In a world where businesses are swiftly moving their operations to the cloud, the necessity for effective monitoring tools has never been more acute.
Ensuring the smooth operation of your applications, analyzing performance data, and maintaining security and compliance are vital aspects of any organization’s cloud strategy.
Yet, when it comes to choosing between the popular Amazon Web Services (AWS) monitoring tools, CloudTrail and CloudWatch, it can be perplexing. The question remains: which tool is better for your specific needs?
AWS offers two potent services, CloudTrail and CloudWatch, for monitoring your cloud environments. Each comes with its unique set of features, capabilities, and use cases.
Selecting the wrong tool could mean missing critical insights into your application’s performance, increasing vulnerability to security threats, or even non-compliance with regulatory standards. Therefore, understanding the nuances between CloudTrail and CloudWatch is essential to optimizing your cloud operations.
This comprehensive guide will delve into an in-depth comparison between CloudTrail and CloudWatch. By exploring their definitions, features, use cases, and how they work, we’ll equip you with the knowledge you need to make an informed decision.
Whether focused on security analysis, compliance auditing, resource monitoring, or performance optimization, this article will help you discern which tool, CloudTrail or CloudWatch, suits your organization’s unique needs.
Let’s demystify the “CloudTrail vs CloudWatch” debate once and for all.
What is AWS CloudTrail?
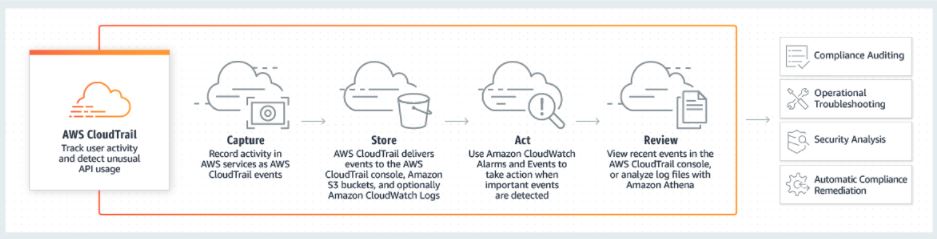
CloudTrail, an integral component of the Amazon Web Services (AWS) suite, is a sophisticated service designed to provide comprehensive visibility and control over the activities within an AWS account. Its core objective revolves around capturing and logging API calls and associated events across the vast AWS infrastructure.
By diligently recording these crucial interactions, CloudTrail empowers organizations with an invaluable audit trail, enriching their compliance, security, and operational analysis endeavors.
Key Features of CloudTrail:-
1. Comprehensive Logging
CloudTrail sets itself apart by offering meticulous logging capabilities, meticulously capturing every API call and event with remarkable attention to detail.
From identifying the entity initiating the call to the precise timestamp, source IP address, executed actions, and the specific resources involved, CloudTrail leaves no stone unturned.
This comprehensive logging ensures meticulous accountability and streamlines troubleshooting processes by providing a reliable reference point for unexpected issues or potential security breaches.
2. Centralized Management
One of the standout features of CloudTrail lies in its ability to consolidate logs from multiple AWS accounts and regions into a centralized Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) bucket.
This centralized management approach simplifies log aggregation, facilitating efficient analysis and allowing organizations to maintain a cohesive, panoramic view of their AWS activities. By embracing this centralized model, businesses gain the advantage of unified log management, significantly improving their operational efficiency.
3. Real-time Monitoring
CloudTrail is not merely a passive logging mechanism; it offers proactive real-time monitoring capabilities that enable organizations to set up custom notifications and triggers for specific events or activity patterns.
By harnessing this functionality, businesses can swiftly detect unauthorized or suspicious actions, triggering immediate response and mitigating potential security threats. This real-time monitoring empowers organizations with heightened situational awareness, ensuring a proactive security posture.
4. Integrations and Analysis
CloudTrail seamlessly integrates with various AWS services, including AWS CloudWatch, AWS Config, and AWS Lambda, unlocking advanced analysis, monitoring, and automation capabilities.
These integrations empower organizations to gain deeper insights into their AWS environment, enforce robust security policies, and automate compliance audits. By harnessing the power of these integrations, businesses can maximize their AWS investment while enhancing their operational efficiency and security posture.
5. Simplified Compliance
Navigating the complex landscape of compliance requirements can be a formidable challenge for organizations. However, CloudTrail is a potent ally in this realm, providing a critical tool to meet regulatory obligations defined by governing bodies.
The detailed logs captured by CloudTrail play a pivotal role in fulfilling audit requirements, effectively demonstrating regulatory compliance, and conducting thorough investigations into potential security incidents. By leveraging CloudTrail’s capabilities, businesses can simplify compliance efforts and establish a strong foundation for a secure and resilient AWS infrastructure.
In conclusion, CloudTrail is a formidable solution that empowers organizations to enhance their AWS environment’s transparency, accountability, and security.
Through its comprehensive logging, centralized management, real-time monitoring, powerful integrations, and simplified compliance mechanisms, CloudTrail delivers a robust framework for monitoring, auditing, and maintaining the integrity of AWS-based infrastructures.
Use Cases of AWS CloudTrail
AWS CloudTrail provides organizations with a powerful toolset for monitoring, auditing, and securing their AWS environments. With its comprehensive logging and advanced features, CloudTrail offers many use cases that address key business needs.
Let’s explore some of the prominent use cases of CloudTrail:
1. Security and Threat Detection
CloudTrail is a vital component in bolstering the security of AWS environments. By capturing and logging API calls and related events, it creates a comprehensive audit trail that aids in identifying potential security threats.
The detailed information recorded by CloudTrail, such as the identity of the entity making the API call, the timestamp, and the source IP address, enables organizations to detect and investigate unauthorized access attempts, potential malicious activities, and security breaches.
CloudTrail empowers security teams to respond swiftly to threats and take necessary remedial actions, thereby enhancing the overall security posture of the AWS infrastructure.
2. Compliance and Audit
Achieving and maintaining regulatory compliance is a top priority for organizations across industries. CloudTrail simplifies compliance by capturing and storing detailed API calls and events logs. These logs serve as concrete evidence during audits and help demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements.
The comprehensive logging capabilities of CloudTrail enable organizations to meet various compliance standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
CloudTrail’s centralized management allows for easy access and retrieval of logs, significantly easing compliance efforts.
3. Operational Troubleshooting
In complex AWS environments, operational issues can impact performance and availability. CloudTrail is crucial in troubleshooting, providing detailed visibility into API calls and events. Operations teams can leverage CloudTrail logs to trace the sequence of actions leading to an issue, helping them identify the root cause more efficiently.
This insight speeds up troubleshooting, reduces downtime, and enhances operational efficiency. Organizations can take corrective measures promptly and maintain a robust AWS infrastructure by pinpointing the source of issues.
4. Change Management and Resource Tracking
Effective change management is crucial for maintaining a secure and stable AWS infrastructure. CloudTrail helps organizations manage changes and track modifications made to AWS resources by capturing the associated API calls.
These logs provide a comprehensive record of resource changes, enabling organizations to review and validate alterations by change management processes.
By monitoring resource changes through CloudTrail, organizations can ensure compliance, prevent unauthorized modifications, and maintain an accurate inventory of resources.
5. User Activity Monitoring
CloudTrail facilitates monitoring and managing user behavior within an AWS account. Organizations can utilize CloudTrail logs to track user activity, including API calls performed, actions taken, and frequency of activities.
This level of visibility enables organizations to enforce security policies, identify potential insider threats, and ensure adherence to best practices. By leveraging CloudTrail’s user activity monitoring capabilities, organizations can detect suspicious behavior, enforce access controls, and maintain a secure environment.
6. Incident Response and Forensics
CloudTrail logs are vital in incident response and forensic investigations during security incidents or suspected breaches. By analyzing the captured logs, security teams can reconstruct the sequence of events, determine the source of an attack, and assess the impact.
CloudTrail’s real-time monitoring capabilities allow for the immediate detection of suspicious activities, enabling rapid incident response and containment of potential damage.
The detailed information provided by CloudTrail logs helps organizations perform thorough forensic analysis, aiding in investigations and supporting legal proceedings if necessary.
7. Governance and Risk Management
CloudTrail contributes to effective governance and risk management by providing a comprehensive record of activities and events within an AWS environment.
These logs offer insights into user behavior, resource changes, and system-level events, which organizations can leverage to enforce security policies, maintain data integrity, and manage risks effectively.
By analyzing CloudTrail logs, organizations can identify potential vulnerabilities, implement appropriate controls, and improve their overall governance framework.
8. Automated Compliance and Security Analysis
CloudTrail’s integration with other AWS services, such as AWS Config, AWS CloudWatch, and AWS Lambda, opens up automated compliance and security analysis opportunities.
Organizations can leverage CloudTrail logs alongside these services to perform continuous monitoring, automate compliance checks, and detect security anomalies.
By combining the power of CloudTrail with other AWS services, organizations can strengthen their security posture, reduce manual efforts, and enhance their overall AWS governance.
In summary, AWS CloudTrail offers a wide range of use cases that cater to the security, compliance, operational, and governance needs of organizations. It’s comprehensive logging, advanced features, and seamless integration with other AWS services make it an invaluable tool for monitoring, auditing, and securing AWS environments.
By leveraging CloudTrail’s capabilities, organizations can proactively identify security threats, maintain regulatory compliance, streamline troubleshooting processes, and enhance their overall governance and risk management practices.
How AWS CloudTrail Works
Understanding how CloudTrail works is crucial for organizations seeking to enhance their security, compliance, and operational analysis capabilities.
Let’s delve into the intricacies of CloudTrail’s operation:
Data Collection: CloudTrail leverages AWS infrastructure to capture data on API activity. Whenever an API call is made within an AWS environment, CloudTrail captures the event and its relevant details. This includes information such as the identity of the caller, the actions performed, and the resources involved.
Logging and Storage: The captured API activity data is then logged and stored in Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service). CloudTrail provides the flexibility to choose the desired S3 bucket for storing the logs, enabling organizations to centralize and consolidate logs from multiple AWS accounts and regions.
