In today’s digital landscape, where security threats loom around every corner, safeguarding our online assets has become more critical.
One area that often falls prey to malicious attacks is the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP).
As a default gateway for remote connections, RDP provides convenient access to remote systems but presents a potential vulnerability if not properly protected.
To combat this vulnerability and fortify your defenses against cyber threats, it’s crucial to take proactive measures.
This article will explore a simple yet effective solution to enhance your network security: change the RDP default port.
By altering the default port used by RDP, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and thwart potential attacks.
We’ll guide you through making this change, empowering you to fortify your system’s defenses against intruders and ensuring a safer and more secure remote connection experience.
So, if you’re ready to elevate your security posture and shield your network from malicious actors, let’s dive into the step-by-step process of changing the RDP default port.
Prepare to take control of your remote access and embrace a more secure digital environment.
What is RDP (Remote Desktop Port)?🤷♂️
Before delving into how to change RDP default port, let me give a detailed explanation of RDP. If you are familiar with this, you can jump to the next session, where I take you on a step-by-step guide.
The Microsoft proprietary protocol known as RDP or Remote Desktop Port enables remote access or computer connections.
It does this using the default TCP 3389 port. The protocol makes use of an encrypted channel to provide network access.
This protocol is especially important to network admins who find it useful for login servers, diagnosing issues, and performing other remote operations.
Users would also find it beneficial for remotely access an organization’s network, using files and services remotely.
CTAs or Cyber threat actors/hackers also find this a very important tool and would use the protocol to gain access to devices and networks in cases where RDP ports are misconfigured.
Once in, they have access to the entire network and can escalate user privileges, access sensitive and confidential files, inject malware and gain access to vital credentials.
When CTAs use this protocol, they can keep a low profile especially since they use a trusted network service. Using a range of tools, they would be able to scan internet devices for open RDP ports.
Once these are located, with some brute force, they may gain access to a vulnerable organization’s network. Unfortunately, in the black market of the dark web, many compromised credentials for Remote Desktop Ports are on sale.
The MS-ISAC in 2018 documented a spike in ransomware variants. Most of these were seen to be strategically targeted at networks through poorly secured or misconfigured RDP ports and in some cases, password brute force attacks.
Recommendations For RDP
Examine the requirement for RDP, port 3389, to be open on workstations and, if necessary, do the following:
- Install a firewall before any machine with an active RDP port and demand users to connect through a VPN.
- To protect against brute-force attacks, use multi-factor authentication, strong passwords, and account lockout rules.
- Connections to certain trustworthy hosts should be whitelisted.
- If feasible, limit RDP logins to approved non-administrator accounts. Follow the principle of lowest privilege, making sure that users only have the access they need to do their tasks;
- Keep a journal and go over it afterward. RDP login attempts should be checked for unusual behavior and kept for at least 90 days. Ensure that this service is only accessible by authorized users.
If RDP isn’t needed, make sure the ports are protected frequently.
Make sure the cloud-based solutions follow your cloud service provider’s best practices. After you’ve set up your cloud infrastructure, make sure RDP ports aren’t activated unless it’s for special reasons.
Activate automatic updates on the operating system to ensure the client and server software is up to speed.
Change RDP Default Port: Step-By-Step
The first step of this process is changing the RDP port in the registry.
Here is the process for it:
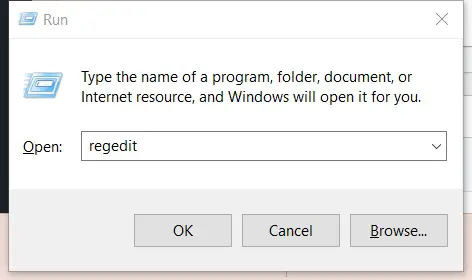
Step 1:- Open your registry Editor (Regedit) – Use the keyboard hotkey Windows + R to open the run box where you should type in “Regedit” followed by hitting enter or clicking the OK button.
When the registry editor opens, navigate to the following location on your left pane:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp
After clicking on RDP-TCP, select the port number option at the right pane.
You should get a pop-up box. In the Value data textbox, edit the values for the new port number update it with 3489 or some other value you choose and click OK. You would have to select the Decimal radio bottom before doing this.
Step2:-
Now we are done with the “Change RDP Default Port” process on the registry, you could close the registry and proceed to the next stage of the process.
This next step would make sure that traffic can pass through the newly assigned Remote Desktop Port.
Here are the steps:
On your Windows 10, navigate Control Panel, All Control Panel Items, and Windows Firewall.
On the left pane, select the option for Advanced Setting.
On the left pane of the new window, select the option for inbound rules, then click on the new rule option.
On the first window that appears, select the port option and click the next bottom.
On the next window, select the “TCP” protocol option (this may be the default). Change the value of the “Specific local ports” option to the value of the updated RDP you created on the registry. After this, click on the Next button.
When the next window appears, leave all the settings in the defaults and click on the Next button.
