You might have spent hundreds and thousands of dollars on your Graphic card and CPU, respectively, but there is one thing that we overlook most of the time,i.e, the Voltage Regulator Module, or VRM.
VRM or the Voltage Regulator Module is also known as the Processor Power Module, and as the name suggests VRM works to manage the voltage and ensure the safety of your most expensive components.
VRM is like a mini power supply that converts high to low voltage. An electronic circuit regulates and steps down the voltage from input to output.
It takes high voltage from the main power supply and converts it to a lower voltage like 1.2V which allows the CPU to “maintain its cool” literally!
VRM doesn’t allow your CPU to burn off because of that 12V mammoth power that a typical CPU’s main power will offer.
The importance of VRM
VRM is like a member of a family who always provides without getting much attention. When your computer starts crashing, and it’s the ugly blue screen that flashes up, screams that your VRM is in desperate need of your attention.
So, if you are looking for a new PC, try taking VRM’s quality in your mind as a good VRM will ensure that your PC will last longer and serve for years and years to come.
VRM is a very crucial component in a motherboard. It ensures your CPU does not overheat and protects your more delicate and expensive components, such as graphic card, RAM, etc.
VRM with a small size can lead to the malfunctioning of your Graphic Card.
Taking this into consideration many modern graphic cards comes with more modern OCP, which stands for Over-current protection.
The Graphic processor is strangled to reduce the amount of current VRM will deliver.
The components, such as RAM, Graphic Card, etc are very stubborn and are prone to overheating if the voltage exceeds the desired voltage.
VRM, on the other hand, does not let this thing happen. It changes the voltage from 12V to 1.2V as 1.2V is the desired voltage we discussed.
What is VRM cooling?
Most of the higher-end PCs are respected more because of their terrific performance. So, because of this heavy workload, your PC becomes vulnerable to heat.
To maintain the performance and the temperature of your PC, most of the higher-end motherboards have a heat sink.
This heat sink is an elongated extension located near the CPU socket, ensuring that the VRM and its MOSFET remain cool. The temperature usually is around 800C and 1000C, but in gaming PCs, it sometimes spikes up to 1200C.
You might be wondering, is the heat sink important, can’t I skip this? Well, there is no hard and fast rule. The use of a heat sink depends on your requirement.
If you are not going to play high graphic games like PlayerUnknown’s Battlegrounds or Grand Theft Auto V you don’t need a heat sink.
Or if you don’t want to run heavy graphic applications such as Adobe Illustrator, you don’t need this.
Working of VRM:-
You might be wondering how does the VRM work? The VRM comprises MOSFET, Choke, Capacitor, and PWM controller. All of the three-component play a major role in the working of VRM.
The choke is a coil that acts as a mini battery. Choke is an inductor, as we know that an inductor is an electronic component and is passive. It allows the user to store electrical energy in a magnetic form.
MOSFET or Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effective Transistor is as the name suggests a field effect transistor. A transistor is a device that controls the flow of current.
And in this case, MOSFET cuts the power of the choke after a certain required limit. MOSFET is well known for its efficiency, making it an ideal candidate for high power loads.
A Capacitor is a device that ensures that the resulting current is free of any spikes. To ensure the purest result possible.
A Pulse Width Modulation Controller or PWM Controller is a controller used to control the output voltage.
Every motherboard consists of a single PWM controller per the required voltage level of the CPU, chipset, etc. By running the controller at a higher frequency one can deliberately increase efficiency.
As mentioned earlier, the VRM converts 12V into 1.2V. But the question is, how does it do that? What’s the algorithm happening internally? Let’s find out!
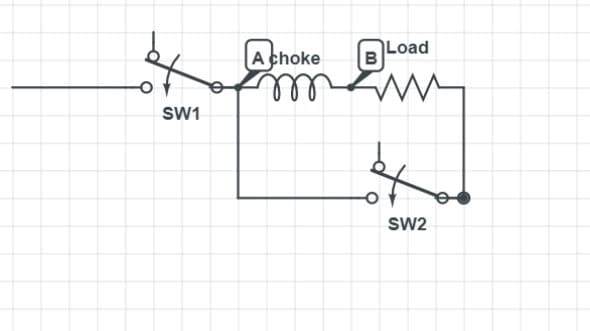
VRM does that with the help of Buck Converter. If we look at the basic circuit diagram of the Buck Converter, we will see that the switch is connected to the choke, which is an inductor(all chokes are inductors but not all inductors are chokes) used for filtering purposes. Which then is connected to a load(in this case the load is the CPU).