Event Notification: CloudTrail can send real-time event notifications through Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS). Organizations can configure CloudTrail to send notifications to designated endpoints whenever specific events occur, enabling timely response to critical activities within the AWS environment.
Access Control and Encryption: CloudTrail integrates with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to ensure data security. IAM allows organizations to define fine-grained access control policies for CloudTrail, restricting access to logs based on user roles and permissions. Additionally, CloudTrail supports encryption of log files using AWS Key Management Service (KMS), ensuring data privacy and compliance.
Log Analysis and Retrieval: Once the logs are collected and stored, organizations can analyze and retrieve them for various purposes. CloudTrail logs can be accessed directly from the S3 bucket, or organizations can utilize services like AWS CloudWatch Logs or third-party log analysis tools for efficient log analysis, monitoring, and alerting.
Integrations: CloudTrail integrates with other AWS services to enhance monitoring and analysis capabilities. Organizations can leverage integrations with AWS CloudWatch to set up alarms and monitor specific API activities, AWS Config for configuration change tracking, and AWS Lambda to automate custom actions based on specific events captured by CloudTrail.
Log File Integrity Validation: CloudTrail generates digital signatures for each log file using SHA-256 hashing to ensure the integrity of log files. These signatures enable organizations to verify the authenticity and integrity of log files, ensuring the logs haven’t been tampered with or modified.
Log Retention and Archival: CloudTrail provides flexibility in defining the retention period for log files, allowing organizations to meet their specific compliance and auditing requirements. Organizations can also configure Amazon Glacier for long-term archival of CloudTrail logs, ensuring data is securely preserved for extended periods.
Global Services and Multi-Region Support: CloudTrail supports AWS global services, such as Amazon S3, Amazon EC2, and AWS Lambda, as well as region-specific services. Organizations can enable CloudTrail in multiple AWS regions, capturing and logging API activity across their global infrastructure.
CloudTrail Insights: CloudTrail offers an additional feature called CloudTrail Insights, which utilizes machine learning algorithms to analyze CloudTrail logs and identify anomalous activity patterns. This feature helps organizations proactively detect and respond to security threats or operational issues.
In summary, AWS CloudTrail captures API calls and related events within an AWS environment, logs them, and stores them in an S3 bucket. The logs can then be analyzed, monitored, and retrieved for security, compliance, and operational analysis purposes.
With its seamless integration with other AWS services, support for global and regional services, and features like CloudTrail Insights, CloudTrail provides organizations with enhanced visibility and control over their AWS environments, strengthening their security posture, ensuring compliance, and optimizing operational efficiency.
What is CloudWatch?🤷♂️
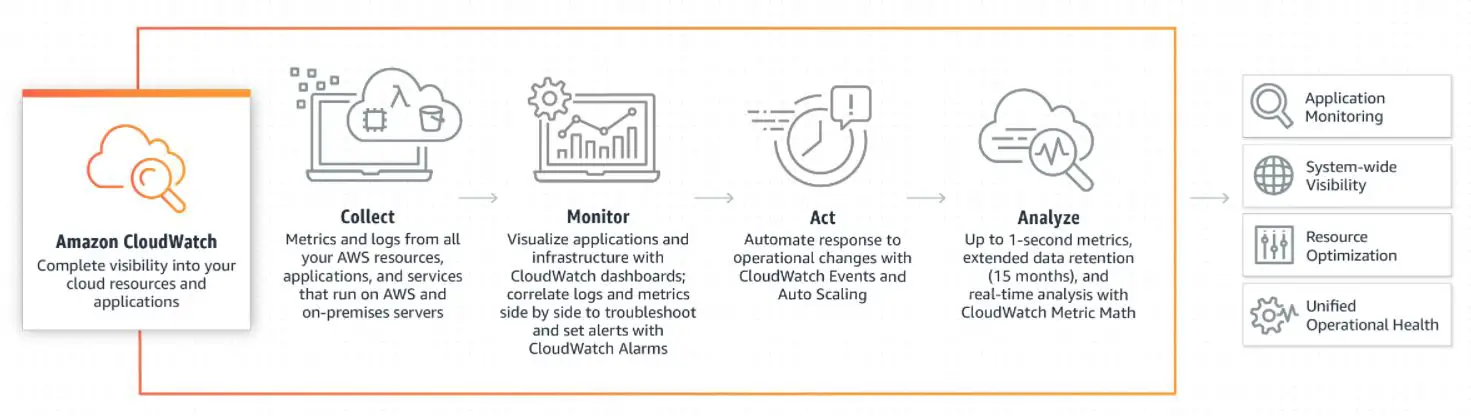
CloudWatch is a comprehensive monitoring and management service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that enables organizations to monitor their AWS resources, applications, and services in real-time.
It offers various features to help organizations gain insights, ensure optimal performance, and take proactive actions in their AWS environments.
At its core, CloudWatch is designed to collect and track metrics and logs from various AWS resources and applications. These metrics and logs are then stored, monitored, and analyzed to provide valuable insights into the health, performance, and operational status of AWS resources.
The primary purpose of CloudWatch is to help organizations gain visibility and gain control over their AWS resources and applications. By collecting and monitoring metrics and logs, CloudWatch enables organizations to monitor performance, troubleshoot issues, optimize resource utilization, and ensure operational efficiency.
Features of CloudWatch:-
1. Metric Collection and Monitoring
CloudWatch enables the collection of metrics from a wide range of AWS resources, including EC2 instances, RDS databases, S3 buckets, and more. These metrics provide essential data points for resource utilization, performance, and operational health.
CloudWatch continuously monitors these metrics and provides real-time visualizations, enabling organizations to gain immediate insights and respond to potential issues promptly.
2. Dashboards and Alarms
CloudWatch allows organizations to create customizable dashboards that consolidate relevant metrics and provide a consolidated view of the AWS resources and applications. Dashboards help visualize key performance indicators and enable at-a-glance monitoring.
Additionally, CloudWatch enables the creation of alarms based on predefined thresholds or custom conditions. These alarms notify organizations of specific events or conditions, ensuring proactive response to critical situations.
3. Logs Collection and Analysis
CloudWatch provides a centralized platform for collecting, storing, and analyzing logs from various AWS services and applications. Organizations can configure their resources to send logs to CloudWatch Logs, where they can be searched, analyzed, and monitored.
This allows for easy troubleshooting, performance analysis, and security investigations. CloudWatch Logs Insights further enhances log analysis capabilities by providing advanced querying and analysis features.
4. Automated Actions and Scaling
CloudWatch enables organizations to automate actions based on predefined conditions using Amazon CloudWatch Events. Organizations can create rules to trigger actions, such as scaling EC2 instances based on CPU utilization, automatically stopping or starting instances, or invoking AWS Lambda functions.
This automation helps ensure that resources are efficiently utilized and that applications can automatically respond to changing demands.
5. Resource Optimization
CloudWatch provides valuable insights into resource utilization, enabling organizations to optimize their AWS environment. With CloudWatch, organizations can identify idle or underutilized resources, optimize database performance and right-size instances, and make informed decisions to optimize cost and operational efficiency.
6. Integration with Other AWS Services
CloudWatch seamlessly integrates with other AWS services, allowing organizations to enhance monitoring and management capabilities. Integration with AWS Lambda, AWS CloudTrail, and AWS X-Ray allows for deeper insights, advanced analysis, and comprehensive monitoring of AWS resources and applications.
7. Third-Party Integration
In addition to AWS services, CloudWatch supports integration with numerous third-party tools and applications. This enables organizations to leverage their existing monitoring and management systems and consolidate data from various sources, providing a unified view of their IT infrastructure.
In conclusion, CloudWatch is a powerful monitoring and management service that empowers organizations to monitor and optimize their AWS resources, applications, and services.
With its extensive metric collection, log analysis capabilities, automated actions, resource optimization features, and seamless integrations, CloudWatch provides organizations with the tools they need to ensure performance, availability, and cost-efficiency in their AWS environments.
Use Cases of AWS CloudWatch
AWS CloudWatch is a comprehensive monitoring and management service that Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides. It offers various use cases that empower organizations to gain insights, ensure optimal performance, and automate actions within their AWS environments.
Let’s explore some of the prominent use cases of CloudWatch:
1. Performance Monitoring
One of the primary use cases of AWS CloudWatch is performance monitoring. CloudWatch enables organizations to collect and monitor metrics from various AWS resources such as EC2 instances, RDS databases, Elastic Load Balancers, and more.
These metrics provide valuable insights into resource utilization, performance, and operational health. By monitoring metrics such as CPU utilization, network traffic, and disk usage, organizations can identify bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and ensure the efficient operation of their AWS infrastructure.
2. Auto Scaling
CloudWatch plays a critical role in auto-scaling environments. By setting up CloudWatch Alarms based on predefined thresholds, organizations can automatically trigger scaling actions to meet changing demand.
For example, if CPU utilization exceeds a specific threshold, CloudWatch can initiate the scaling process by adding additional EC2 instances to handle increased traffic. This automated scaling helps organizations ensure that their applications are responsive, perform optimally, and efficiently utilize resources.
3. Application Monitoring
CloudWatch enables organizations to gain insights into the performance and health of their applications running on AWS. By integrating with services such as AWS Lambda and Elastic Beanstalk, CloudWatch collects application-specific metrics, logs, and traces.
This allows organizations to monitor key performance indicators, identify bottlenecks, and troubleshoot issues in real-time. With CloudWatch, organizations can ensure their applications run smoothly, respond promptly to anomalies, and deliver a seamless user experience.
4. Log Analytics and Troubleshooting
CloudWatch Logs offers powerful log analytics capabilities, allowing organizations to centralize and analyze logs from various AWS services and applications. Organizations can set up filters, search for specific log patterns, and create custom metrics based on log data. This facilitates troubleshooting, performance analysis, and security investigations.
CloudWatch Logs Insights further enhances log analysis by providing advanced querying and analysis features. Organizations can gain valuable insights from log data, identify trends, and take proactive actions to optimize their systems.
5. Infrastructure Monitoring and Dashboards
CloudWatch allows organizations to create customizable dashboards that consolidate relevant metrics and provide a visual representation of the state of their AWS infrastructure.
