first.
After the reset, restart the computer.
How to Fix broken registry items on Windows 11
Is your Windows 11 system plagued by broken registry items? Fret not, as there are effective solutions to restore the integrity of your registry and ensure smooth performance.
Follow these steps to fix broken registry items in Windows 11 and reclaim the optimal functioning of your computer.
1. Create a System Restore Point: Before delving into any changes, it’s essential to create a system restore point to safeguard your system. In case any issues arise during the registry repair process, you can revert back to a stable state.
2. Utilize the Registry Editor: Windows 11 provides a powerful built-in tool called the Registry Editor. Access it by pressing Win + R, typing “regedit,” and hitting Enter. Exercise caution while making changes here, as modifying the wrong keys can lead to severe consequences.
3. Back up the Registry: Before making any modifications, it’s wise to create a backup of the registry. In the Registry Editor, click on File and choose Export. Save the backup file in a secure location, enabling easy restoration if needed.
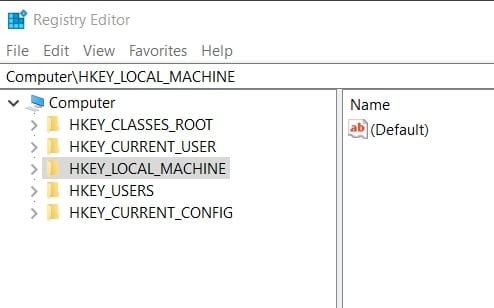
4. Identify Broken Registry Items: Navigate through the registry’s hierarchical structure, looking for invalid entries, orphaned keys, or corrupted values. Pay attention to areas such as HKEY_CURRENT_USER, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, and HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT.
5. Manually Fix Broken Items: To fix broken registry items manually, right-click on the problematic key or value and select the appropriate action. This could involve deleting, modifying, or repairing the entry. Exercise caution and ensure accuracy to avoid unintended consequences.
6. Use Reliable Registry Cleaning Software: For a more automated approach, consider utilizing reputable registry cleaning software. These tools scan your registry, identify broken items, and provide options for fixing them. Choose a reliable software with positive reviews and be cautious of potential scams.
7. Regularly Maintain and Monitor the Registry: Prevention is better than cure. To minimize the occurrence of broken registry items, adopt regular maintenance practices. Perform system scans, keep your operating system and applications up to date, and avoid installing untrusted software.
By following these steps, you can effectively fix broken registry items in Windows 11 and ensure the stability and performance of your system.
Remember, exercising caution and backing up your registry before making any changes is crucial. Stay proactive in maintaining a healthy registry to enjoy a smooth computing experience.
📗FAQ’s
Do I need to fix broken registry items?
If your computer is experiencing issues or errors, fixing broken registry items might be a good first step. However, not all broken registry items cause problems, and some items that registry cleaners label as “broken” might not be harmful.
So, it’s not always necessary to fix every single broken registry item that you come across.
What causes broken registry items?
Broken registry items can be caused by several things, including software that doesn’t uninstall completely, hardware driver issues, and malware infections.
In general, any time something goes wrong with a program or system component, it’s possible that the registry could be affected.
Is it safe to delete broken registry items?
In most cases, it is safe to delete broken registry items. However, it’s important to ensure you’re not deleting something important to your system’s functioning.
It’s also a good idea to create a backup of your registry before making any changes, just in case something goes wrong.
What program fixes broken registry items?
Several programs can fix broken registry items, including CCleaner, Auslogics Registry Cleaner, and Wise Registry Cleaner.
However, it’s important to research before using any registry cleaner, as some programs can cause more harm than good.
Should I worry about broken registry items?
In general, you do not need to worry too much about broken registry items. While they can potentially cause issues with your computer, many broken registry items are harmless and don’t cause any problems.
Can a broken registry slow down the computer?
Yes, broken registry items can potentially slow down your computer. However, the extent to which they affect your computer’s performance will depend on several factors, including how many broken registry items you have and which parts of the registry they affect.
How do I clean up a broken registry?
You can use a registry cleaner program to clean up a broken registry. However, it’s important to ensure that you’re using a reputable program and create a backup of your registry before making any changes.