Inductors resist the current changes. They are called inductors because they induce magnetic fields. When the inductor is producing a magnetic field simultaneously, there will be a voltage drop across the inductor.
In normal circumstances that voltage drop is converted to heat because of the ‘law of energy conversation’ which states that energy can neither be created nor be destroyed, it only changes its form, but in the scenario, that voltage drop is converted to magnetic fields.
This saves the load from heat strokes and it will receive 1.2 units of Voltage which was the required amount.
But eventually, when the inductor is charged afterward, voltage will again spike and it will try to nullify the effect of the inductor.
The less the inductance the less time the inductor will take to charge and for a very small amount of time it will hold that voltage.
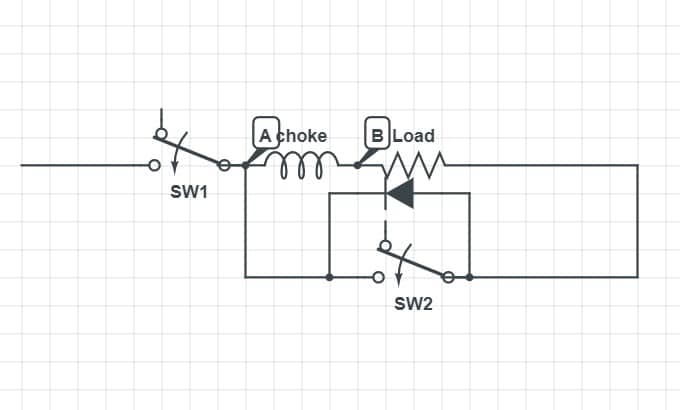
This means that the circuit is not yet complete. To complete the circuit, we will add a diode parallel to switch 2.
Now, our circuit is complete. But there is still some small issue. As of right now even after the addition of the diode, our current is still flowing through the switch, and you might be wondering why that is a problem. 🤔
It is a problem as after some time when the inductor starts discharging it will hit the ground and eventually your CPU will stop working. So, it will act as a fuse.
It will don’t let any harm happen to your CPU by switching it off. I don’t know about you guys, but it is my problem. So to fix that, we will make the current flow through the diode, not the switch.
What it will do is when the inductor starts discharging, and the voltage drops from 1.2V. It will spike it up to 1.2 before it hits the 0V margin.
This is how the Single Phase VRM works. If we add more phases, the efficiency will increase, and your system will perform better.
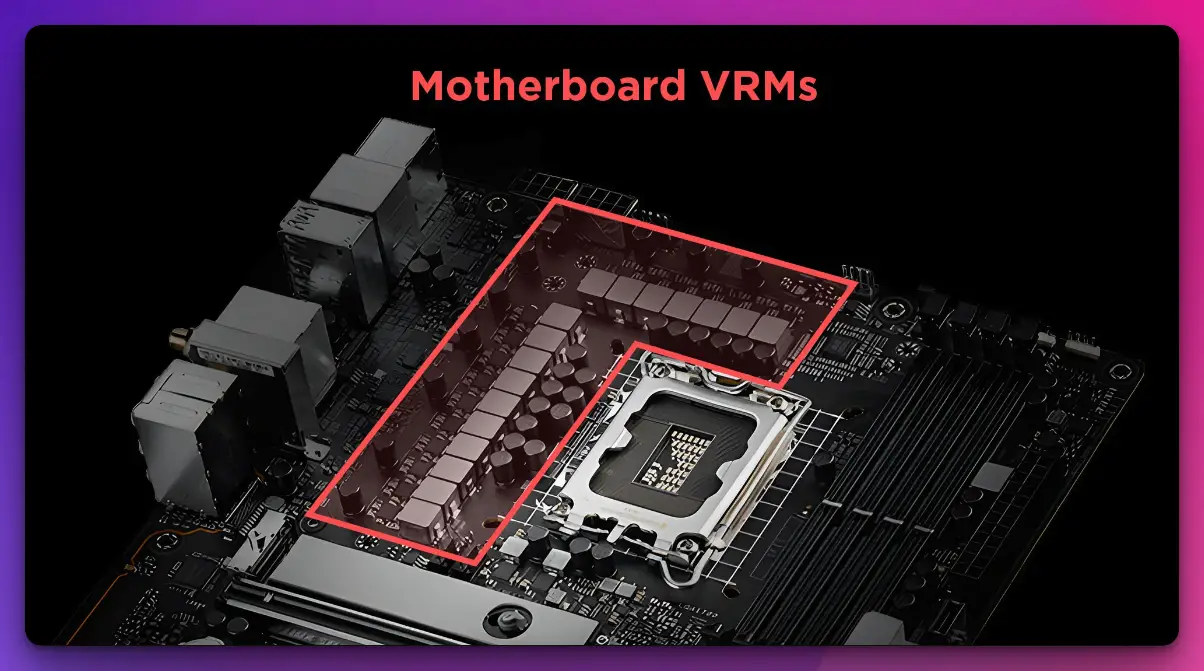
VRM is located near the CPU socket of your motherboard, as mentioned above in the article. VRM’s circuit is prominent and can easily be identified because it is the only circuit that uses the inductor(choke).