These dashboards allow organizations to monitor critical metrics, visualize trends, and gain real-time resource visibility. With CloudWatch, organizations can create personalized dashboards that display key performance indicators, alarms, and operational metrics, empowering them to make informed decisions, optimize resource utilization, and ensure the efficient operation of their infrastructure.
6. Event-Driven Actions
CloudWatch Events enable organizations to automate actions in response to specific events within their AWS environment.
By creating rules based on events from various sources, such as changes in AWS resources or scheduled time intervals, organizations can trigger actions such as invoking AWS Lambda functions, sending notifications, or starting and stopping instances.
This allows organizations to automate routine tasks, streamline workflows, and ensure timely responses to critical events.
7. Cost Optimization
CloudWatch helps organizations optimize costs by providing insights into resource utilization. By monitoring CPU, memory, and network usage metrics, organizations can identify underutilized or over-provisioned resources and take appropriate actions to optimize resource allocation.
CloudWatch also offers the ability to set up billing alerts, allowing organizations to monitor their AWS costs and take proactive measures to control expenses.
8. Compliance and Auditing
CloudWatch plays a vital role in ensuring compliance and supporting auditing efforts. Organizations can generate reports and gain visibility into their AWS environment’s compliance posture by collecting and monitoring relevant metrics and logs.
CloudWatch logs can be integrated with other services, such as AWS CloudTrail, to provide a comprehensive audit trail for compliance auditing and security investigations.
In conclusion, AWS CloudWatch offers many use cases that empower organizations to monitor, analyze, and automate their AWS resources and applications.
Whether it’s performance monitoring, auto-scaling, application monitoring, log analytics, infrastructure monitoring, event-driven actions, cost optimization, or compliance auditing, CloudWatch provides the tools and insights necessary to ensure optimal performance, efficient resource utilization, and compliance with organizational and industry standards.
By leveraging CloudWatch’s capabilities, organizations can proactively monitor their AWS environment, optimize operations, and deliver a seamless experience to their users.
How AWS CloudWatch works
Understanding how AWS CloudWatch works is essential for organizations seeking insights, ensuring optimal performance, and automating actions within their AWS environments.
Architecture and Components:-
At its core, AWS CloudWatch consists of several key components that work together to deliver comprehensive monitoring capabilities:
Metrics: CloudWatch collects metrics from various AWS resources, such as EC2 instances, RDS databases, and Lambda functions. These metrics provide essential data points for resource utilization, performance, and operational health.
Namespaces: Metrics are organized within namespaces, which act as containers for related metrics. Namespaces help categorize and differentiate metrics from different AWS services or custom applications.
Dimensions: Metrics are refined with dimensions, providing additional context to differentiate resources within a namespace. For example, dimensions for an EC2 instance may include instance ID, instance type, and availability zone.
Data Points: CloudWatch captures data points for metrics at regular intervals, typically every minute. Each data point includes a timestamp and a value representing the metric measurement at that specific time.
Alarms: Organizations can define alarms based on predefined thresholds or custom conditions. Alarms monitor metrics and trigger actions when specific conditions are met, such as sending notifications or invoking AWS Lambda functions.
Dashboards: CloudWatch allows organizations to create customizable dashboards that consolidate relevant metrics and visually represent the state of their AWS resources. Dashboards help visualize key performance indicators and enable at-a-glance monitoring.
CloudWatch Logs: Besides metrics, CloudWatch can collect and analyze logs generated by AWS services, applications, and custom sources. Logs are stored in CloudWatch Logs and can be searched, filtered, and analyzed to gain insights and troubleshoot issues.
Data Collection and Storage:-
AWS CloudWatch works by continuously collecting and storing metric and log data:
Metric Collection: AWS services automatically publish metrics to CloudWatch at regular intervals. Organizations can also publish custom metrics using the CloudWatch API or SDKs.
Metric Data Points: CloudWatch stores metric data points for a configurable period, typically up to 15 days. These data points can be retrieved for analysis, visualization, and troubleshooting.
CloudWatch Logs: Organizations can configure AWS services, applications, and custom sources to send logs to CloudWatch Logs for centralized storage and analysis. Log data is stored durably and can be retained for extended periods.
Retention and Archiving: CloudWatch allows organizations to specify the retention period for logs, typically ranging from a few days to indefinitely. Logs can be exported to Amazon S3 or Amazon Glacier for long-term archiving.
Monitoring and Analysis:-
AWS CloudWatch provides various tools and features for monitoring, analyzing, and acting upon the collected data:
Console and APIs: Organizations can access CloudWatch through the AWS Management Console, AWS CLI, or APIs. These interfaces allow for configuration, monitoring, and analysis of metrics and logs.
Dashboards: CloudWatch enables the creation of customized dashboards that display metrics and alarms in a centralized and visually appealing format. Dashboards provide a consolidated view of key performance indicators, enabling real-time monitoring and analysis.
Alarms and Notifications: Organizations can define alarms based on predefined thresholds or custom conditions. When an alarm is triggered, CloudWatch can send notifications via email, SMS or invoke AWS Lambda functions, enabling automated responses to critical events.
CloudWatch Logs Insights: CloudWatch Logs Insights is a powerful feature that enables ad-hoc querying and analysis of log data. It provides an interactive query language and supports advanced functions, allowing organizations to extract valuable insights from their log data.
Integration with AWS Services: CloudWatch seamlessly integrates with various AWS services, such as AWS Lambda, Amazon EC2, Amazon RDS, and Amazon S3. These integrations provide enhanced monitoring capabilities, enabling organizations to gain deeper insights and take proactive actions based on the collected data.
CloudWatch Events: CloudWatch Events enables organizations to automate actions based on events within their AWS environment. Events can be triggered by changes to AWS resources, scheduled time intervals, or custom events. These events can invoke AWS Lambda functions, perform automated scaling, or trigger other actions.
In summary, AWS CloudWatch collects and stores metrics and logs from AWS resources and applications. It provides organizations with the tools and capabilities to monitor, analyze, and act upon the collected data.
With its flexible architecture, intuitive interfaces, and extensive integration with AWS services, CloudWatch empowers organizations to maintain optimal performance, troubleshoot issues, and ensure efficient resource utilization within their AWS environments.
Cloudtrail vs Cloudwatch: Similarities
Regarding monitoring and management in the Amazon Web Services (AWS) ecosystem, two prominent services stand out: CloudTrail and CloudWatch. While they serve different purposes, the two have some noteworthy similarities.
Let’s explore these similarities and understand how they contribute to AWS operations.
1. Log-based Monitoring
CloudTrail and CloudWatch rely on logs to provide valuable insights into an AWS environment. CloudTrail primarily focuses on auditing and compliance, capturing detailed API activity and events records.
On the other hand, CloudWatch covers a broader range of monitoring needs, including infrastructure and application performance. However, both services leverage log data to offer visibility and operational intelligence.
2. Integration with AWS Services
CloudTrail and CloudWatch seamlessly integrate with various AWS services, enabling comprehensive monitoring and analysis capabilities.
CloudTrail supports integration with services such as Amazon S3, Amazon EC2, and AWS Lambda, capturing API activity across the AWS ecosystem.
CloudWatch, similarly, integrates with a wide range of AWS services, including EC2, RDS, and Lambda, allowing organizations to monitor and analyze resource-specific metrics and logs.
3. Centralized Log Storage
Both services offer centralized log storage, simplifying log management and analysis. CloudTrail stores API activity logs, providing a detailed audit trail of AWS API calls.
CloudWatch, on the other hand, enables organizations to consolidate logs from various sources, such as EC2 instances, Lambda functions, and custom applications. Centralized log storage ensures ease of access, simplifies troubleshooting and aids in compliance and security investigations.
4. Alerting and Notifications
CloudTrail and CloudWatch offer alerting and notification capabilities to notify organizations of specific events or conditions.
CloudTrail can trigger SNS (Simple Notification Service) notifications for critical events, such as unauthorized API access or configuration changes.
CloudWatch, on the other hand, enables organizations to set up alarms based on predefined thresholds or custom conditions. These alarms can trigger notifications via email, SMS or even invoke actions through AWS Lambda.
5. Real-time Monitoring
Both CloudTrail and CloudWatch provide real-time monitoring capabilities, empowering organizations to gain immediate visibility into their AWS environments.
CloudTrail captures and delivers API activity logs in near real-time, ensuring timely access to critical information. CloudWatch offers real-time monitoring of resource-specific metrics, enabling organizations to detect anomalies and proactively respond to performance issues.
6. Access Control and Security
Security is a paramount concern in any AWS environment, and both CloudTrail and CloudWatch offer features to enhance access control and security.
CloudTrail integrates with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), allowing organizations to define fine-grained access control policies for the service. CloudWatch, similarly, provides IAM integration, enabling organizations to control access to metrics, logs, and dashboards.
7. Flexible Querying and Analysis
Both services offer capabilities for querying and analyzing log data. CloudTrail allows organizations to search and filter API activity logs based on specific criteria, such as time range, event type, or resource.
CloudWatch Logs provides a powerful feature called CloudWatch Logs Insights, enabling ad-hoc querying and analyzing log data using a query language. These features facilitate troubleshooting, performance analysis, and compliance investigations.
In conclusion, while CloudTrail and CloudWatch have different primary focuses and use cases, they share several similarities that contribute to effective monitoring and management in AWS environments.
Both services leverage logs for monitoring and analysis, integrate with various AWS services, offer centralized log storage, provide alerting and notification capabilities, support real-time monitoring, enhance access control and security, and facilitate querying and analysis of log data.
By understanding and utilizing the strengths of both CloudTrail and CloudWatch, organizations can gain comprehensive insights, ensure operational excellence, and meet their monitoring and compliance requirements in AWS.
Differences Between CloudTrail and CloudWatch
1. Cloudtrail vs Cloudwatch: Data types captured and processed
When comparing CloudTrail and CloudWatch, two prominent services offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS), it’s important to understand the types of data they capture and process. While both services contribute to monitoring and management in AWS environments, they focus on different aspects and capture distinct data types.
