Some confusion between terms is normal when shopping for advanced technical solutions. Proxies are no exception, but it shouldn’t stop you from making a good decision. We will discuss how a proxy service differs from proxy servers and which one you actually need (most probably, both).
What is a proxy?
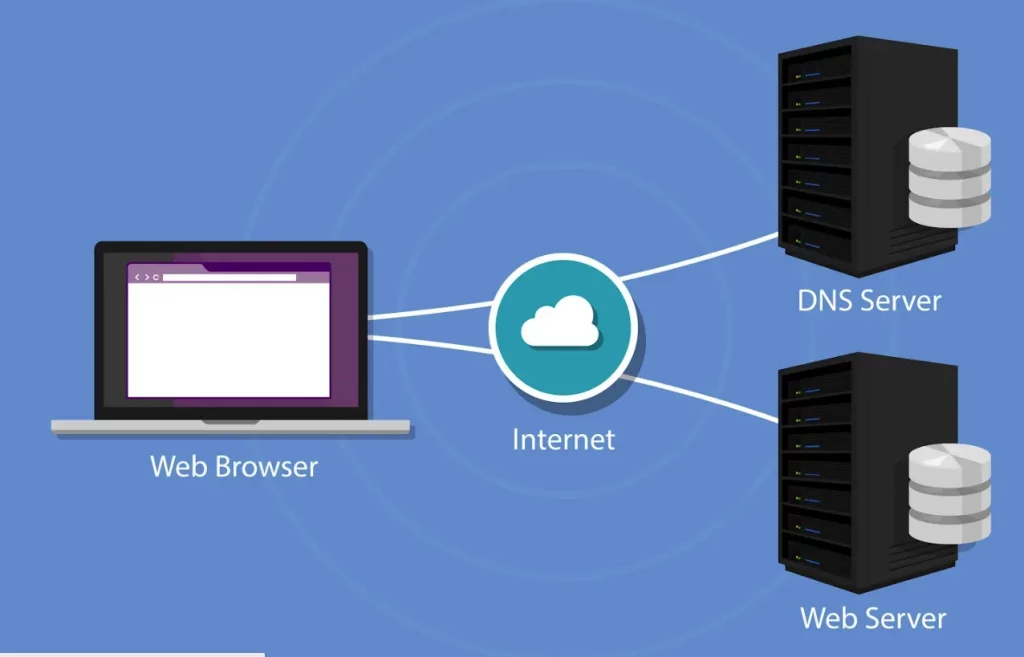
When connecting to the internet directly, your device sends a request to the web server. A proxy changes this by acting as a middleman. If you use one, that request first goes to the proxy server and only then reaches the destination. After that, the data is forwarded to you, and the website is loaded.
Since a proxy acts as an intermediary, the web server doesn’t see the original IP address, only that of a proxy. By checking IP addresses, websites can know their visitors’ approximate location and the internet service provider (ISP), which allows them to trace their activity and restrict content.
In short, a proxy is a device (usually a server) that ensures privacy and increases security by allowing others to use its connection. But proxies can achieve this in different ways, depending on their setup. So to understand proxies, it is important to know how main types can be categorized.
Types of proxy servers
The first thing to note about types of proxy servers is how many users can access the IP addresses:
- If more than one user can access a proxy, it is shared.
- If access to the proxy is limited to one user, it is dedicated or private.
Shared proxies are significantly cheaper but can get slower if user count and traffic suddenly rise. That is why spending a bit more and purchasing dedicated proxies (at least for tasks you deem important) is recommended.
Proxies can be set up almost anywhere in the world with an internet connection. But the way proxies acquire access to the web can differ, resulting in variations in performance and legitimacy.
- Residential proxies acquire IP addresses from internet service providers (ISPs) and are connected through physical devices, just like you would in your home. They are best in cases where you need to avoid IP bans and have accurate location targeting.
- Datacenter proxies do not have their IP addresses verified by ISPs. These proxies are created in large numbers and run in specialized data centers. They are best when you need a lot of IPs and a fast connection.
There are some in-between options, such as ISP proxies and mobile proxies. The first is residential proxies located in a data center that aim to be both legitimate and fast. Mobile proxies originate from portable devices (tablets, smartphones, etc.) using mobile internet, so they are neither home connections nor based in data centers.
We can combine shared and dedicated access with other types and increase the variety even further. For example, datacenter proxies can have both shared and dedicated versions. With such vast choices, every user will find what fits them. But can every proxy service deliver?
Proxy service
Proxy service is the whole infrastructure that can connect all the hardware of proxy servers and provide easy access to users. Proxy service shouldn’t be confused with a “service proxy” – a reverse proxy used in networks to balance loads.
In theory, you could create a proxy service yourself by setting up a server in a distant location and connecting through its IP address. However, in practice, it is an expensive task, requiring 24/7 maintenance. Even the biggest companies choose to outsource this and pay for a third-party proxy service instead.
Most proxy services are subscription-based, meaning you will have to pay for them monthly (see here to find more info on paid proxy services). It is a fair exchange as running proxies accumulates costs that need to be covered, from internet and electricity bills to equipment and staff.
There are some websites providing free proxy services, but let’s be honest; this is mostly a scam. They are painstakingly slow because they are often used to spread malware. More importantly, using a proxy service routes all your data through their servers, so your privacy can be at stake.
What makes a good proxy service?
Since it is better to pay for a proxy service, the next question is which ones are worth your money. Of course, the choice depends on your needs, and the price-quality ratio will shift accordingly. Still, some fairly universal criteria exist to know when a provider is worth your time.