MULTE I-PHASVRM:-
Most computers nowadays use multiphase VRMs. Because as we increase the number of phases the efficiency of the VRM will increase. As the MOSFETs are connected parallel to each other the switching will not be instant.
Therefore, this time delay will equal the on-time of the PWM signal. And because they are cascaded the switching will happen in sequence. So, having multi-phase VRM will allow the heat to spread evenly, which will be more profitable in the long run. However, the initial cost will be more
Another benefit of using Multi-phase VRM is that since it allows multiple switching the output voltage which is a damped transient voltage will have less time to drop off
Using multi-phase VRM also allows the PWM frequency of the MOSFET to be lower as the output voltage will be covered because of multi-stage switching. So, the drop, in this case, will always be less than the drop in the case of Single-phase VRM.
One question that you might have is, Hey! Writer, “Does VRM matter if I am not overclocking?” This question does not have a very straightforward answer.
If you are not overclocking, you can run the PC without VRM, but the quality of your PC will determine whether you should use VRM.
Suppose you have a very high-end motherboard like Asus ROG Maximum XII Extreme, Gigabyte Z390 Auros Ultra, Asus Rog Maximum XI Hero, etc. In that case, you must consider adding a VRM your cart while checking out (Note: most of these motherboards come with in-built VRM).
If you plan to buy lower-end motherboards, you can go without VRM.
✅FAQ
What VRM means?
VRM stands for Voltage Regulator Module, an electronic component that regulates the voltage supplied to the processor or CPU of a computer.
It is responsible for converting the high voltage supplied by the power supply unit (PSU) into a lower voltage required by the CPU.
Is VRM important for gaming?
Yes, VRM is important for gaming because it determines the stability and reliability of the power supply to the CPU, which affects the performance of the system.
A good VRM design with efficient power delivery ensures stable and consistent performance, crucial for smooth and uninterrupted gaming.
What is the VRM on a motherboard?
The VRM on a motherboard is a set of electronic components that regulate and distribute the power supply to the CPU.
It is typically located near the CPU socket and consists of power phases, inductors, capacitors, and MOSFETs, which work together to convert and deliver the voltage required by the CPU.
How much VRM is good?
The amount of VRM required depends on the power requirements of the CPU. Generally, higher power phases and better quality components in the VRM design lead to better power delivery and stability, which is important for overclocking or running high-performance CPUs.
Is high VRM bad?
A high VRM is not inherently bad. However, many power phases in the VRM design may not necessarily result in better performance. The quality of the components and the VRM design itself plays a crucial role in determining the stability and reliability of the power supply to the CPU.
Where is the VRM?
The VRM is typically located near the CPU socket on the motherboard. It is identifiable by the arrangement of power phases, inductors, capacitors, and MOSFETs that make up the VRM circuit.
What motherboard has the best VRM?
The best motherboard for VRM depends on the specific needs and requirements of the system. Motherboards from ASUS, MSI, Gigabyte, and ASRock are known for their quality VRM designs and efficient power delivery.
How do I know if my VRM is bad?
A bad VRM can cause system instability, overheating, or even damage to the CPU. Symptoms of a bad VRM can include crashes, freezes, or system shutdowns, particularly under high loads. Monitoring the VRM temperature and voltage can help identify potential issues.
Does VRM affect GPU?
The VRM does not directly affect the GPU. However, a stable and efficient power supply to the CPU, which the VRM regulates, can indirectly affect the performance of the GPU by allowing the CPU to perform at its best.
Why do we need VRM?