CloudTrail:-
CloudTrail primarily captures and processes audit logs related to API activity and events within an AWS environment. These logs provide a detailed record of actions taken by users, services, or AWS resources. CloudTrail captures the following types of data:
Management Events: CloudTrail records management events related to the creation, deletion, modification, or configuration changes of AWS resources. These events provide valuable insights into administrative activities within an AWS account.
Data Events: CloudTrail captures data events related to accessing and modifying data resources. These events provide visibility into actions performed on resources such as Amazon S3 buckets, Amazon DynamoDB tables, or AWS Lambda functions.
CloudTrail Insights: CloudTrail Insights goes beyond standard audit logs by using machine learning algorithms to analyze and identify unusual API activity patterns. It helps organizations detect potential security threats, unauthorized access attempts, or unusual resource utilization.
Global Services: CloudTrail captures data for global services such as AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), AWS CloudFormation, and AWS Security Token Service (STS). This allows organizations to gain visibility into activities related to authentication, resource provisioning, and temporary security credentials.
CloudWatch:-
CloudWatch monitors and analyzes metrics and logs from AWS resources and applications. It captures and processes various performance and operational data to provide insights and facilitate proactive actions. CloudWatch captures the following types of data:
Metrics: CloudWatch collects and processes resource utilization, performance, and operational health metrics. These metrics include CPU usage, network throughput, disk I/O, latency, error rates, etc. CloudWatch offers pre-defined metrics for various AWS services and supports custom metrics publication.
Logs: CloudWatch captures and analyzes log data from AWS services, applications, and custom sources. It provides centralized storage for logs and enables real-time analysis, search, and filtering. Log data can include application logs, system logs, and other event logs. CloudWatch Logs Insights allows for advanced log analysis, including ad-hoc querying and trend identification.
Alarms: CloudWatch allows organizations to define alarms based on predefined thresholds or custom conditions. These alarms monitor metric data and trigger notifications or automated actions when specific conditions are met. Alarms help organizations proactively respond to critical events, such as high CPU utilization or increased error rates.
Events: CloudWatch Events capture and process events related to changes in AWS resources or scheduled time intervals. Organizations can define rules to trigger actions based on these events, such as invoking AWS Lambda functions, starting or stopping instances, or sending notifications. CloudWatch Events enable organizations to automate operational tasks and streamline workflows.
Differences and Complementary Capabilities:-
While CloudTrail and CloudWatch capture different data types, they complement each other to provide a comprehensive monitoring and management solution for AWS environments. CloudTrail captures audit logs for compliance, security, and governance purposes, while CloudWatch focuses on real-time performance monitoring and analysis.
CloudTrail’s audit logs provide a detailed record of API activity and events, facilitating compliance audits, security investigations, and governance analysis. It helps organizations ensure accountability, track resource changes, and meet regulatory requirements.
On the other hand, CloudWatch’s metrics and logs enable organizations to monitor resource utilization, troubleshoot performance issues, detect anomalies, and automate actions based on predefined conditions.
CloudWatch provides real-time visibility into the health and performance of AWS resources and applications, helping organizations ensure operational excellence and deliver a seamless user experience.
In summary, CloudTrail and CloudWatch capture and process distinct data types to support monitoring and management aspects in AWS environments. CloudTrail focuses on capturing audit logs for compliance and security, while CloudWatch provides real-time monitoring and analysis of performance and operational data.
These services provide organizations with comprehensive tools to ensure visibility, compliance, performance optimization, and proactive management in their AWS deployments.
2. Cloudtrail vs Cloudwatch: Use-case scenarios
Regarding monitoring and management in Amazon Web Services (AWS) environments, CloudTrail and CloudWatch are two prominent services catering to different use-case scenarios. Understanding the specific scenarios where each service excels can help organizations make informed decisions about monitoring and auditing requirements.
CloudTrail:-
CloudTrail is primarily designed for auditing and compliance purposes. It captures detailed records of API activity and events within an AWS environment, making it an essential service for organizations seeking to ensure accountability, track resource changes, and meet regulatory requirements.
Some common use-case scenarios for CloudTrail include:-
Compliance Auditing: CloudTrail provides a comprehensive audit trail of API calls and actions performed within an AWS account. This makes it an invaluable tool for organizations undergoing compliance audits or needing to demonstrate adherence to regulatory standards.
Security Analysis: CloudTrail enables organizations to perform security analysis and investigation by capturing API activity logs. It helps detect unauthorized access attempts, identify potential security threats, and track the source of suspicious activities.
Change Management: CloudTrail allows organizations to track and analyze changes made to AWS resources. It provides insights into who made the changes, what changes were made, and when they occurred. This facilitates change management processes and helps understand resource configurations clearly.
Operational Troubleshooting: CloudTrail logs can be used for operational troubleshooting, providing a historical record of API calls. This allows organizations to investigate incidents, troubleshoot issues, and identify the root cause of problems within their AWS environments.
CloudWatch:-
CloudWatch is a versatile monitoring and management service that caters to various use-case scenarios, including performance monitoring, log analytics, and automation. It provides real-time insights into resource utilization, application performance, and operational health.
Here are some common use-case scenarios for CloudWatch:
Infrastructure Monitoring: CloudWatch helps organizations monitor the health and performance of their AWS resources, such as EC2 instances, RDS databases, and Lambda functions. It provides metrics and alarms to track resource utilization, enabling organizations to optimize performance and ensure efficient resource allocation.
Application Performance Monitoring: CloudWatch allows organizations to monitor the performance of their applications running on AWS. It captures and analyzes application-specific metrics, logs, and traces, enabling organizations to troubleshoot performance bottlenecks, identify errors, and optimize application performance.
Log Analytics: CloudWatch logs provide centralized storage and analysis capabilities for logs generated by AWS services, applications, and custom sources. Organizations can use CloudWatch Logs and its Insights feature to search, filter, and analyze log data, facilitating troubleshooting, performance analysis, and security investigations.
Automated Actions: CloudWatch enables organizations to automate actions based on predefined conditions. It allows the creation of alarms to trigger notifications or invoke AWS Lambda functions, facilitating automated responses to critical events, such as scaling resources based on demand or invoking remediation actions.
Cost Optimization: CloudWatch helps organizations optimize costs by monitoring resource utilization metrics. It allows organizations to identify underutilized resources, adjust capacity, and implement cost-saving measures, improving cost efficiency within AWS environments.
Dashboards and Reporting: CloudWatch provides customizable dashboards that consolidate metrics and visually represent the state of AWS resources. Organizations can create personalized dashboards to monitor key performance indicators, track operational health, and generate reports for stakeholders.
In summary, while CloudTrail and CloudWatch serve different purposes, they offer distinct use-case scenarios within AWS environments. CloudTrail excels in auditing and compliance, providing a detailed audit trail of API activity.
CloudWatch, on the other hand, offers versatile monitoring and management capabilities, including performance monitoring, log analytics, automation, and cost optimization.
By understanding each service’s strengths, organizations can leverage CloudTrail and CloudWatch to meet their specific monitoring, auditing, and compliance needs in AWS.
3. Cloudtrail vs Cloudwatch: Alerting capabilities
Regarding monitoring and managing resources in Amazon Web Services (AWS) environments, both CloudTrail and CloudWatch offer powerful alerting capabilities. These services allow organizations to set up notifications and triggers based on predefined conditions. However, there are key differences in how each service handles alerting.
Let’s explore the alerting capabilities of CloudTrail and CloudWatch.
CloudTrail Alerting Capabilities:-
CloudTrail focuses on auditing and compliance, providing detailed logs of API activity and events within an AWS environment. While CloudTrail doesn’t offer native alerting features, it can still play a role in alerting through integration with other AWS services, such as Amazon CloudWatch Events.
By leveraging CloudWatch Events, organizations can define rules and triggers based on CloudTrail events to initiate automated actions or send notifications.
Some use cases for CloudTrail alerting capabilities include:-
Security Monitoring: Organizations can set up CloudWatch Events rules to trigger alerts when CloudTrail records indicate unauthorized access attempts, changes to security policies, or suspicious activity within the AWS environment.
Compliance Monitoring: CloudTrail logs can monitor compliance-related activities, such as changes to IAM roles or modifications to security groups. Organizations can create CloudWatch Events rules to trigger alerts when specific compliance requirements are violated.
Operational Insights: By configuring CloudWatch Events to monitor CloudTrail logs, organizations can gain operational insights and receive alerts for activities such as resource deletions, changes to EC2 instances, or modifications to critical infrastructure components.
Integration with Third-Party Tools: CloudTrail logs can be sent to third-party log management or Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, where advanced alerting and correlation capabilities can be leveraged to enhance security monitoring and incident response.
CloudWatch Alerting Capabilities:-
CloudWatch, being a comprehensive monitoring service, offers rich native alerting capabilities. Organizations can create alarms based on metrics and logs collected by CloudWatch. These alarms allow organizations to define thresholds or custom conditions that trigger actions when specific events occur.
Some key features of CloudWatch alerting capabilities include:
Metric-Based Alarms: CloudWatch enables organizations to set up alarms based on predefined thresholds or custom metrics. For example, an organization can create an alarm to trigger when CPU utilization exceeds a certain threshold or when the number of errors in an application exceeds a specific count.
Log-Based Alarms: CloudWatch can also analyze log data and trigger alarms based on specific log patterns or the absence of expected log entries. This allows organizations to receive alerts when certain events or errors are detected within their application or infrastructure logs.
Multiple Actions: CloudWatch alarms support multiple actions when triggered, including sending notifications via Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS), executing AWS Lambda functions, or even stopping or starting EC2 instances based on predefined conditions.
Auto Scaling Integration: CloudWatch alarms can be used with Auto Scaling groups to scale resources up or down based on predefined thresholds automatically. This helps organizations maintain optimal resource utilization and ensures application availability during high-demand or resource-intensive workloads.
Dashboards and Visualization: CloudWatch provides customizable dashboards that allow organizations to visualize alarm status, metrics, and trends in real time. This enables at-a-glance monitoring and quick identification of any issues or anomalies.
Notification Suppression: CloudWatch provides a ” Throttling ” feature that allows organizations to suppress alarm notifications for a specified period to prevent excessive alerting during known maintenance windows or expected resource fluctuations.