After this, you would have the option to apply the rule to all your network profiles, click the Next button.
In the next screen that appears you would need to type a recognizable name in the name textbox. You should choose any name that you like for this section. Once it is done, click the Next button again.
Once this is done, you would have to start the steps all over from when you created a new inbound rule. When you get to the step where you selected TCP, this time, select the option for UDP.
Restart your PC after establishing the 2 (two) incoming rules, and you’ll be able to connect to your computer from a remote desktop using the newly created port number.
Suppose you are using the custom RDP port number 8888 then you need to put the port like Remote_IP_address:8888
📗Change RDP Default Port FAQ📗
How do I change my default RDP port?
To change the default RDP port, you need to edit the registry settings on your computer.
You can do this by accessing the Registry Editor, navigating to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp subkey, and changing the value of the PortNumber key to the desired port number.
How do I change my default RDP port on Windows 10?
To change the default RDP port on a Windows 10 computer, you need to follow the same steps as changing the default RDP port on any other version of Windows.
You can do this by accessing the Registry Editor, navigating to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp subkey, and changing the value of the PortNumber key to the desired port number.
How do I change my RDP port 3389?
To change the RDP port from the default value of 3389, you need to edit the registry settings on your computer.
You can do this by accessing the Registry Editor, navigating to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp subkey, and changing the value of the PortNumber key to the desired port number.
How do I change my default port from 3389 to 3390?
To change the default RDP port from 3389 to 3390, you need to edit the registry settings on your computer. You can do this by accessing the Registry Editor, navigating to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp subkey, and changing the value of the PortNumber key to 3390.
Should I change the default RDP port?
Changing the default RDP port can help improve security by making it harder for attackers to identify and target your system.
However, it is not a foolproof method of securing your system, and it is important to take other security measures, such as using strong passwords and enabling network-level authentication.
Is RDP port open by default?
Yes, RDP port 3389 is open by default on most Windows systems. This can be a security risk, making it easier for attackers to target your system.
How do I change my RDP settings?
You can change your RDP settings by accessing your computer’s Remote Desktop Connection client, clicking the “Show Options” button, and then navigating to the “Advanced” tab. From there, you can change various settings, including the display settings, audio settings, and more.
How do I know what port my RDP is listening on?
You can determine the port number RDP is listening on by accessing the Registry Editor, navigating to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp subkey, and looking at the value of the PortNumber key.
What is the default RDP port in Windows 10?
The default RDP port in Windows 10 is also 3389.
How can I tell if RDP port 3389 is open?
You can use a port scanner tool like Nmap to determine if RDP port 3389 is open. Alternatively, check the Windows Firewall settings to see if the port is allowed.
Can default port number be changed?
Yes, the default port number can be changed by editing the registry settings on your computer. By default, RDP listens on port 3389, but you can change this to any port number you wish.
How do I change my default port from 80 to 8080?
To change the default port from 80 to 8080, you need to modify the web server configuration file you are using. This will vary depending on which web server you are using but generally involves changing the port number in the server configuration file and restarting the web server.
Does changing RDP port make it more secure?
Changing the RDP port can help improve security by making it harder for attackers to identify and target your system.
However, it is not a foolproof method of securing your system, and it is important to take other security measures, such as using strong passwords and enabling network-level authentication.
Can RDP use other ports?
Yes, RDP can use other ports besides the default port, 3389. You can change the port number that RDP uses by editing the registry settings on your computer.
Is RDP default TCP or UDP?
RDP uses TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) by default.
Is Remote Desktop port 3389 or 443?
Remote Desktop port is typically 3389, although it is possible to configure RDP to use other ports.
How do I make my RDP more responsive?
To make RDP more responsive, you can try several things, such as disabling unnecessary visual effects, reducing the display resolution, and closing any unnecessary applications running on the remote desktop. You can also try adjusting the connection speed settings in the Remote Desktop Connection client.
Can I change RDP IP?
Yes, you can change the IP address that RDP uses by modifying the network settings on your computer.
What are RDP settings?
RDP settings are configuration options that control how Remote Desktop Protocol operates. These include display settings, audio settings, device redirection settings, and more.
On what port is the remote server running?
The port that the remote server is running on depends on how it is configured. By default, most servers run on port 80 (HTTP) or port 443 (HTTPS), but it is possible to configure servers to use other ports.
How do I know if my remote server port is open?
You can use a port scanner tool like Nmap to determine if a specific port is open on a remote server.
Why is my RDP port not opening?
There are several reasons why an RDP port may not be opening, including firewall issues, network configurations, or incorrect settings on the remote computer.
How to configure RDP in Windows?
To configure RDP in Windows, you must enable Remote Desktop and configure the necessary settings. This can be done through the System Properties window or the Local Group Policy Editor.
How do I change the RDP port in Windows Firewall?
