Are you tired of spending hours downloading large files, only to have the download fail at the last moment? Traditional downloading methods are slow and susceptible to numerous problems, such as file corruption, slow server speeds, and unstable connections.
And if you’re using .torrent files for peer-to-peer sharing, you’ve likely experienced the frustration of dead torrent links and inaccessible tracker servers. These challenges are all too common, making sharing and accessing files tedious.
Consider the case when downloading a critical piece of software or an important document you need for an urgent project. You’ve allocated time for the download, but it fails halfway through.
Or perhaps, you’ve been searching for a rare documentary and found a torrent file for it, but the tracker is offline. It’s not just about wasting time—these issues could lead to missed deadlines, lost opportunities, and frustration.
Enter Magnet Links—a revolutionary file-sharing approach that addresses many issues. Magnet Links have been gaining popularity for their efficiency, resilience against data loss, and reduced server dependency.
These unique identifiers for content on the network ensure that your downloads are faster, more reliable, and can be resumed if interrupted, eliminating the most common pain points of traditional downloading methods.
In this article, we’ll delve into Magnet Links, how they work, and how they could streamline your file-sharing and downloading experiences.
Understanding the Basics
BitTorrent, a peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing protocol, revolutionized how we distribute and download large files over the internet.
The fundamental principle of BitTorrent lies in its decentralization approach, where users called “peers” cooperate to share fragments of a file. These fragments are known as “pieces,” and this collaborative approach accelerates downloads and reduces the burden on individual servers.
Hash values, crucial components of the BitTorrent ecosystem, are unique alphanumeric strings generated by a hash function, such as SHA-256. These hashes serve as digital fingerprints for each file piece and are essential in maintaining data integrity.
When a peer downloads a piece, it computes the hash value and compares it to the expected value. Any discrepancy indicates data corruption or tampering, leading to the automatic rejection of the compromised piece.
Magnet links play a pivotal role in modern BitTorrent systems. Rather than using traditional .torrent files, magnet links utilize hash values to identify the torrent content.
When you click on a magnet link, your BitTorrent client calculates the hash values of the files involved and connects to the decentralized network to locate the required pieces. This eliminates the need for centralized trackers, making the system more resilient and censorship-resistant.
The BitTorrent protocol, powered by its ingenious use of hash values and the revolutionary concept of magnet links, has proven to be a robust and efficient method for sharing large files across the internet.
Its decentralized nature ensures continued availability and redundancy, making it a reliable and preferred choice for file distribution in the digital age.
The Anatomy of a Magnet Link
In the realm of peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing, Magnet links have emerged as a powerful and efficient means of distributing digital content. These links have transformed how we access and share files, and understanding the components that constitute a magnet link is crucial for fully comprehending its inner workings.
We will take a detailed exploration of each component, including the Display Name (DN), Exact Topic (XT), Acceptable Source (AS), and more, to unravel the mysteries behind this ingenious technology.
1. Display Name (DN)
The DN component is an optional but user-friendly element within a magnet link. It serves as a convenient label, allowing users to quickly identify the content before initiating the download process. When included, the DN provides relevant and descriptive information about the linked resource, enhancing the user experience by offering context and ensuring clarity.
2. Exact Topic (XT)
At the heart of a magnet link lies the XT component, which plays a critical role in ensuring the integrity and consistency of the shared content. It usually consists of a unique identifier or a hash value generated through a hash function like SHA-256.
This hash value acts as a digital fingerprint of the target file, representing its exact content. The presence of the XT component allows the recipient’s BitTorrent client to verify the authenticity of the downloaded data, ensuring that it matches the source and has not been altered during transmission.
3. Acceptable Source (AS)
The AS component within a magnet link is an indispensable feature that contributes to the robustness and resilience of the P2P file-sharing ecosystem. It enumerates acceptable sources or locations from which the content can be downloaded.
By listing multiple sources, the AS component enables a decentralized distribution model where users, known as “peers,” can fetch fragments of the file from different locations simultaneously. This redundancy enhances download speed and ensures that the content remains available even if some sources become unavailable.
4. Keyword Topic (KT)
An optional element that may be found in some magnet links is the KT component. This component allows users to include additional keywords or metadata related to shared content.
Including relevant keywords enhances searchability and improves the chances of users discovering the shared files efficiently. The KT component acts as a valuable tag, categorizing the content and facilitating its discoverability within the vast network of P2P file sharing.
5. File Size (FS)
While not mandatory, the FS component can provide vital information about the file size associated with the magnet link. For users with limited bandwidth or storage capacity, knowing the FS helps them make informed decisions regarding the feasibility of downloading the content. Users can gauge the potential impact on their internet data usage and device storage by being aware of the file size upfront.
Magnet links have transformed the landscape of file sharing, offering a decentralized and efficient approach to distributing digital content.
By understanding the various components, such as the Display Name (DN), Exact Topic (XT), Acceptable Source (AS), and others, users can navigate the world of magnet links with confidence and optimize their file-sharing experiences.
These components work harmoniously to ensure data integrity, improve download speeds, and foster a resilient network where users can access and share content seamlessly.
Embracing the power of magnet links unlocks a new era of P2P file sharing, revolutionizing how we interact with digital media.
How To Open Magnet Links In Chrome
Chrome has a particular setting that allows users to use magnet links; the first task you have to perform is to ensure that the setting is allowed or turned on.
Here’s how to do that.