In summary, while CloudTrail integrates with CloudWatch Events for alerting capabilities, CloudWatch offers comprehensive native alerting features. CloudTrail can play a vital role in security monitoring and compliance.
At the same time, CloudWatch provides organizations with metric-based and log-based alarms, integration with Auto Scaling, customizable dashboards, and multiple notification options. By understanding the alerting capabilities of CloudTrail and CloudWatch, organizations can effectively monitor their AWS environments and proactively respond to critical events and conditions.
3. Cloudtrail vs Cloudwatch: Security Features
Regarding security in Amazon Web Services (AWS) environments, CloudTrail and CloudWatch offer a range of robust features to help organizations protect their resources and data. While both services contribute to security, they do so in different ways.
Let’s explore the security features of CloudTrail and CloudWatch and understand how they enhance the overall security posture of AWS environments.
CloudTrail Security Features:-
CloudTrail focuses on providing detailed auditing and compliance capabilities, making it an essential tool for organizations seeking to maintain a secure AWS environment. Here are some key security features of CloudTrail:
Auditing API Activity: CloudTrail captures and logs detailed records of API activity and events within an AWS environment. This auditing capability enables organizations to track and review every API call to their AWS resources, providing essential security control for detecting unauthorized access attempts or potentially malicious actions.
Compliance Support: CloudTrail helps organizations meet compliance requirements by providing a comprehensive audit trail of API activity. The detailed logs enable organizations to demonstrate adherence to regulatory standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), or the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
Log File Integrity Validation: CloudTrail enhances security by validating the integrity of log files. Each log file generated by CloudTrail is digitally signed, ensuring that it cannot be tampered with or modified without detection. This integrity validation feature assures that the captured log data remains unchanged and reliable for security investigations and compliance audits.
Monitoring and Alerting: CloudTrail can integrate with other AWS services, such as Amazon CloudWatch and AWS Lambda, to enable monitoring and alerting based on CloudTrail events. This integration allows organizations to proactively detect and respond to security-related events or policy violations, helping to strengthen overall security posture.
CloudWatch Security Features:-
CloudWatch offers a wide range of security features that focus on monitoring, analyzing, and securing AWS resources and applications. These features contribute to maintaining the security and integrity of AWS environments.
Here are some notable security features of CloudWatch:
Metrics-Based Monitoring: CloudWatch provides organizations with the ability to monitor key performance metrics of their AWS resources, such as CPU utilization, network traffic, and disk I/O. By monitoring these metrics, organizations can identify anomalies and potential security breaches, allowing them to take proactive measures to address security threats.
Log Analytics: CloudWatch enables centralized storage and analysis of logs generated by AWS services, applications, and custom sources. By leveraging log analytics, organizations can identify security events, detect unauthorized access attempts, and gain valuable insights for incident response and forensic analysis.
Alarms and Alerting: CloudWatch allows organizations to set up alarms based on predefined thresholds or custom conditions. This feature enables real-time monitoring of security-related metrics, such as high CPU utilization or increased network traffic, triggering alarms and sending notifications when abnormal or potentially malicious activities occur.
Integration with AWS Services: CloudWatch seamlessly integrates with various AWS services, enabling enhanced security monitoring capabilities. For example, integration with AWS Lambda allows organizations to monitor and analyze security-related events and take automated actions in response to specific security incidents.
Encryption: CloudWatch supports encryption at rest for log data stored in CloudWatch Logs. This ensures that log data remains secure, even if accessed by unauthorized parties.
Access Control: CloudWatch integrates with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), allowing organizations to manage access to CloudWatch resources and control user actions. Fine-grained access control ensures only authorized individuals can view and manage CloudWatch metrics, logs, and alarms.
In summary, both CloudTrail and CloudWatch offer security features that contribute to the overall security of AWS environments. CloudTrail excels in auditing and compliance, providing detailed logs of API activity, while CloudWatch focuses on monitoring, analysis, and alerting capabilities.
By leveraging the security features of CloudTrail and CloudWatch, organizations can enhance their security posture, detect and respond to security incidents, and meet regulatory requirements within their AWS deployments.
When to use CloudTrail over CloudWatch and vice versa
In Amazon Web Services (AWS) environments, CloudTrail and CloudWatch offer powerful monitoring and management capabilities. While they serve different purposes, understanding when to use each service can help organizations optimize their AWS deployments.
Let’s explore the scenarios where CloudTrail excels over CloudWatch and vice versa.
When to Use CloudTrail:-
CloudTrail is specifically designed for auditing and compliance purposes, making it the ideal choice in the following scenarios:
Auditing and Compliance: CloudTrail should be used when organizations require detailed logs of API activity and events within their AWS environment. It captures every API call to AWS resources, enabling organizations to track changes, detect unauthorized access attempts, and demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards.
Governance and Accountability: CloudTrail provides a clear audit trail of actions taken by users, services, or AWS resources. It helps organizations maintain governance and accountability by tracking who performed specific actions, what changes were made, and when they occurred. This is crucial for effective resource management and risk mitigation.
Security Analysis and Forensics: CloudTrail logs enable security analysis and forensic investigations. By capturing API activity, organizations can identify potential security threats, trace the source of suspicious activities, and perform root cause analysis during security incidents.
Change Management: CloudTrail is essential for change management processes. It allows organizations to track and review changes made to AWS resources, helping ensure that only authorized modifications are made and providing visibility into the history of resource configurations.
When to Use CloudWatch:-
CloudWatch offers a wide range of monitoring and management capabilities, making it suitable for various scenarios:
Performance Monitoring: CloudWatch excels in monitoring resource utilization, application performance, and operational health. It provides real-time insights into CPU usage, network throughput, and disk I/O metrics. Organizations can leverage CloudWatch to optimize resource utilization, detect performance bottlenecks, and ensure efficient operation of their AWS resources.
Infrastructure Monitoring: CloudWatch is the go-to choice for monitoring the health and performance of AWS resources. It allows organizations to track metrics specific to services like EC2 instances, RDS databases, and Lambda functions. This enables proactive monitoring, capacity planning, and efficient resource allocation.
Log Analysis: CloudWatch provides centralized log storage and analysis capabilities. It allows organizations to collect, store, and analyze logs from AWS services, applications, and custom sources. CloudWatch Logs Insights offers advanced log analysis features, empowering organizations to troubleshoot issues, perform root cause analysis, and gain operational insights.
Automation and Alarms: CloudWatch enables organizations to set up alarms based on predefined thresholds or custom conditions. These alarms trigger notifications or automated actions when specific events or metrics exceed or fall below-defined thresholds. CloudWatch alarms are vital in proactive monitoring, enabling organizations to respond to critical events and ensure system availability.
Choosing the Right Service:-
Choosing between CloudTrail and CloudWatch depends on the specific requirements of an organization. Here are some key considerations:
Compliance and Auditing: If compliance and auditing are the primary concerns, CloudTrail is the appropriate choice. It captures detailed API activity logs and provides the necessary audit trail for regulatory compliance.
Real-Time Monitoring: If real-time monitoring and performance optimization are essential, CloudWatch is the preferred service. It offers real-time insights into metrics, supports customizable dashboards, and provides extensive alerting capabilities.
Security and Governance: While both services contribute to security, CloudTrail focuses on security analysis, forensic investigations, and change management. CloudWatch complements this by offering log analysis, metrics-based monitoring, and automation capabilities.
In some cases, organizations may need to utilize both CloudTrail and CloudWatch to effectively address different aspects of their AWS environment. By leveraging each service’s strengths, organizations can ensure compliance, optimize performance, enhance security, and maintain operational excellence in their AWS deployments.
Use cases showcasing the combined use of CloudTrail and CloudWatch
The combination of CloudTrail and CloudWatch offers powerful monitoring and management capabilities in Amazon Web Services (AWS) environments. By leveraging the strengths of both services, organizations can enhance security, achieve compliance, and optimize the performance of their AWS resources.
Let’s explore some use cases that showcase the synergistic use of CloudTrail and CloudWatch.
Use Case 1: Security Monitoring and Incident Response
By combining CloudTrail and CloudWatch, organizations can strengthen their security posture and improve incident response capabilities. Here’s how it works:
CloudTrail: CloudTrail captures detailed logs of API activity and events, providing an audit trail for security analysis and compliance.
CloudWatch Alarms: Organizations can create CloudWatch alarms based on CloudTrail events to detect suspicious activities, unauthorized access attempts, or policy violations.
Real-time Monitoring: CloudWatch monitors metrics such as CPU utilization, network traffic, and log data, providing real-time insights into the operational health of AWS resources.
Automated Actions: When a CloudWatch alarm is triggered based on a CloudTrail event, organizations can configure CloudWatch to initiate automated actions, such as sending notifications, invoking AWS Lambda functions, or even isolating affected resources.
Use Case 2: Compliance and Governance
Organizations must adhere to regulatory requirements and maintain governance over their AWS resources. The combined use of CloudTrail and CloudWatch helps achieve these goals:
CloudTrail: CloudTrail captures API activity logs, enabling organizations to track and review changes made to AWS resources, ensuring accountability and compliance.
CloudWatch Logs: CloudWatch collects and analyzes logs, providing centralized storage and analysis capabilities for compliance audits and security investigations.
Alerting and Reporting: CloudWatch alarms can be set up to trigger alerts when specific compliance requirements are violated. Customized dashboards and reports help organizations visualize and communicate compliance status.
Use Case 3: Performance Optimization and Resource Management
The combination of CloudTrail and CloudWatch facilitates performance optimization and efficient resource management:
CloudTrail: CloudTrail captures API activity logs, allowing organizations to understand changes made to AWS resources and track resource usage patterns.
CloudWatch Metrics: CloudWatch collects and monitors metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and network traffic. This data helps organizations identify underutilized resources, optimize performance, and plan for capacity needs.
Automation: By using CloudWatch alarms and AWS Lambda functions, organizations can automate actions such as scaling resources based on demand or optimizing resource allocation based on predefined thresholds.
Cost Optimization: CloudWatch metrics and analysis provide insights into resource utilization, enabling organizations to identify cost-saving opportunities and optimize their AWS spending.