To change the RDP port in Windows Firewall, you must create a new rule allowing incoming traffic on the new port number. You can do this through the Windows Firewall settings in the Control Panel.
Is RDP port 3389 exposed to the Internet?
RDP port 3389 is exposed to the internet by default on most Windows systems. This can be a security risk, making it easier for attackers to target your system.
Is port 3389 RDP secure?
Port 3389 is not inherently secure, as it is susceptible to brute force attacks and denial-of-service attacks. However, you can take steps to improve RDP security, such as changing the port number and enabling network-level authentication.
How do I test port 3389?
You can test port 3389 using a port scanner tool, such as Nmap. Alternatively, you can use the telnet command to connect to the port and see if it is open.
For example, you can open a command prompt and type “telnet <ip-address> 3389” to attempt to connect to the RDP port on the specified IP address.
How do I change the RDP port in Windows Server 2016?
To change the RDP port in Windows Server 2016, you need to edit the registry settings on the server.
You can do this by accessing the Registry Editor, navigating to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp subkey, and changing the value of the PortNumber key to the desired port number.
Creating a new inbound rule in the Windows Firewall would be best to allow traffic on the new port number.
To create the new inbound rule in Windows Firewall, you can open the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security tool and create a new rule that allows incoming traffic on the new port number.
Alternatively, you can use the netsh command to create the new rule from the command line.
For example, you can open a command prompt and type “netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=<name> dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=<port-number> profile=any” to create a new inbound rule that allows incoming traffic on the specified port number.
Once you have changed the port number and created the new inbound rule, you must restart the Remote Desktop Services to apply the changes.
Does (RDP) Remote Desktop use any additional ports to transmit traffic?
The one port specified above will be used for primary remote desktop communication. Streaming will be tried directly over UDP if sound is enabled. If this connection isn’t possible, Remote Desktop will use the primary remote desktop port to transmit sound via a virtual channel.
Why do you get an error message that says “Insufficient privileges”?
You do not have permission to connect to the session you are attempting to connect to. You’re probably attempting to login to an administrator session.
Administrators can only access the console. In the remote desktop’s advanced settings, be mindful that the console switch is disabled. Please contact your system admin for additional help if this is not the cause of the issue.
What caused the “Access Denied” error?
The Remote Desktop Gateway generates the “Access Denied” error due to improper credentials being entered during the connection attempt. Double-check that you have the correct password and username are correct.
If the connection functioned before but the problem happened later, it’s possible that you modified the Windows user account credentials and it has not been updated it in the remote desktop settings yet.
Final Words on Change RDP Default Port
In conclusion, changing the default port for Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a vital step in enhancing the security of your system.
Implementing this simple adjustment can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and potential attacks on your network.
Remember, the default RDP port is well-known to hackers, making it an easy target for malicious activities. Following the steps outlined in this article, you can safeguard your system and protect sensitive information from potential threats.
Changing the RDP default port involves a straightforward process, requiring you to modify the registry settings and update your firewall rules.
While it may seem like a minor adjustment, its impact on your system’s security is substantial. Choosing a unique and less predictable port makes it much harder for potential attackers to locate and exploit your RDP services.
Take proactive measures to ensure the safety of your system by following the guidelines in this article. Protecting your network from unauthorized access is crucial in today’s interconnected world, where cyber threats continue to evolve.
By making the necessary changes to your RDP default port, you fortify your system’s defenses and reduce the likelihood of falling victim to malicious activities.
Don’t wait until it’s too late. Implement the change today and enjoy the peace of mind of knowing your system is protected. Security is an ongoing process; staying ahead of potential threats is key.
By being proactive and securing your RDP connection, you are taking an important step toward safeguarding your digital environment.
Embrace the power of change and prioritize the security of your system by changing the RDP default port now.

























![How To Change RDP Default Port [Step-By-Step Guide]](https://technicalustad.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/rdp-.jpg)
![How To Change RDP Default Port [Step-By-Step Guide]](https://technicalustad.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/pnumber.jpg)
![How To Change RDP Default Port [Step-By-Step Guide]](https://technicalustad.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/decimal.jpg)
![How To Change RDP Default Port [Step-By-Step Guide]](https://technicalustad.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/firewall.jpg)
![How To Change RDP Default Port [Step-By-Step Guide]](https://technicalustad.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/advanced-settings.jpg)
![How To Change RDP Default Port [Step-By-Step Guide]](https://technicalustad.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/new-rule.jpg)
![How To Change RDP Default Port [Step-By-Step Guide]](https://technicalustad.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/next.jpg)
![How To Change RDP Default Port [Step-By-Step Guide]](https://technicalustad.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/val.jpg)
![How To Change RDP Default Port [Step-By-Step Guide]](https://technicalustad.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/udp.jpg)
![How To Change RDP Default Port [Step-By-Step Guide]](https://technicalustad.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/chnage-rdp-port.jpg)