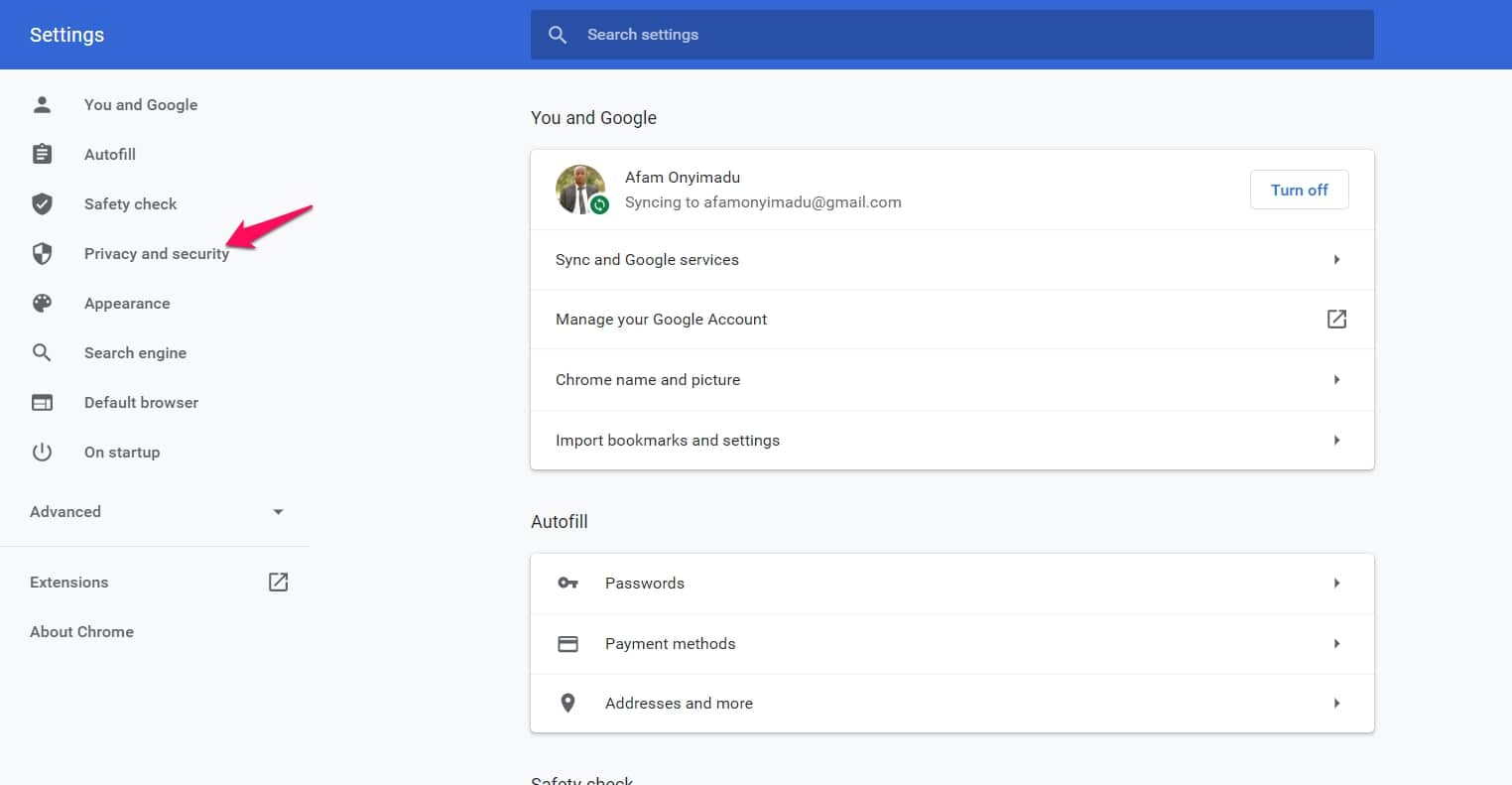
Go to Settings, click on the menu icon at the top left corner of your screen, and click on “Privacy and Security.”
Note: These clicks are sequential, click on one, and it’ll lead you to the next.
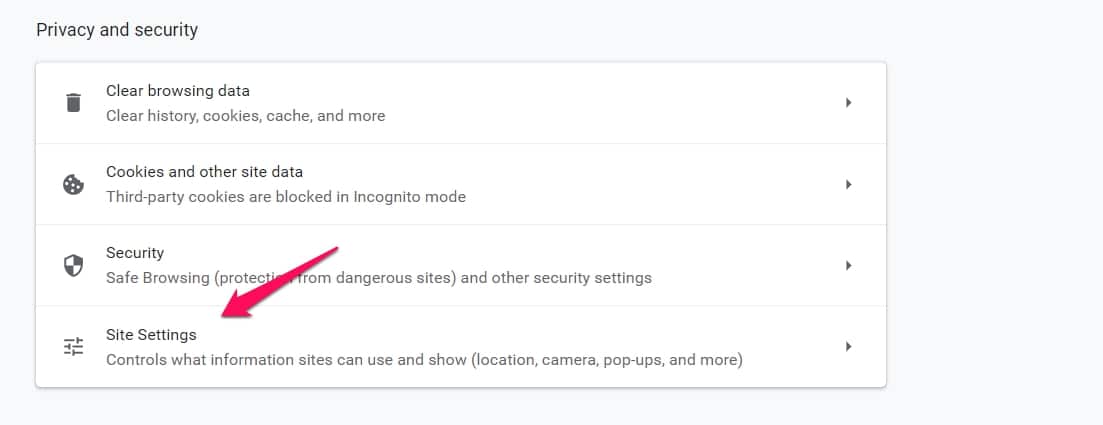
In Privacy and Security, click on site Settings.
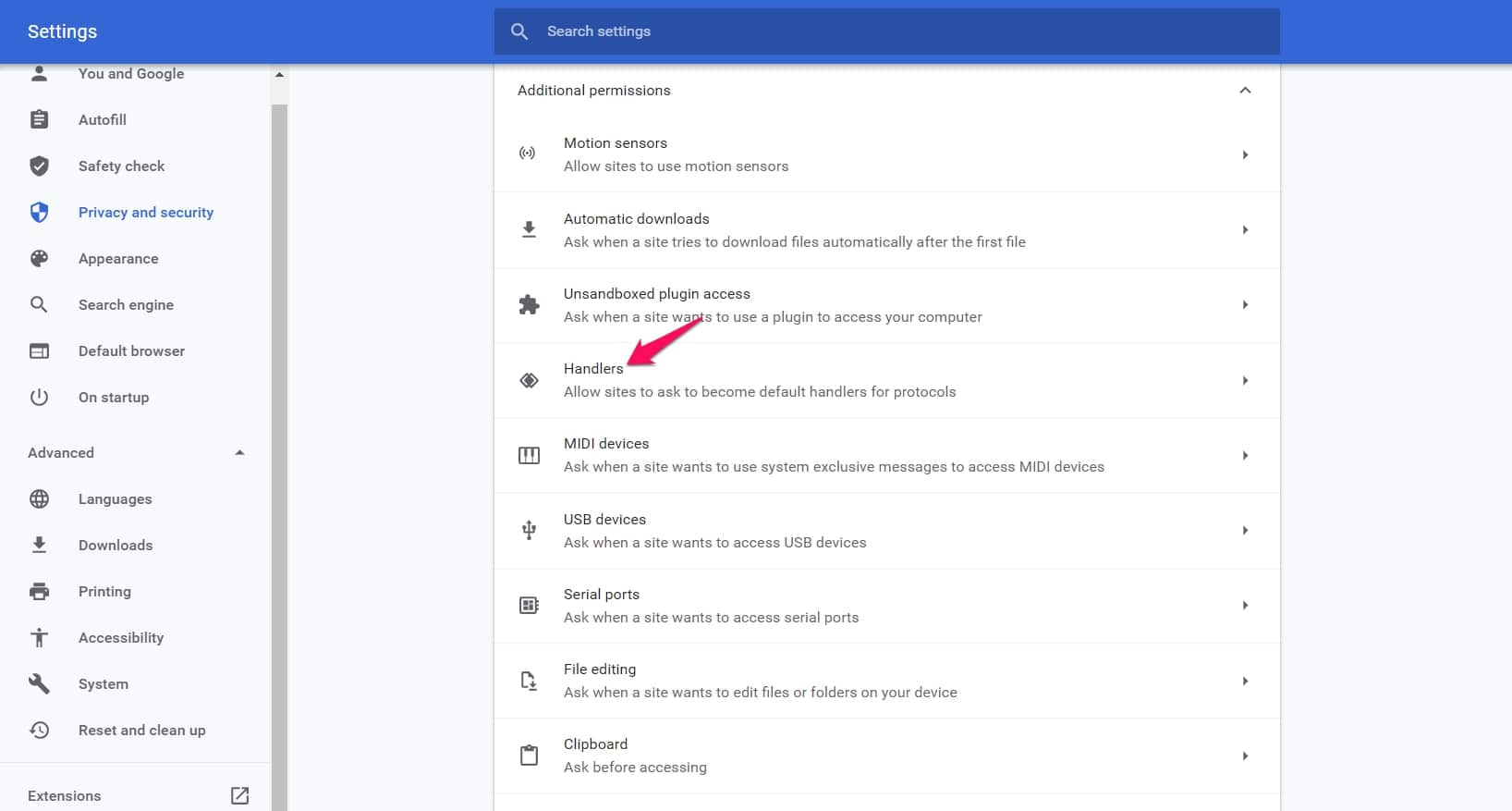
Next, Handlers and “Allow sites to become default handlers for protocols“.