Use Case 4: Troubleshooting and Root Cause Analysis
The combined use of CloudTrail and CloudWatch enhances troubleshooting and root cause analysis capabilities:
CloudTrail: CloudTrail captures detailed logs of API activity, facilitating the investigation of security incidents or operational issues.
CloudWatch Logs: CloudWatch provides centralized storage and analysis capabilities for logs generated by AWS services and applications. Organizations can search, filter, and analyze log data to troubleshoot issues and identify the root cause of problems.
CloudWatch Metrics: CloudWatch metrics help organizations correlate log events with performance metrics, enabling effective troubleshooting and identifying performance-related issues.
Dashboards and Visualization: CloudWatch offers customizable dashboards that consolidate logs, metrics, and alarms, providing a comprehensive view of AWS resources. This aids in visualizing trends, identifying anomalies, and streamlining troubleshooting efforts.
In summary, the combined use of CloudTrail and CloudWatch offers a wide range of use cases that enhance security, compliance, performance optimization, troubleshooting, and resource management in AWS environments.
By leveraging the strengths of both services, organizations can achieve a holistic monitoring and management solution, maximizing the benefits of AWS and ensuring operational excellence.
AWS CloudTrail vs CloudWatch – What Are the Main Differences?
AWS CloudTrail and CloudWatch are critical services that serve different purposes in AWS environments. AWS CloudTrail provides an audit trail for auditing and compliance, while CloudWatch offers real-time monitoring, metrics analysis, and alerting capabilities.
Organizations can achieve comprehensive visibility, compliance, and operational excellence in their AWS deployments by understanding their differences and utilizing them in the appropriate use cases.
Here’s a detailed comparison chart between AWS CloudTrail and AWS CloudWatch:-
| Features | CloudTrail | CloudWatch |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Auditing, compliance, and governance | Real-time monitoring and management |
| Primary Focus | API activity logging | Metrics monitoring and analysis |
| Log Collection | Detailed logs of API activity and events within AWS environment | Metrics from AWS resources, applications, and custom sources |
| Integration | Integrates with CloudWatch and Lambda for automation and analysis | Integrates with other AWS services for enhanced monitoring |
| Compliance Support | Aids in meeting regulatory requirements | Assists in performance optimization and resource management |
| Alerting | Requires integration with CloudWatch Events for alerting capabilities | Native alerting with customizable alarms |
| Log Analysis | Limited log analysis capabilities | Centralized log collection and analysis |
| Use Cases | Compliance monitoring, security analysis, and change management | Performance optimization, troubleshooting, and resource management |
| Dashboards | No native dashboard capabilities | Customizable dashboards for visualization |
| Automation | Requires integration with CloudWatch and Lambda for automation | Automation through alarms and actions |
| Use with AWS Services | Captures activity from all AWS services | Collects metrics from various AWS resources |
| Pricing | Event-based pricing | Usage-based pricing |
CloudTrail vs CloudWatch vs GuardDuty
While CloudTrail focuses on auditing and compliance, CloudWatch offers comprehensive monitoring and management capabilities, and GuardDuty specializes in threat detection and analysis.
Each service plays a crucial role in maintaining your AWS environment’s security and operational excellence. By combining CloudTrail, CloudWatch, and GuardDuty, organizations can achieve a robust security posture, ensure compliance, and proactively detect and respond to potential threats.
Here’s a detailed chart comparing CloudTrail, CloudWatch, and GuardDuty:-
| Feature | CloudTrail | CloudWatch | GuardDuty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Record AWS API calls and events for auditing/tracing | Monitor AWS resources and applications | Detects malicious activity in AWS accounts and workloads |
| Data | Logs of API calls and events | Metrics, logs, and events | Threat detections and findings |
| Deployment | Enabled at the AWS account level | Enabled at the resource or application level | Enabled at the AWS account level |
| Cost | Based on the number of events recorded | Based on the amount of data ingested | Based on the number of monitored resources and findings |
| Use cases | Compliance, security, and operational auditing | Monitoring system and application health | Threat detection and incident response |
| Integration | Can be integrated with CloudWatch for log monitoring | It can be integrated with CloudTrail for auditing | It can be integrated with CloudWatch for monitoring and alerting |
| Alerting | Not built-in, but it can be integrated with CloudWatch | Built-in alerting and alarms | Built-in alerting and notifications |
| Analytics | Can be analyzed using Amazon Athena or other tools | Can be analyzed using Amazon CloudWatch Logs Insights | Can be analyzed using Amazon GuardDuty API or other tools |
| Security | Supports AWS Key Management Service (KMS) encryption | Supports encryption and IAM permissions | Uses machine learning to detect and alert on security issues |
| Management | Management console and APIs for configuration | Management console and APIs for configuration | Management console and APIs for configuration |
Cloudwatch vs Datadog:-
The choice between CloudWatch and Datadog depends on your requirements, infrastructure setup, and preferences. If you have a predominantly AWS environment and require native monitoring for AWS resources, CloudWatch is a solid choice.
However, suppose you need a more extensive monitoring solution that can span multiple cloud providers and technologies and offers advanced features such as log analytics and AIOps.
In that case, Datadog may be a better fit. Consider your needs, evaluate the features and capabilities of both solutions and choose the one that aligns best with your monitoring goals.
Here’s a detailed chart comparing Cloudwatch and Datadog:-
| Feature | Cloudwatch | Datadog |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring capabilities | Monitoring of AWS resources like EC2, RDS, DynamoDB, and more. | Monitoring of AWS resources as well as on-premises and hybrid cloud infrastructure, applications, and containers. |
| Integrations | Integrates with AWS services and some third-party tools. | Integrates with AWS and other cloud providers, over 450 infrastructure, application, and logs integrations. |
| Alerting | Basic alerting capabilities for AWS resources. | Advanced alerting capabilities with customizable thresholds, intelligent alerting, and anomaly detection. |
| Visualization | Basic graphs and charts for AWS resources. | Advanced dashboards with customizable widgets, annotations, and note-taking. |
| Pricing | Pay-per-use pricing with a free tier for basic monitoring. | Flexible pricing options with pay-per-use, per-host, and custom plans. |
| Scalability | Can handle large-scale monitoring of AWS resources. | Can monitor large-scale hybrid infrastructure and handle high-volume data processing. |
CloudWatch vs CloudTrail vs Config:-
Regarding monitoring and managing your Amazon Web Services (AWS) environment, CloudWatch, CloudTrail, and Config are three powerful services that offer distinct functionalities. Each service is crucial in monitoring, logging, and configuration management. To understand their unique contributions and use cases, let’s compare CloudWatch, CloudTrail, and Config.
CloudWatch:-
CloudWatch is a monitoring and observability service that provides real-time insights into your AWS resources’ operational health and performance. It offers a wide range of features, including:
Metrics Monitoring: CloudWatch collects and monitors CPU utilization, network traffic, and disk I/O for AWS resources. It helps you understand the resource utilization and performance of your infrastructure.
Log Management: CloudWatch allows you to collect, store, and analyze logs generated by AWS services, applications, and custom sources. It facilitates troubleshooting, security analysis, and compliance monitoring.
Alarms and Notifications: CloudWatch enables you to set up alarms based on predefined thresholds or custom metrics. These alarms trigger notifications or automated actions when specific conditions are met, helping you stay informed about critical events.
CloudTrail;-
CloudTrail focuses on auditing and compliance by providing detailed logs of API activity and events within your AWS environment. Key features of CloudTrail include:
API Activity Logging: CloudTrail captures and logs every API call made within your AWS account, allowing you to monitor and review actions performed by users, services, or AWS resources. It provides an audit trail for security analysis and regulatory compliance.
Compliance Support: CloudTrail aids in meeting regulatory requirements by providing an immutable activity record. It helps organizations demonstrate accountability, track changes, and ensure adherence to compliance standards.
Integration with Other Services: CloudTrail integrates with other AWS services, such as CloudWatch and AWS Lambda, allowing you to automate actions, set up alerts, and perform in-depth analysis of the captured data.
AWS Config:-
Config is a service that helps you assess, audit, and evaluate the configuration of your AWS resources. It provides a detailed inventory of your resources and tracks changes over time. Key features of Config include:
Resource Configuration Tracking: Config continuously monitors the configuration of your AWS resources and records any changes. It helps you understand how your resources are configured and detect unauthorized or unintended changes.
Configuration Compliance: Config allows you to define and enforce configuration rules to ensure compliance with internal policies or industry regulations. It provides a comprehensive view of your resource compliance status and identifies areas that require attention.
Configuration History and Visualization: Config retains the configuration history of your resources, enabling you to visualize and analyze changes over time. This helps you understand the relationships between resources and troubleshoot issues more effectively.
Use Cases:-
CloudWatch: CloudWatch is suitable for real-time monitoring, performance optimization, and log management. It helps you identify bottlenecks, optimize resource utilization, and troubleshoot issues quickly.
CloudTrail: CloudTrail is ideal for auditing, compliance, and security analysis. It provides an audit trail of API activity and helps you track changes, detect unauthorized access, and ensure accountability.
Config: Config is valuable for configuration management, compliance monitoring, and change management. It helps you maintain a secure and compliant environment by tracking resource configurations and detecting any configuration drift or non-compliant changes.
In summary, CloudWatch, CloudTrail, and Config are essential to an effective AWS monitoring and management strategy. CloudWatch focuses on real-time monitoring, CloudTrail on auditing and compliance, and Config on configuration management.
By leveraging the strengths of these services, organizations can achieve comprehensive visibility, ensure compliance, and proactively manage their AWS resources.