How do I clean up my registry issues?
To clean up registry issues, you can use a registry cleaner program. However, it’s important to ensure that you’re not deleting anything important and that you create a backup of your registry before making any changes.
How often should you clean your registry?
There’s no hard and fast rule for how often you should clean your registry. Some experts recommend doing it once a month, while others say you only need to clean it if you’re experiencing problems with your computer.
Can broken registry cause crashes?
Yes, broken registry items can potentially cause crashes and other issues with your computer. However, the extent to which they affect your system will depend on several factors.
Does CCleaner fix broken registry items?
Yes, CCleaner is a program that can fix broken registry items. However, it’s important to use it carefully, as making changes to the registry can potentially cause issues with your computer.
Should I run a registry cleaner?
Whether or not you should run a registry cleaner depends on your situation. Running a registry cleaner might be a good idea if you’re experiencing issues with your computer and you suspect that the registry might be the cause. However, you might not need to do anything if everything is running smoothly.
What is the warning about editing the registry?
The warning about editing the registry is a cautionary message meant to prevent users from accidentally making changes to their system that could cause harm.
The registry is a sensitive part of the operating system, and making changes without understanding what you’re doing can potentially cause serious issues.
Is registry cleaner good or bad?
Whether a registry cleaner is good or bad depends on the program and how you use it. Some registry cleaners can be helpful in fixing issues and improving system performance, while others can cause more harm than good.
It’s important to research and use a reputable program if you decide to use a registry cleaner.
How do I know if my registry is corrupted?
If your registry is corrupted, you might experience various issues with your computer, including crashes, slow performance, and error messages. To determine if your registry is the cause of these issues, you can use a registry cleaner or diagnostic tool to scan for problems.
Is there a Windows registry Cleaner?
Yes, Windows includes a built-in registry cleaner called “Registry Editor”. However, it’s important to use this tool carefully, as making changes to the registry can potentially cause issues with your computer.
Is there a registry cleaner in Windows 10?
Yes, Windows 10 includes the Registry Editor, which allows users to view and edit the registry. However, as with previous versions of Windows, it’s important to use this tool carefully.
What is an alternative to registry cleaner?
If you’re looking for an alternative to a registry cleaner, consider using a system optimization tool like CCleaner or Advanced SystemCare. These programs can help clean up your system and improve performance without targeting the registry.
Is it safe to use CCleaner to clean the registry?
CCleaner is generally a safe program to clean the registry, as long as you use it carefully and make a backup of your registry before making any changes.
However, it’s important to note that CCleaner has had some security issues, so it’s important to keep the program updated and use it carefully.
Why shouldn’t you mess with the registry editor?
You shouldn’t mess with the registry editor unless you know what you’re doing, as making changes to the registry can potentially cause serious issues with your computer.
The registry is a sensitive part of the operating system, and making changes without understanding what you’re doing can potentially cause irreversible damage.
Does Windows have a free registry cleaner?
Yes, Windows includes the built-in Registry Editor tool, which allows users to view and edit the registry. However, as with any registry cleaner, it’s important to use this tool carefully and back up your registry before making any changes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dealing with broken registry items is crucial for maintaining the optimal performance of your computer system.
As we have explored throughout this article, broken registry items can lead to various issues such as slow performance, software crashes, and system errors.
By understanding the causes behind these broken items and implementing effective solutions, you can ensure a smooth and efficient computing experience.
Remember, prevention is key when it comes to broken registry items. Regularly scanning your registry for errors, using reputable registry cleaning software, and practicing safe computing habits can help keep your system in shape.
Don’t ignore the warning signs or wait for problems to escalate before taking action. Taking proactive steps to address broken registry items will enhance your computer’s performance and extend its lifespan.
Furthermore, if you’re unsure about handling registry issues alone, don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance.
Qualified technicians can diagnose and repair registry problems efficiently, ensuring your computer operates at its best.
Investing time and effort in maintaining a healthy registry is a small price to pay for the long-term benefits it provides.
You’ll enjoy improved system speed, stability, and overall performance by keeping your registry free from broken items.
So, take charge of your computer’s health today and say goodbye to the troubles caused by broken registry items. Your computer will thank you!