You’re pretty much set up for downloads now.
Magnet link Utorrent
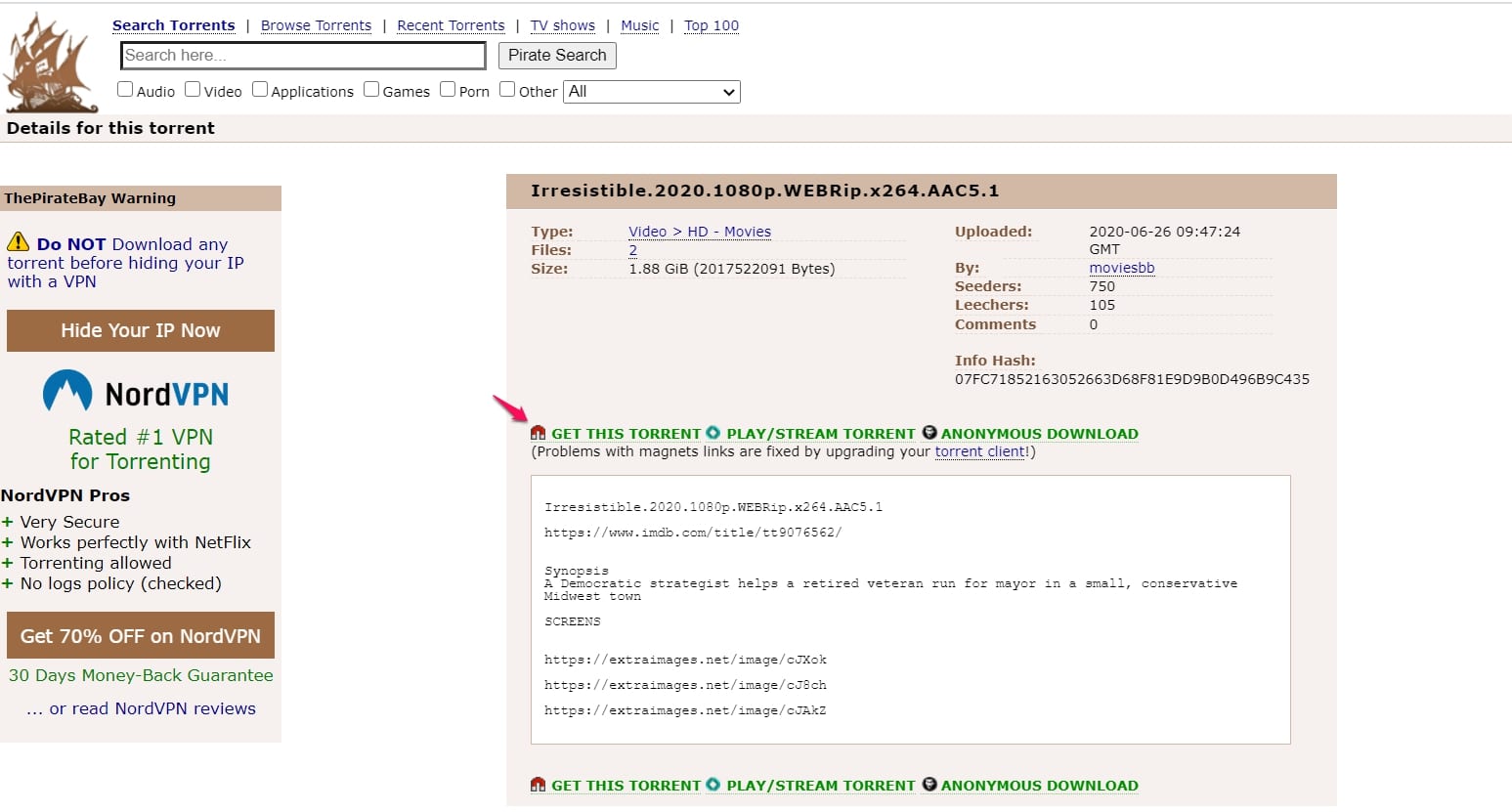
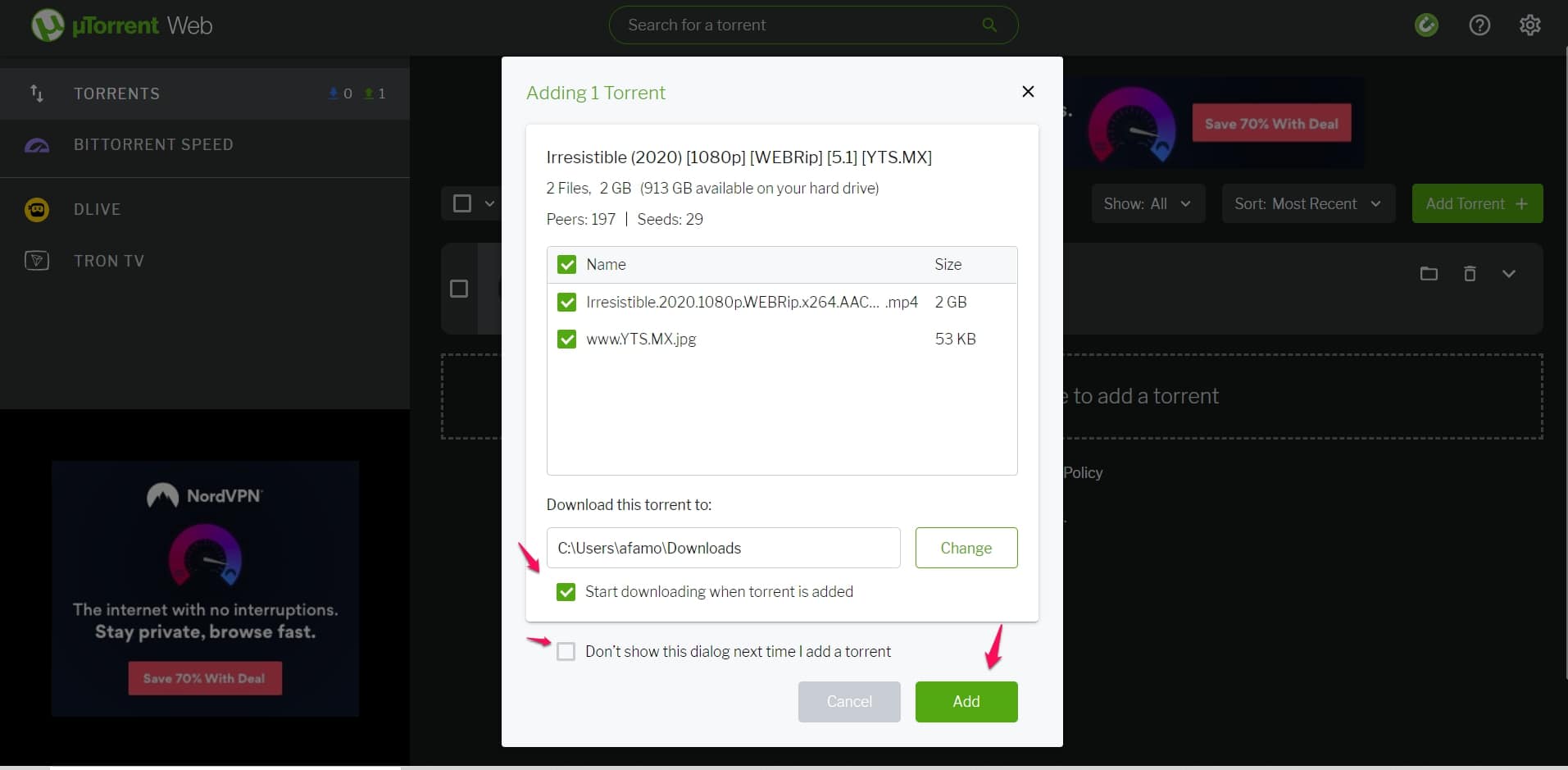
After setting up your Chrome or any other browser for magnet links, as shown above, you have to visit your favorite torrent site and click on the magnet links (chances are the normal download icon is a magnet link), and a message will pop up.