Locations choice is an important factor if you want to target some specific areas. Most sites limit their content according to the IP addresses of visitors. The more variety of locations, the more possibilities a proxy service has.
Responsive customer support is more crucial than most think. Setting up a proxy service or dealing with technical issues might be impossible without timely assistance. Most of us don’t have time to wait long for a reply, so look for a provider that works 24/7 and has dedicated account managers.
Ethical sourcing of IP addresses is especially critical for residential proxies as providers often hide the true origin of their proxies. Look for a provider that is transparent in their dealings. You don’t want to use proxies sourced without consent or from hacked devices.
A convenient dashboard and supplementary software can make or break your projects. Spending hours to figure out the interface often leads to canceling proxy service subscriptions. Some other tasks require more specific functions, such as proxy rotation. Good providers invest heavily in developing software to help you maximize the efficiency of proxies.
Wrapping up
The one major difference is this – a proxy server is an intermediary between you and the internet, while a proxy service is a subscription to a provider offering access to such servers. These terms are quite close to each other, so whichever you look for, you will probably find both.
The major differences between a proxy service and a proxy server
Some confusion between terms is normal when shopping for advanced technical solutions. Proxies are no exception, but it shouldn’t stop you from making a good decision. We will discuss how a proxy service differs from proxy servers and which one you actually need (most probably, both).
What is a proxy?
When connecting to the internet directly, your device sends a request to the web server. A proxy changes this by acting as a middleman. If you use one, that request first goes to the proxy server and only then reaches the destination. After that, the data is forwarded to you, and the website is loaded.
Since a proxy acts as an intermediary, the web server doesn’t see the original IP address, only that of a proxy. By checking IP addresses, websites can know their visitors’ approximate location and the internet service provider (ISP), which allows them to trace their activity and restrict content.
In short, a proxy is a device (usually a server) that ensures privacy and increases security by allowing others to use its connection. But proxies can achieve this in different ways, depending on their setup. So to understand proxies, it is important to know how main types can be categorized.
Types of proxy servers
The first thing to note about types of proxy servers is how many users can access the IP addresses:
- If more than one user can access a proxy, it is shared.
- If access to the proxy is limited to one user, it is dedicated or private.
Shared proxies are significantly cheaper but can get slower if user count and traffic suddenly rise. That is why spending a bit more and purchasing dedicated proxies (at least for tasks you deem important) is recommended.
Proxies can be set up almost anywhere in the world with an internet connection. But the way proxies acquire access to the web can differ, resulting in variations in performance and legitimacy.
- Residential proxies acquire IP addresses from internet service providers (ISPs) and are connected through physical devices, just like you would in your home. They are best in cases where you need to avoid IP bans and have accurate location targeting.
- Datacenter proxies do not have their IP addresses verified by ISPs. These proxies are created in large numbers and run in specialized data centers. They are best when you need a lot of IPs and a fast connection.
There are some in-between options, such as ISP proxies and mobile proxies. The first is residential proxies located in a data center that aim to be both legitimate and fast. Mobile proxies originate from portable devices (tablets, smartphones, etc.) using mobile internet, so they are neither home connections nor based in data centers.
We can combine shared and dedicated access with other types and increase the variety even further. For example, datacenter proxies can have both shared and dedicated versions. With such vast choices, every user will find what fits them. But can every proxy service deliver?
Proxy service
Proxy service is the whole infrastructure that can connect all the hardware of proxy servers and provide easy access to users. Proxy service shouldn’t be confused with a “service proxy” – a reverse proxy used in networks to balance loads.
In theory, you could create a proxy service yourself by setting up a server in a distant location and connecting through its IP address. However, in practice, it is an expensive task, requiring 24/7 maintenance. Even the biggest companies choose to outsource this and pay for a third-party proxy service instead.
Most proxy services are subscription-based, meaning you will have to pay for them monthly (see here to find more info on paid proxy services). It is a fair exchange as running proxies accumulates costs that need to be covered, from internet and electricity bills to equipment and staff.
There are some websites providing free proxy services, but let’s be honest; this is mostly a scam. They are painstakingly slow because they are often used to spread malware. More importantly, using a proxy service routes all your data through their servers, so your privacy can be at stake.
What makes a good proxy service?
Since it is better to pay for a proxy service, the next question is which ones are worth your money. Of course, the choice depends on your needs, and the price-quality ratio will shift accordingly. Still, some fairly universal criteria exist to know when a provider is worth your time.
Locations choice is an important factor if you want to target some specific areas. Most sites limit their content according to the IP addresses of visitors. The more variety of locations, the more possibilities a proxy service has.
Responsive customer support is more crucial than most think. Setting up a proxy service or dealing with technical issues might be impossible without timely assistance. Most of us don’t have time to wait long for a reply, so look for a provider that works 24/7 and has dedicated account managers.
Ethical sourcing of IP addresses is especially critical for residential proxies as providers often hide the true origin of their proxies. Look for a provider that is transparent in their dealings. You don’t want to use proxies sourced without consent or from hacked devices.
A convenient dashboard and supplementary software can make or break your projects. Spending hours to figure out the interface often leads to canceling proxy service subscriptions. Some other tasks require more specific functions, such as proxy rotation. Good providers invest heavily in developing software to help you maximize the efficiency of proxies.
Wrapping up
The one major difference is this – a proxy server is an intermediary between you and the internet, while a proxy service is a subscription to a provider offering access to such servers. These terms are quite close to each other, so whichever you look for, you will probably find both.

