Here’s a detailed comparison chart between AWS CloudWatch, AWS CloudTrail, and AWS Config:-
| Aspect | AWS CloudWatch | AWS CloudTrail | AWS Config |
|---|---|---|---|
| Function | Monitoring service for AWS resources and applications | Auditing service for AWS account activity and resource usage | Configuration management service for resource compliance and change tracking |
| Scope | Collects and tracks metrics, logs, and events for AWS resources and applications | Captures API calls and events for AWS services and resources | Tracks configuration changes for AWS resources |
| Data Storage | Metrics, logs, and events are stored in CloudWatch Logs or S3 buckets | Event logs are stored in S3 buckets | Configuration snapshots are stored in S3 buckets |
| Use Cases | Application performance monitoring, operational troubleshooting, capacity planning, and automated scaling | Security and compliance auditing, troubleshooting, and anomaly detection | Compliance and governance, risk management, security, and operational troubleshooting |
| Pricing Model | Based on the number of custom metrics, log data ingested, and alarms set up | Based on the number of events logged and delivered to S3 or CloudWatch Logs | Based on the number of active resources being tracked and the number of configuration changes recorded |
| Integration | Integrates with AWS services, such as EC2, RDS, S3, and Lambda, as well as third-party tools | Integrates with AWS services and security information and event management (SIEM) tools | Integrates with AWS services and third-party tools |
| Automation | Allows you to create and configure alarms, dashboards, and automated actions using CloudWatch Events and Lambda | Allows you to configure trails and automate analysis and response using CloudWatch Events and Lambda | Allows you to define and enforce compliance rules using AWS Config Rules and automate remediation using Lambda |
Cloudwatch vs Cloudtrail vs X-Ray:-
CloudWatch: CloudWatch is well-suited for monitoring AWS resources and applications in real-time. It helps you gain insights into resource utilization, monitor logs, and set up alarms for critical events.
CloudTrail: CloudTrail is ideal for auditing and compliance purposes. It provides an audit trail of API activity, allowing you to track changes, analyze security events, and ensure compliance with regulations.
X-Ray: X-Ray is specifically designed for distributed applications and microservices architectures. It helps you identify and troubleshoot performance bottlenecks, latency issues, and errors in your application stack.
In conclusion, CloudWatch, CloudTrail, and X-Ray are essential AWS monitoring and debugging toolbox components. While CloudWatch focuses on real-time monitoring and log analysis, CloudTrail provides audit trail capabilities, and X-Ray specializes in analyzing and debugging distributed applications.
By leveraging the strengths of these services, organizations can gain valuable insights, ensure compliance, and optimize the performance of their AWS environments.
Here’s a detailed comparison chart between AWS CloudWatch, AWS CloudTrail, and X-Ray:-
| Feature | CloudWatch | CloudTrail | X-Ray |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Monitoring AWS resources and applications | Logging AWS API activity | Analyzing and debugging distributed applications |
| Data Collected | Metrics, logs, events | API activity, management events, data events | Traces, service maps |
| Data Storage | Retained for a specified retention period | Retained indefinitely | Retained for a specified retention period |
| Data Analysis | Real-time monitoring, alerting, dashboarding | Searchable event history, auditing, compliance | Trace analysis, service maps, anomaly detection |
| Use Cases | Resource monitoring, application performance monitoring, troubleshooting | Auditing, security analysis, compliance reporting | Performance optimization, root cause analysis |
| Integration | Integrates with other AWS services and supports custom metrics | Integrates with AWS services can export to S3 for archiving | Integrates with AWS and non-AWS services and supports custom instrumentation |
| Pricing Model | Usage-based pricing for metrics and logs, free tier available | Usage-based pricing for events and logs, free tier available | Usage-based pricing for traces and maps, free tier available |
📗Cloudtrail vs Cloudwatch FAQs
Why use CloudTrail?
CloudTrail is an essential service for auditing and compliance purposes in AWS. It captures and logs every API call within your AWS account, providing an audit trail for security analysis, change tracking, and regulatory compliance.
How does CloudTrail work with CloudWatch?
CloudTrail can be integrated with CloudWatch to enable real-time monitoring and alerting. CloudTrail can send logs to CloudWatch, allowing you to set up alarms and trigger notifications based on specific events or API activity.
What is Amazon CloudFront vs AWS CloudTrail?
Amazon CloudFront is a content delivery network (CDN) service that accelerates content delivery to users worldwide. On the other hand, AWS CloudTrail is a service that logs and tracks API activity within your AWS account for auditing and compliance purposes.
What is CloudWatch used for?
CloudWatch is a comprehensive monitoring and observability service in AWS. It collects and monitors metrics, logs, and events from various AWS resources, enabling you to gain insights into resource utilization, troubleshoot issues, and set up alarms for proactive monitoring.
Is CloudTrail a logging service?
CloudTrail can be considered a logging service as it captures and logs API activity within your AWS account. It provides a detailed record of user actions, resource changes, and service events, facilitating security analysis, compliance monitoring, and operational troubleshooting.
Is CloudTrail a storage service?
No, CloudTrail is not primarily a storage service. It captures and logs API activity and stores the logs in an S3 bucket, which can be configured as the destination for storing the logs.
Does CloudTrail send logs to CloudWatch?
Yes, CloudTrail can send logs to CloudWatch. By integrating CloudTrail with CloudWatch, you can centralize the logs and use CloudWatch’s powerful monitoring and alerting capabilities to analyze and respond to specific events or patterns.
Does CloudWatch collect logs?
Yes, CloudWatch can collect logs generated by AWS services and applications. It provides a centralized location for storing, analyzing, and monitoring logs, enabling you to gain insights and troubleshoot issues within your AWS environment.
How do I link CloudTrail to CloudWatch?
To link CloudTrail to CloudWatch, you can configure CloudTrail to deliver log files to an S3 bucket. Then, you can create a CloudWatch Logs subscription filter to automatically forward the logs from the S3 bucket to CloudWatch Logs for further analysis and monitoring.
What does CloudTrail monitor?
CloudTrail monitors API activity within your AWS account. It captures and logs information about user actions, resource changes, and service events, allowing you to track and monitor all API calls made within your AWS environment.
What is the disadvantage of CloudWatch?
One potential disadvantage of CloudWatch is that it can become costly as the volume of monitored resources and logs increases. Additionally, setting up and managing alarms and metrics configuration may require some initial effort and configuration.
Does CloudWatch use S3?
CloudWatch does not directly use Amazon S3 for storing its logs or metrics data. However, you can configure CloudWatch to store logs in S3 buckets using CloudWatch Logs and S3 integration.
Which service is CloudWatch?
CloudWatch is an AWS service that provides monitoring and observability capabilities for AWS resources and applications. It allows you to collect and monitor metrics, logs, and events and set up alarms and dashboards for proactive monitoring and troubleshooting.
Where logs are stored in CloudTrail?
CloudTrail logs are stored in Amazon S3 buckets. You can configure CloudTrail to deliver log files to an S3 bucket in your AWS account, where they are securely stored and can be accessed for analysis and compliance purposes.
What is CloudTrail API?
The CloudTrail API is an interface that allows you to interact with the CloudTrail service programmatically. It enables you to perform various operations, such as creating and configuring trails, retrieving and analyzing logs, and managing CloudTrail settings.
Does CloudTrail store logs in S3?
Yes, CloudTrail stores logs in Amazon S3 buckets. The logs capture API activity and are delivered to the designated S3 bucket for long-term storage and easy access.
Why is CloudTrail so expensive?
The cost of CloudTrail can vary depending on factors such as the number of API events, the volume of logs generated, and the storage duration. The comprehensive nature of CloudTrail’s logging and compliance features and the need for long-term log retention can contribute to its cost.
What fields does CloudTrail track?
CloudTrail tracks various fields in its logs, including the timestamp of the API call, the caller’s identity, the source IP address, the requested resource, the response elements, and additional contextual information related to the event.
Are CloudWatch logs in JSON?
Yes, CloudWatch logs can be formatted in JSON. JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format commonly used for structuring and transmitting data. It provides a readable and easy-to-parse format for logs.
Where are CloudWatch logs stored?
CloudWatch logs are stored in a centralized, scalable, and highly available service within AWS. They can be accessed and analyzed using the CloudWatch console, APIs, or other monitoring and analytics tools.
Can CloudWatch send emails?
No, CloudWatch itself does not send emails. However, you can configure CloudWatch alarms to trigger actions such as sending notifications via Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service), which can deliver email notifications to specified recipients.
How long CloudWatch logs are stored?
By default, CloudWatch retains logs for 14 days. However, you can create custom retention periods and store logs for up to 10 years using CloudWatch Logs.
What are the different types of logs in AWS?
AWS generates different types of logs, including CloudTrail logs for auditing and compliance, CloudWatch logs for monitoring and troubleshooting, and VPC Flow Logs for network traffic analysis within Amazon VPC.
Does CloudWatch monitor memory?
Yes, CloudWatch can monitor memory utilization metrics for EC2 instances. It provides insights into memory usage, enabling you to track performance and optimize resource allocation.
How are logs sent to CloudWatch?
Logs can be sent to CloudWatch using the CloudWatch agent installed on your EC2 instances or through integration with AWS services and applications. You can configure log streams and log groups to organize and manage logs efficiently.
How do I view CloudTrail logs?
You can view CloudTrail logs by accessing the CloudTrail console in the AWS Management Console. From there, you can search, filter, and analyze the logs to gain insights into your AWS account’s API activity and events.
How do I enable CloudTrail logs?
To enable CloudTrail logs, you need to create a CloudTrail trail and specify the desired settings, such as the S3 bucket for log storage, the logging regions, and any advanced configuration options. Once enabled, CloudTrail starts capturing and logging API activity.
Are CloudTrail logs encrypted?
Yes, CloudTrail logs can be encrypted for enhanced security. You can encrypt the log files at rest using AWS Key Management Service (KMS) and control access to the encryption keys.
How do I protect my CloudTrail?
To protect your CloudTrail logs, you should follow security best practices such as enabling encryption, implementing secure access controls to the S3 bucket storing the logs, regularly monitoring and analyzing the logs for suspicious activity, and setting up appropriate AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies.
Are CloudTrail logs immutable?
Yes, CloudTrail logs are designed to be immutable, meaning they cannot be modified or deleted. This immutability ensures the integrity and non-repudiation of the logs, making them suitable for compliance and auditing purposes.
Is CloudWatch a PaaS or SaaS?
CloudWatch is an infrastructure-level service provided by AWS, making it part of the infrastructure as a service (IaaS) offering. It provides monitoring and observability capabilities for your AWS resources and applications.
Is CloudWatch data encrypted?