The pop-up will ask you to open the magnet link with a BitTorrent client (like uTorrent, Vuze, and Transmission).
Accept it, and your uTorrent client will open the magnet link. Note that you should have downloaded and installed Utorrent first.
Chrome also has a feature that makes this process easier the next you want to download using magnet links.
When Chrome asks if you want to use your BitTorrent client app to open the magnet link, it will also ask if you want to “always open these types of links with the associated app“.
Click this box, and you won’t be asked again another time to confirm your choice. It will just go straight to the BitTorrent client app and open the link.
How To Open Magnet Links In Mozilla Firefox
For Mozilla Firefox, the method is pretty much the same. You must visit your favorite torrent site, click on the magnet links, and a message will pop up.
The pop-up will ask you to open the magnet link with a BitTorrent client (uTorrent, Vuze, Transmission). Accept it, and your uTorrent client will open the magnet link.
A question that might arise is this:
“What if I have already checked the “always open these types of links” box for a particular BitTorrent client, and I want to change to another BitTorrent client?
The answer is pretty simple. It is possible to do it, and here’s how it’s done. It is called “resetting the association.”
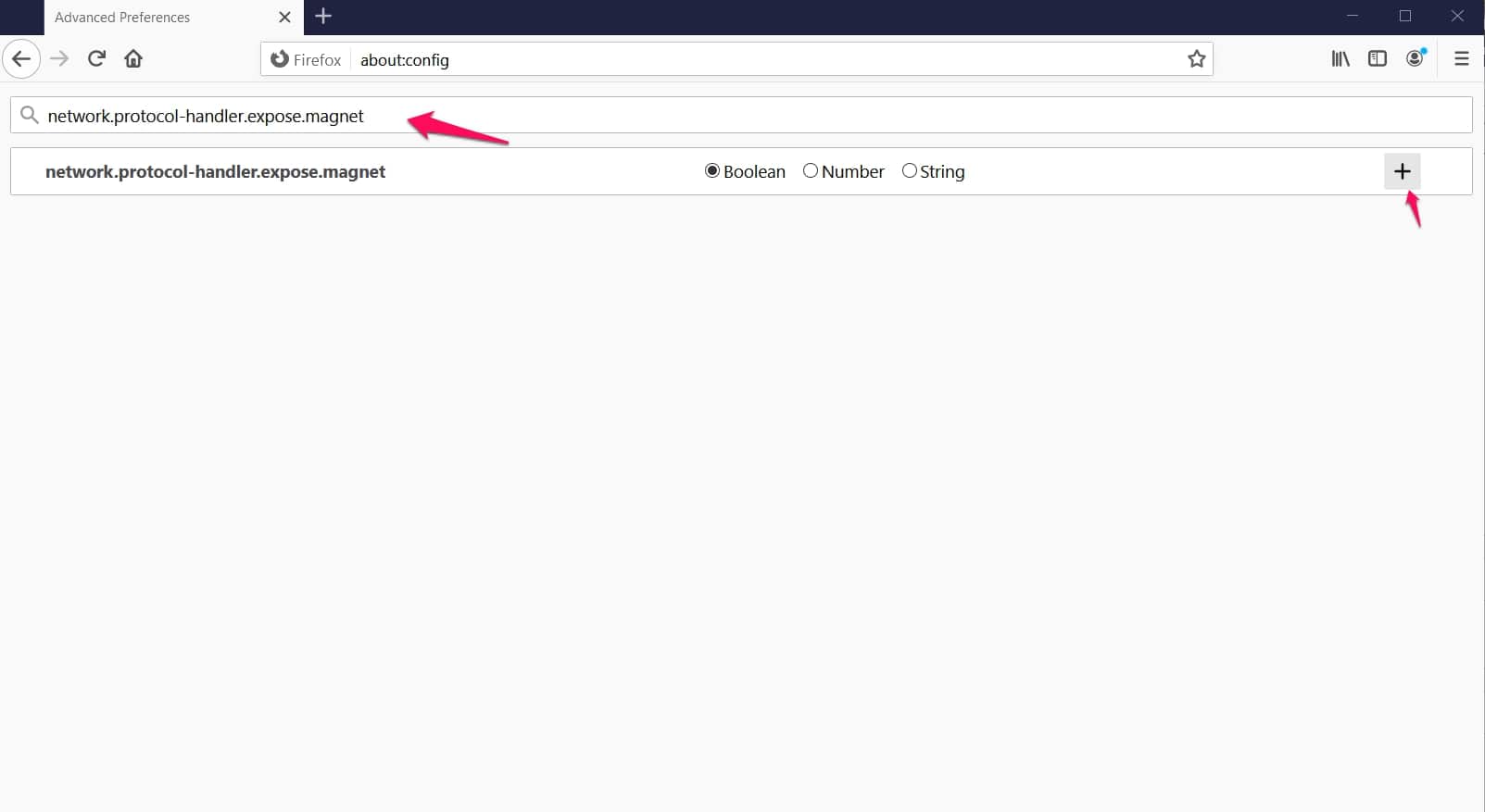
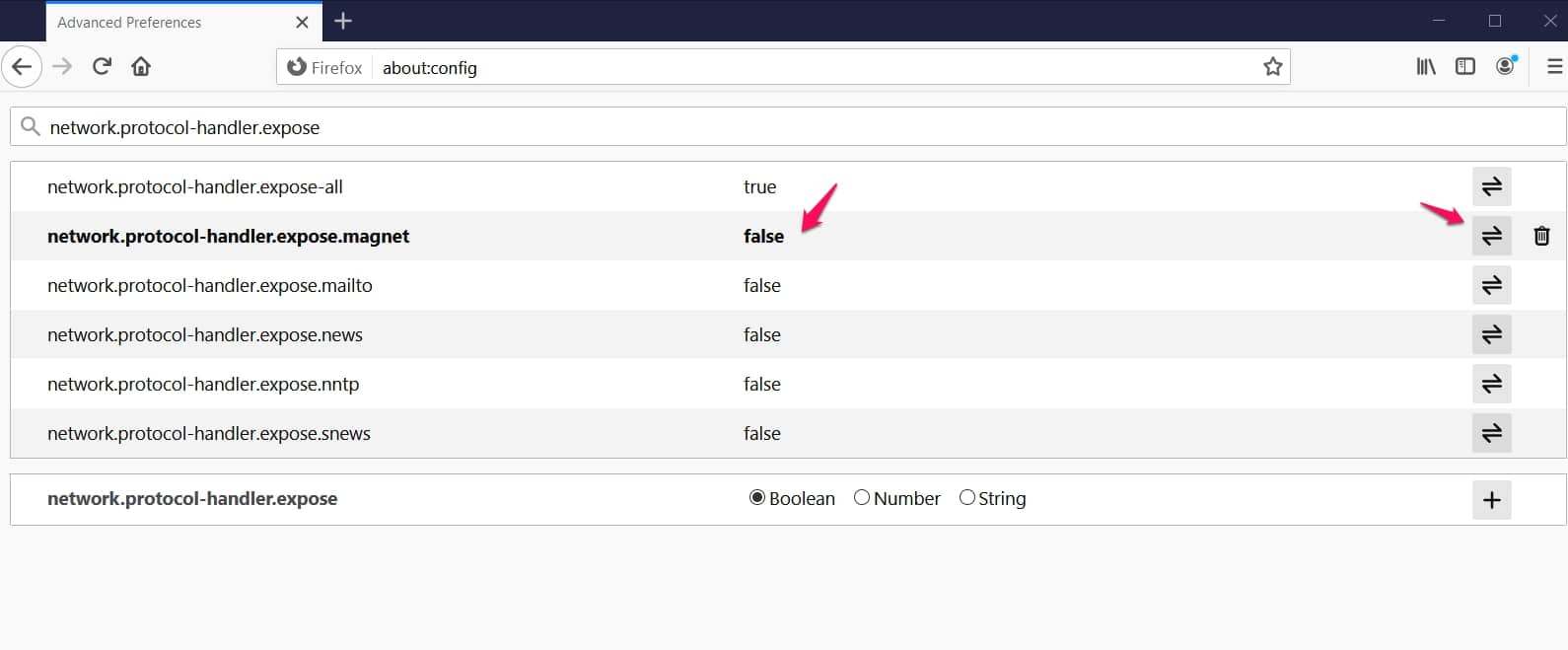
First, locate the Firefox address bar, enter “about:config” and then when a page shows, search for “network.protocol-handler.expose.magnet“.
Right-click the preference (making a particular BitTorrent client your default app) you made earlier and clicked “Toggle” to ensure the value is set to “False“.
Once the “value” is set to false, you can try the magnet link and use another torrent client.
Go back to the torrent and click on the magnet link, and that pop-up box asking which app you’d like to use as the default option for opening magnet links will show again, and now you can choose the new BitTorrent client you want to use.
How To Open Magnet Links In Other Browsers
For generic browsers, most browsers will automatically ask you if you want to use your BitTorrent client to open magnet links when you click on them. But sometimes, this might not happen, and you must manually create a file association.
The above issue was about resetting an association already made by browsers like Chrome or Mozilla Firefox. Still, the browser hasn’t even made any association here, so the user has to create one manually.
Here’s a play-by-play on how it’s done.
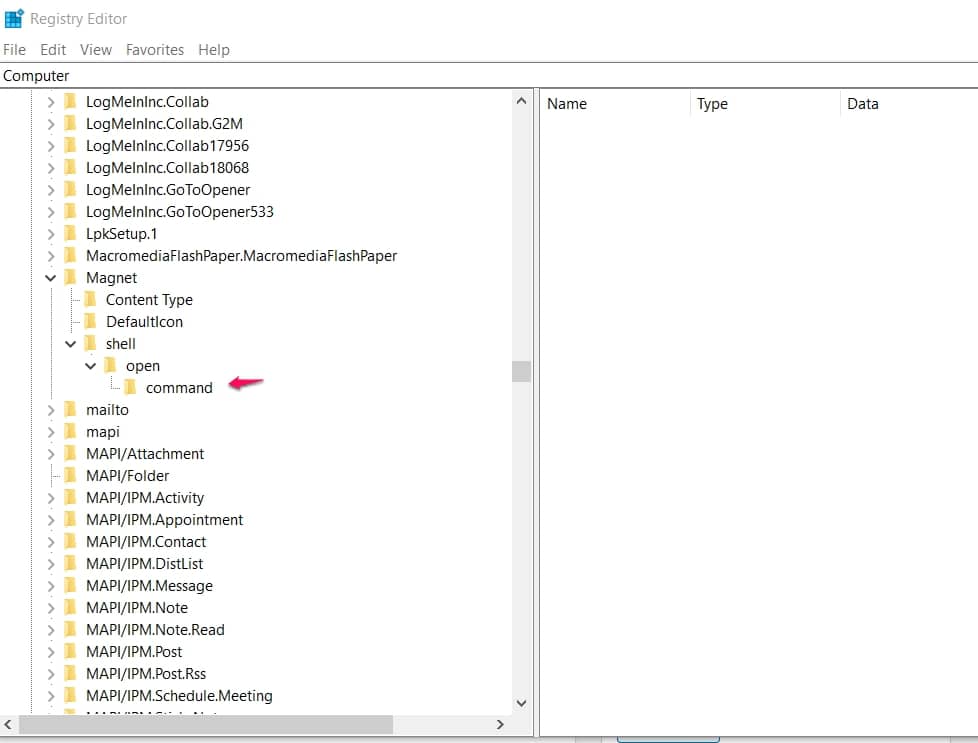
Go to the Windows Registry Editor “Win + R ” and enter regedit into the box.”