Yes, CloudWatch data can be encrypted to ensure its confidentiality and integrity. You can enable encryption at rest for CloudWatch Logs using AWS Key Management Service (KMS) and control access to the encryption keys.
Is CloudWatch like Splunk?
While both CloudWatch and Splunk provide log management and monitoring capabilities, they are different in terms of their scope and deployment models. CloudWatch is a native AWS service that primarily focuses on monitoring AWS resources. At the same time, Splunk is a third-party log management and analysis platform that can integrate with various data sources.
Is CloudWatch in a VPC?
CloudWatch itself is not directly deployed within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). However, it can monitor and collect metrics and logs from resources running within a VPC, including EC2 instances, RDS databases, and ELB load balancers.
Is CloudWatch automatically enabled?
CloudWatch is automatically enabled for most AWS services, capturing metrics and logs related to those services without requiring additional configuration. However, you may need to enable detailed monitoring or customize the metrics collected for certain resources.
Does AWS CloudWatch have an API?
Yes, AWS CloudWatch provides a comprehensive API that allows developers to interact with CloudWatch programmatically. The CloudWatch API enables you to perform various operations, such as retrieving metrics, creating alarms, and accessing log data.
Does Azure have CloudWatch?
No, Azure does not have a service called CloudWatch. CloudWatch is an AWS-specific service provided by Amazon Web Services. Azure has its monitoring and observability services, such as Azure Monitor and Azure Application Insights.
Can CloudWatch be used as SIEM?
While CloudWatch provides monitoring and alerting capabilities, it is not designed as a full-fledged security information and event management (SIEM) solution. However, CloudWatch can be integrated with other AWS security services, such as AWS Security Hub and AWS Config, to enhance security monitoring and compliance.
What is the difference between AWS logs and CloudWatch?
AWS logs refer to various logs that AWS services, applications, and resources generate. CloudWatch is a comprehensive monitoring and observability service that collects, analyzes, and stores logs, metrics, and events. In other words, CloudWatch is the service used to manage and monitor AWS logs.
Is CloudTrail automatically enabled?
CloudTrail is not automatically enabled by default. You need to create a CloudTrail trail and configure it to capture the desired API events and specify the S3 bucket for storing the logs.
Where do EC2 logs go?
Logs generated by EC2 instances can be sent to various destinations, depending on the configuration. They can be stored locally on the instance, sent to CloudWatch Logs for centralized storage and analysis, or streamed to an external logging service or SIEM platform.
What are the benefits of CloudTrail?
CloudTrail offers several benefits, including enhanced security and compliance auditing, improved visibility into API activity and changes within your AWS account, simplified troubleshooting and root cause analysis, and the ability to track user actions and resource modifications.
Is CloudTrail a global service?
CloudTrail is a global service that can capture API activity and events across multiple AWS regions. The logs are stored in the specified S3 bucket, allowing centralized access and analysis.
Does CloudTrail log failed API calls?
Yes, CloudTrail logs successful and failed API calls made within your AWS account. This includes information about the API request, the response, and associated error codes or messages.
Do CloudTrail logs expire?
CloudTrail logs do not automatically expire. By default, they are stored in the designated S3 bucket until you manually delete them or implement a lifecycle policy to manage log retention.
Can CloudTrail logs be deleted?
Yes, you can manually delete CloudTrail logs stored in the S3 bucket by deleting the corresponding log files. Additionally, you can configure lifecycle policies to automatically manage the retention and deletion of log files based on specific criteria.
What are CloudTrail logs used for?
CloudTrail logs are used for auditing and compliance purposes, security analysis, change tracking, troubleshooting, and investigating security incidents or unauthorized access attempts within your AWS account.
What is the maximum number of CloudTrail?
No fixed maximum number of CloudTrail trails can be created in an AWS account. However, AWS sets a soft limit of 500 trails per region by default. If you require more trials, you can request a limit increase from AWS Support.
What is the maximum file size for CloudTrail?
The maximum file size for a single CloudTrail log file is 256 MB. CloudTrail automatically creates a new file to continue logging the API activity if a log file exceeds this size.
Is CloudTrail a paid service?
CloudTrail is a combination of free and paid service. The creation and storage of CloudTrail logs in S3 are free. Still, there are charges for additional features such as log file integrity validation, multi-region trails, and delivering CloudTrail logs to CloudWatch Logs or other destinations.
What file type are CloudTrail logs?
CloudTrail logs are stored in JSON format. JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a widely used data interchange format that provides a human-readable and structured data representation.
How do I check my IAM role in CloudTrail?
You can check the IAM role associated with a CloudTrail trail by accessing the CloudTrail console in the AWS Management Console. Select the trail and navigate to the “Trail Details” page, where you can view the IAM role under the “Management” section.
Do CloudWatch logs use S3?
CloudWatch logs can be configured to use Amazon S3 as a storage destination. By enabling the export of CloudWatch logs to S3, you can centralize log storage and leverage the scalability and durability of S3.
How does CloudWatch log work?
CloudWatch Logs collects log data from various sources, such as EC2 instances, AWS services, and applications, and stores it in log groups. You can then configure log streams and use filters to search, analyze, and extract valuable information from the log data.
Is CloudWatch a monitoring service?
Yes, CloudWatch is a monitoring service provided by AWS. It allows you to monitor and collect metrics, logs, and events from various AWS resources and applications, providing insights into your AWS environment’s operational health and performance.
Do CloudWatch metrics expire?
No, CloudWatch metrics do not expire. Once you publish a metric to CloudWatch, it remains available for monitoring and analysis until you explicitly delete it.
What are the 3 types of log files?
The three types of log files commonly found in AWS are CloudTrail logs, which capture API activity and events within your AWS account, CloudWatch logs, which collect and store log data from AWS services and applications, and VPC Flow Logs, which capture network traffic information within Amazon VPC.
How many log types are there?
There are multiple log types in AWS, including CloudTrail logs, CloudWatch logs, VPC Flow Logs, ELB access logs, S3 access logs, RDS logs, and more. Each log type captures specific information about the corresponding AWS resource or service.
How do I monitor RAM in EC2 instances?
You can monitor RAM utilization in EC2 instances using CloudWatch. By enabling detailed monitoring for your EC2 instances, you can collect and analyze metrics related to memory usage, such as FreeableMemory and memory utilization.
What logs does CloudWatch collect?
CloudWatch collects various logs from AWS services and applications, including logs related to EC2 instances, Lambda functions, VPC Flow Logs, Route 53, RDS databases, ELB load balancers, and more. It provides centralized storage and analysis of these logs.
What events does CloudTrail log?
CloudTrail logs a wide range of events, including API calls to AWS services, management console sign-in events, resource creation and modification events, and AWS service events. It provides a detailed record of activity and changes within your AWS account.
How do I send CloudTrail logs to S3?
To send CloudTrail logs to Amazon S3, you need to configure a CloudTrail trail and specify an S3 bucket as the destination for log storage. Once configured, CloudTrail automatically delivers the logs to the specified S3 bucket.
How do I enable CloudWatch logging?
To enable CloudWatch logging, you can use the CloudWatch console or the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) to create log groups and log streams. Once created, you can configure your applications or AWS resources to send logs to the corresponding log groups.
How long are CloudTrail logs stored?
The retention period for CloudTrail logs depends on your specific configuration. By default, CloudTrail stores logs for 90 days. However, if required, you can extend the retention period or archive the logs to a separate storage solution.
Are CloudTrail logs sensitive?
CloudTrail logs may contain sensitive information such as API request parameters, user identities, and resource details. It is important to handle and protect these logs with appropriate security measures to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of their information.
Is CloudTrail a monitoring service?
CloudTrail is primarily a logging and auditing service rather than a monitoring service. It captures and logs API activity within your AWS account for security analysis, compliance monitoring, and troubleshooting.
Is CloudWatch immutable?
CloudWatch itself does not enforce immutability on the logs it collects or stores. However, you can implement access controls and security measures to ensure the integrity and non-repudiation of the logs within your AWS environment.
Why integrate CloudTrail with CloudWatch?
Integrating CloudTrail with CloudWatch allows you to leverage the monitoring and alerting capabilities of CloudWatch to gain real-time insights into API activity and events captured by CloudTrail. This integration enhances your ability to monitor and respond to security incidents and operational issues proactively.
What are the 3 types of storage in AWS?
The three types of storage commonly used in AWS are object storage, which includes services like Amazon S3 and Amazon Glacier, block storage, which includes services like Amazon EBS, and file storage, which includes services like Amazon EFS.
Is CloudWatch enabled by default for EC2?
CloudWatch is not enabled by default for EC2 instances. You must manually configure CloudWatch monitoring and choose the metrics and logs you want to collect from your EC2 instances.
What kind of monitoring does CloudWatch offer?
CloudWatch offers comprehensive monitoring capabilities for AWS resources and applications. It monitors metrics, logs, and events, allowing you to gain insights into resource utilization, troubleshoot issues, set up alarms, create dashboards, and perform operational and performance optimization analyses.
CloudTrail vs CloudWatch: Final Thoughts
The journey through the dense fog of “CloudTrail vs CloudWatch” has been insightful, illuminating AWS services’ unique features, use cases, and functionalities. They both play integral roles in managing and monitoring AWS environments yet serve distinctly different purposes.
CloudTrail, with its prowess in auditing and recording API activity, ensures you always have a bird’s eye view of your infrastructure’s operations. This makes it a powerful tool for compliance and security.
On the other hand, CloudWatch’s strength lies in real-time performance monitoring, providing detailed insights into your applications and enabling you to make data-driven decisions to optimize performance.
Rather than asking which tool is better, CloudTrail or CloudWatch, the more pertinent question is, how can these tools be employed to give you a comprehensive overview of your cloud environment? Used together, they offer a robust solution for managing your AWS operations, ensuring optimal performance, and maintaining a high level of security and compliance.
In conclusion, there’s no one-size-fits-all regarding CloudTrail vs CloudWatch. The choice ultimately hinges on your unique needs, the nature of your workloads, and your specific use cases.
By understanding the capabilities of each, you can leverage these powerful services to ensure your cloud environment is secure, efficient, and effective.