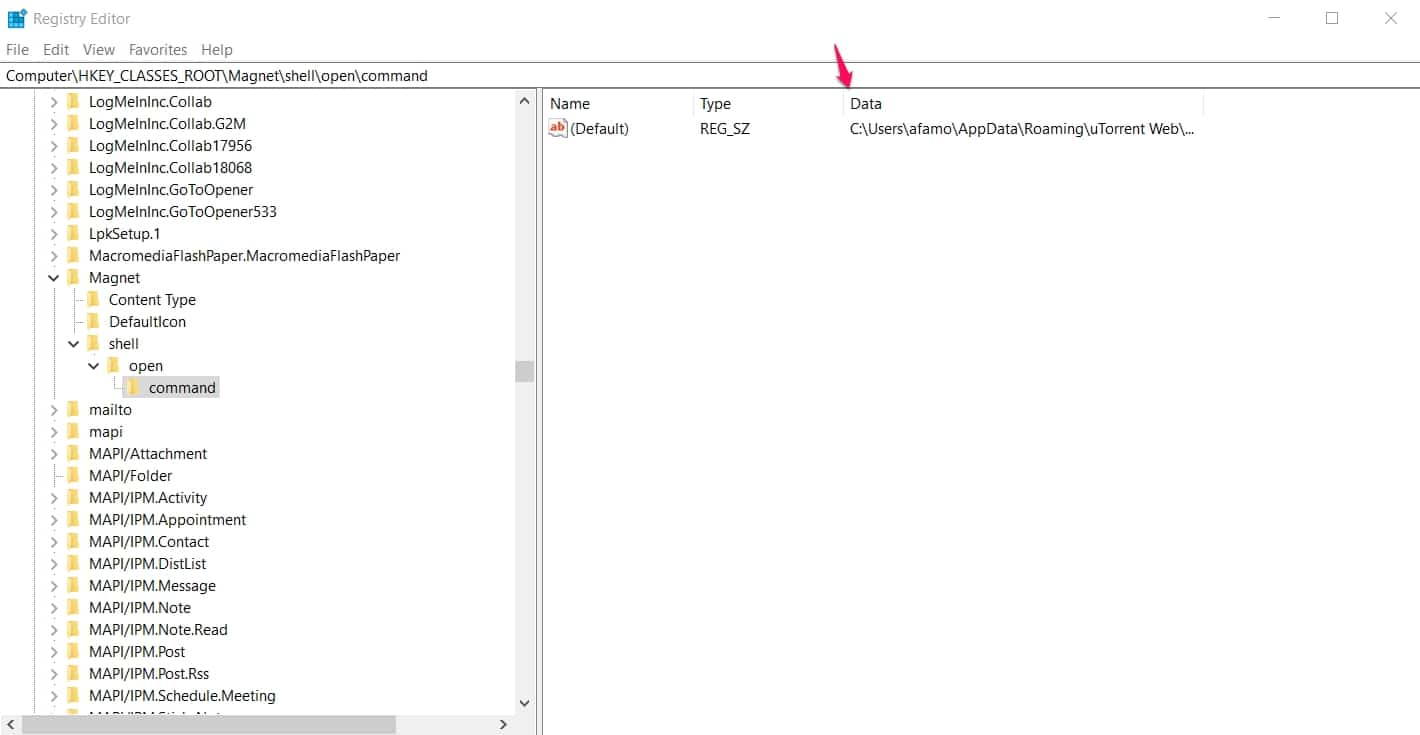
Find this location Computer -> HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT -> Magnet -> shell -> open -> command
Just by the right, in the registry pane under “Data“, you will find info about the directory of the BitTorrent client app you currently use and some other info.
In this case, we are going with uTorrent as our client, so the default directory info will look a lot like this:
“C: UsersUserAppDataRoaminguTorrentuTorrent.exe “%1” /SHELLASSOC
Another question that could pop up would be:
What if the information on the data pane doesn’t match my BitTorrent client’s directory? What should I do?
Here’s what you should do-
Assuming you’ve already taken the steps outlined above to get to “Data” in the registry pane.
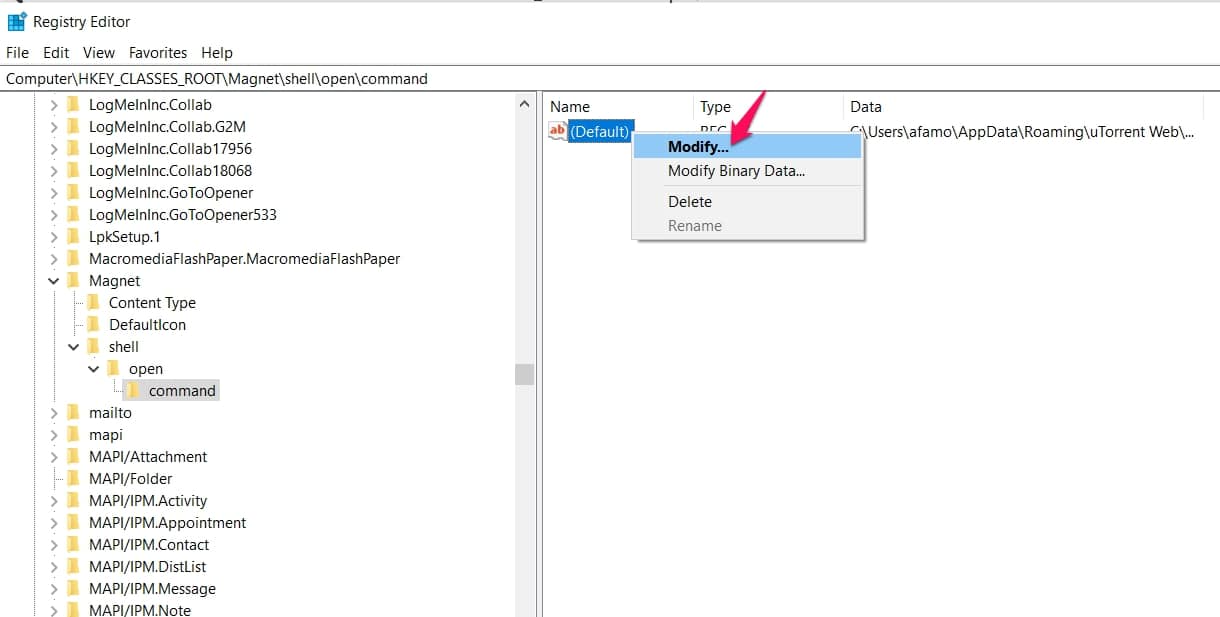
Then right-click “Default” and click “Modify” when it pops up.
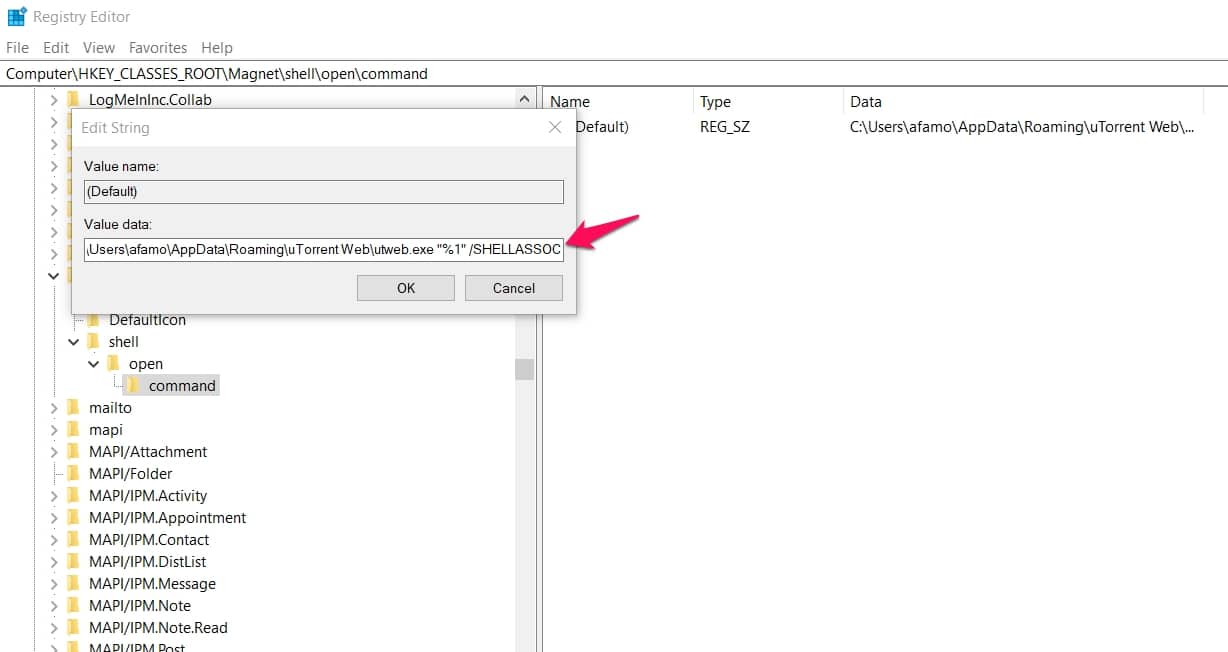
An option to edit the directory will appear, and now you can enter the correct directory for the BitTorrent client you’re using.
It is important to follow it up by “%1” /SHELLASSOC
After that, most generic browsers will link your BitTorrent client app with magnet links when you try to use them.
The Advantages of Using Magnet Links
In the ever-evolving landscape of peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing, Magnet links have emerged as a groundbreaking technology offering many advantages over traditional methods.
These innovative links have revolutionized how we access and distribute digital content, providing users with a seamless and efficient file-sharing experience.
Let’s delve into the significant advantages of using Magnet links:
1. Seamless Download Experience
One of the most significant advantages of using Magnet links is their seamless download experience. Unlike traditional file-sharing methods that rely on centralized servers or trackers, Magnet links facilitate direct communication between peers.
This decentralized approach ensures that the download process remains robust and resilient, as there is no single point of failure. Users can effortlessly access and share content without intermediary servers, enhancing overall efficiency.
2. No Dependency on External Files
Traditional torrenting methods involve the use of .torrent files to initiate downloads. However, with Magnet links, there is no need for external files.
The link contains all the necessary information, including the file’s hash value and the network location of potential sources. This self-containment makes Magnet links more convenient and reduces the risk of broken or outdated .torrent files.
3. Faster and More Reliable Downloads
Due to the decentralized nature of Magnet links, users can enjoy faster and more reliable downloads. When a user clicks on a Magnet link, their BitTorrent client can immediately access the distributed network of peers.
The client can fetch data from multiple sources simultaneously, significantly improving download speeds. Additionally, the redundancy offered by multiple sources ensures that if one peer becomes unavailable, the download can seamlessly switch to another, enhancing reliability.
4. Resilience and Availability
Magnet links inherently promote a resilient file-sharing ecosystem. Traditional torrents heavily rely on centralized trackers to coordinate communication between peers.
In contrast, Magnet links eliminate this dependency, making it challenging for authorities or malicious entities to control or shut down the distribution of specific files. This enhanced resilience ensures that the content remains available and accessible to users, regardless of external interference.
5. Reduced Bandwidth and Storage Usage
Another advantage of using Magnet links is bandwidth and storage usage reduction. Since Magnet links contain only the essential metadata required for sharing files, they are significantly smaller than .torrent files. This saves bandwidth for users initiating downloads and minimizes the strain on hosting websites and networks.
6. Improved Privacy and Security
Magnet links contribute to improved privacy and security for users. As there are no .torrent files involved, initiating a download is more discreet.
Users can click the Magnet link without leaving any activity traces on external websites. Additionally, using hash values in Magnet links ensures data integrity, reducing the risk of downloading corrupted or malicious files.
In conclusion, Magnet links offer many advantages that have propelled them to the forefront of modern P2P file sharing.
From providing a seamless download experience and eliminating dependencies on external files to enabling faster, more reliable downloads and enhancing privacy and security, Magnet links have revolutionized how we share and access digital content.
Embracing this innovative technology opens up new possibilities for a decentralized and resilient file-sharing future. As we navigate the digital age, Magnet links stand as a testament to the power of technological innovation in enhancing the way we interact with and exchange digital media.
Common Magnet Links Use Cases and Applications
Magnet links, a revolutionary peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing technology, have witnessed a meteoric rise due to their versatile applications and user-friendly attributes.
From facilitating faster and decentralized downloads to enabling seamless content access, Magnet links have found extensive use in various domains.
Let’s explore some of the common use cases and applications where Magnet links have made a significant impact:
1. P2P File Sharing Platforms
Magnet links are the backbone of popular P2P file-sharing platforms, enabling users to distribute and access a wide range of digital content.
Whether it’s sharing media files, software, or documents, the decentralized nature of Magnet links ensures faster and more reliable downloads. P2P platforms benefit from this approach, as it reduces their server loads while promoting a robust network of interconnected peers.
2. Torrent Indexing Websites
Torrent indexing websites leverage Magnet links as a more efficient alternative to traditional .torrent files. By offering Magnet links for each listed torrent, these platforms make it easier for users to initiate downloads directly without needing external files.
This simplification enhances the user experience, while the decentralized nature of Magnet links contributes to the overall resilience of the torrent ecosystem.
3. Content Distribution Networks
Content distribution networks (CDNs) utilize Magnet links to streamline the delivery of large files and software updates to users worldwide. The ability to fetch data from multiple sources simultaneously enhances download speeds and ensures content availability. CDNs benefit from the reduced server load, as users share the data through the Magnet links.
4. Academic Research and Data Sharing
In academic and research communities, Magnet links facilitate sharing of large datasets, scientific papers, and research findings. Researchers can disseminate their work quickly and efficiently to peers in the field, ensuring faster access to critical information.
This application of Magnet links accelerates the pace of research and collaboration among scholars across the globe.
5. Open-Source Software Distribution
The open-source software community relies heavily on Magnet links to distribute software packages. With many developers and users involved, the decentralized nature of Magnet links ensures that the distribution process remains smooth, even during peak demand.
Furthermore, Magnet links promote authenticity and data integrity by including hash values, mitigating the risk of downloading compromised software.
6. Media and Entertainment Industry
The media and entertainment industry also harnesses the power of Magnet links to share large files like movies, TV shows, and music albums. With an extensive user base, Magnet links help distribute the content quickly, reducing server strain and improving end-users overall download experience.
7. Collaboration in Online Communities
Online communities and forums often employ Magnet links to share content relevant to their interests. Whether it’s sharing e-books, artwork, or custom software modifications, Magnet links provide a convenient way for community members to access and discuss shared content efficiently.
In conclusion, Magnet links have become a cornerstone of modern file sharing and content distribution across various domains. Their decentralized nature, faster download speeds, and ability to eliminate dependencies on external files make them highly versatile and efficient.
From P2P file-sharing platforms and torrent indexing websites to academic research and open-source software distribution, Magnet links are pivotal in streamlining data dissemination and promoting collaboration in the digital age.
As technology advances, Magnet links will likely remain a fundamental tool in enhancing how we share and access digital content.
Potential Drawbacks and Concerns of Magnet Links
While Magnet Links have undoubtedly transformed the landscape of peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing and content distribution, it’s essential to acknowledge that every technology comes with its challenges.
As we explore the world of Magnet links, it becomes apparent that certain potential drawbacks and concerns are associated with their usage.
Let’s delve into these aspects to gain a comprehensive understanding:
1. Centralization of Magnet Link Repositories
One of the primary concerns surrounding Magnet links is the potential centralization of repositories that host these links. While the links promote a decentralized approach to file sharing, the repositories that index and curate Magnet links may become centralized, leading to a dependency on a few platforms. This situation could lead to limited access, censorship, or vulnerability to external control.
2. Metadata Privacy and Security
As Magnet links include metadata and keyword information, there are potential privacy and security concerns. While this data is essential for discovering and categorizing content, it can also reveal user preferences and behavior. To address this concern, users must exercise caution while sharing Magnet links, especially when dealing with sensitive or personal data.
3. Hash Collisions and Data Integrity
Although Magnet links employ hash values to ensure data integrity, the possibility of hash collisions cannot be entirely ruled out.
A hash collision occurs when two different files generate the same hash value, potentially leading to incorrect or corrupted content downloading. While such occurrences are rare, they can sometimes compromise the reliability of Magnet links.
4. Over-Reliance on Magnet Links
The increasing reliance on Magnet links for file sharing may create an over-dependency on this technology. Traditional torrenting methods, such as .torrent files, are gradually being phased out, reducing diversity in the file-sharing landscape. An over-reliance on a single approach may limit innovation and hinder the exploration of alternative solutions.
5. Limited Support in Some Clients
While major BitTorrent clients support Magnet links, some older or less popular clients may not provide full support. Users relying on such clients may face compatibility issues when using Magnet links for file sharing. Developers need to ensure backward compatibility and widespread support to avoid user frustration.
6. Legitimacy and Copyright Concerns
The ease of sharing content through Magnet links also raises concerns about copyright infringement and distributing of illegal or pirated material. Since Magnet links allow seamless access to copyrighted content, ensuring responsible usage and adherence to intellectual property laws becomes crucial.
While Magnet links enable decentralized downloads, they are still susceptible to the availability of peers in the network. Users may experience slower download speeds or a complete inability to access the content if a particular file has very few active sources. This situation is more likely to occur with rare or niche files.
In conclusion, while Magnet links offer significant advantages in P2P file sharing, it’s vital to recognize the potential drawbacks and concerns associated with their usage. These aspects require careful consideration, from concerns about centralization and metadata privacy to the possibility of hash collisions and copyright issues.
As technology evolves, developers and users must work together to address these concerns and ensure responsible and secure usage of Magnet links. By acknowledging and mitigating these challenges, we can further enhance the efficiency and reliability of this innovative file-sharing technology.
Are Magnet Links Untraceable?
Whether magnet links are untraceable is a subject of much debate and misunderstanding in peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing. To answer this question, we must investigate how magnet links function and impact user privacy and anonymity.
Magnet links, in essence, are a form of metadata that contains cryptographic hash values representing the target files. When a user clicks on a magnet link, their BitTorrent client uses these hash values to connect to the decentralized network of peers and initiate the download process. The absence of .torrent files in magnet links is often misconstrued as complete untraceability.
However, it’s essential to understand that while magnet links do not directly expose users to external .torrent files, they do not provide complete anonymity.
When a user initiates a download through a magnet link, their IP address becomes visible to other peers in the network. This visibility can be leveraged to trace the user’s online activities back to their connection.
Many users employ virtual private networks (VPNs) while engaging in P2P file sharing through magnet links to bolster privacy and security. VPNs route the user’s internet traffic through encrypted tunnels, masking their true IP addresses from prying eyes.
This measure adds an extra layer of protection, enhancing anonymity and making it more challenging to trace the user’s activities back to their original connection.
It’s worth noting that while magnet links themselves do not inherently reveal user identities, other factors, such as user behavior, data shared, and interactions with the network, can still be analyzed to infer potential identities.
In conclusion, while magnet links offer convenience and avoid using external .torrent files, they are not entirely untraceable. Users should be aware of the potential risks associated with P2P file sharing and take appropriate measures, such as using VPNs, to enhance privacy and protect their online identities.
Achieving true untraceability in the digital realm requires a combination of secure practices and proactive measures to safeguard user anonymity.
📗FAQ’s
Are magnet links illegal?
No, magnet links themselves are not illegal. They are a technology used for P2P file sharing, enabling users to download and share content without relying on centralized servers or .torrent files.
What is a magnet link?
A magnet link is a form of metadata that contains cryptographic hash values representing the target files. When clicked, it connects the user’s BitTorrent client to a network of peers to initiate downloads directly.
How do I access magnet links?
To access magnet links, simply click on the link, and your BitTorrent client will handle the rest, connecting you to the decentralized network.
Can magnet links be tracked?
While magnet links themselves do not reveal user identities, user behavior and IP addresses can be tracked. Utilizing a VPN can enhance privacy and make tracking more challenging.
What happens if you get caught Torrenting?
Getting caught Torrenting copyrighted material without permission can lead to legal consequences, including fines and potential lawsuits.
Can I get caught Torrenting with VPN?
While using a VPN enhances privacy, there is no guarantee of absolute protection.
Why can’t I open magnet links?
Issues opening magnet links can be due to browser settings or a lack of a compatible BitTorrent client.
What do I do with a magnet link?
Click on the magnet link, and your BitTorrent client will handle the download process.
Does magnet attract WIFI?
No, magnet links have no impact on WiFi signals. They are unrelated technologies.
How to download magnet links for free?
Magnet links are inherently free to use. No cost is associated with accessing and using them.
What software opens magnet links?
BitTorrent clients like uTorrent, qBittorrent, and BitComet can open magnet links.
How do you make a magnet link?
Creating a magnet link involves generating a cryptographic hash value from the target file and appending it to a magnet URI.
What happens if your ISP catches you torrenting?
If your ISP detects illegal Torrenting, they may take actions like issuing warnings or throttling your internet speed.
Can an ISP tell if you are Torrenting?
ISPs can monitor internet traffic, and certain Torrenting activities can be detected.
Do stores detect magnets?
Stores use security tags and surveillance cameras to prevent theft, not magnets.
Can you go to jail for Torrenting in USA?
Engaging in illegal Torrenting can result in fines and, in extreme cases, jail time.
How long can you go to jail for Torrenting?
Jail sentences for Torrenting depend on the severity of the offense and applicable laws.
Is Torrenting illegal in the US?
Torrenting copyrighted material without permission is illegal in the US.
How do I not get caught while Torrenting?
Using a VPN and avoiding illegal downloads can reduce the risk of getting caught.
Do people get sued for Torrenting?
Yes, copyright holders may sue individuals for illegal Torrenting.
Does AT&T care about Torrenting?
AT&T and other ISPs actively monitor network activity to prevent illegal Torrenting.
How does a magnet link look like?
A magnet link typically starts with “magnet:?” followed by hash values and optional parameters.
How to download magnet links without uTorrent?
Use alternative BitTorrent clients like qBittorrent or BitComet to download magnet links.
Why can’t you put two magnets together?
When similar poles (north-north or south-south) of magnets are placed together, they repel each other.
Is it safe to download magnet links?
Downloading magnet links is generally safe, but ensure the content is legal and from trusted sources.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we’ve explored the intricacies of Magnet Links, their operational structure, and how they play a significant role in making data transfer more efficient and resilient.
Magnet Links is a revolutionary approach in file sharing, addressing several pain points that users often face with traditional .torrent files.
However, while they offer numerous benefits, navigating this technology responsibly is important. Users should respect the legal and ethical boundaries of file sharing, ensuring they use Magnet Links for legitimate and legal purposes.
The increasing acceptance and use of Magnet Links could transform the file sharing landscape, ensuring seamless and efficient data transfer. We encourage you to use this technology, making your downloading experiences smoother and more reliable.
Always remember a fair understanding of the technology, its advantages, and its potential drawbacks will equip you with the power to utilize it most effectively. Stay informed, stay responsible, and harness the power of Magnet Links for your file-sharing needs.