We need VRM to regulate the voltage supplied to the CPU, which is crucial for stable and consistent performance. The VRM design ensures that the power supplied to the CPU is reliable, efficient, and within safe limits, which is necessary for the proper functioning of the computer.
Do I need VRM cooling?
VRM cooling can benefit high-performance systems, particularly during overclocking or using high-performance CPUs. Efficient VRM cooling ensures that the components are not overheated and can deliver stable and reliable power to the CPU.
What is the max VRM voltage?
The maximum VRM voltage depends on the specific components used in the VRM circuit, as well as the power requirements of the CPU. Generally, VRM voltages in the range of 1.3-1.4V are considered safe for most CPUs.
What happens if VRM gets too hot?
If the VRM gets too hot, it can cause instability or damage the CPU. The VRM components may also throttle down the power supply to the CPU to avoid overheating, which can result in reduced performance or system shutdown.
What are the different types of VRM?
There are several types of VRM, including analog VRM, digital VRM, multiphase VRM, and hybrid VRM. Analog VRM is an older technology that uses analog circuitry, while digital VRM uses digital circuitry for more precise control.
Multiphase VRM uses multiple power phases to distribute power more evenly, while hybrid VRM combines analog and digital technologies to balance performance and efficiency.
What is VRM frequency?
VRM frequency refers to the speed at which the VRM circuitry switches the voltage to the CPU. Higher VRM frequency can lead to more precise control over the voltage supply, but can also generate more heat and noise.
Does VRM matter if not overclocking?
VRM still matters even if not overclocking, as it regulates the voltage supplied to the CPU for stable and consistent performance. A high-quality VRM design can also help prolong the CPU’s lifespan and other system components.
Can I use thermal paste on GPU VRM?
Using thermal paste on GPU VRM components is generally not recommended, as it can cause shorts and damage to the components. Instead, it is better to use thermal pads or specialized VRM heatsinks.
Is VRM heatsink important?
VRM heatsink is important for efficient cooling and heat dissipation of the VRM components. Efficient VRM cooling ensures stable and reliable power delivery to the CPU, which is important for optimal performance and longevity of the system.
Can you add heatsink to VRM?
Yes, adding heatsinks to VRM components is possible, which can help improve heat dissipation and cooling efficiency. However, care should be taken to ensure that the heatsinks are compatible with the specific VRM components and do not interfere with other components on the motherboard.
Is VRM input or output?
The VRM is both an input and output component, as it receives input voltage from the power supply unit and outputs regulated voltage to the CPU.
How do I check my motherboard VRM temperature?
Using specialized software or hardware monitoring tools, you can check your motherboard VRM temperature. Some motherboards also have built-in temperature sensors for the VRM that can be accessed through the BIOS or other system utilities.
What is the maximum safe voltage for GPU?
The maximum safe voltage for GPU depends on the specific GPU model and the cooling solution used. Generally, GPU voltages in the range of 1.2-1.3V are considered safe for most GPUs.
What can I do with a VRM?
The VRM is vital in regulating and delivering power to the CPU, which is important for optimal system performance. Efficient VRM design and cooling can also help prolong the CPU’s lifespan and other system components.
How do I change my VRM?
Changing the VRM requires advanced technical knowledge and should only be done by experienced professionals. It involves replacing the VRM components on the motherboard, which can be difficult and risky.
What is the power phase of VRM?
The power phase of VRM refers to the number of power stages or components that make up the VRM circuit. A higher number of power phases can provide more efficient and stable power delivery to the CPU, which is important for optimal system performance.
How to check motherboard VRM?
Several monitoring software programs can provide information about your motherboard’s VRM. Some popular options include HWMonitor, CPU-Z, and AIDA64.
Is VRM important in the motherboard?
Yes, VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) is an important motherboard component. It is responsible for regulating and stabilizing the voltage supplied to the CPU.
How much VRM is good?
The VRM required depends on the CPU’s specific requirements and the motherboard’s intended use.
A motherboard with a simpler VRM configuration may suffice for basic computing tasks, while a more robust VRM setup may be necessary for more demanding applications or overclocking.
What is the function of VRM in the motherboard?
The VRM in a motherboard converts the incoming power from the PSU into a form the CPU can use. It regulates and stabilizes the voltage to ensure the CPU receives a consistent and safe power level.
Does VRM matter if not overclocking?
While VRM is primarily associated with overclocking, it is still an important component, even when not overclocking. It helps to ensure stable and consistent power delivery to the CPU, which is important for overall system stability and performance.
Is higher VRM better?
A higher VRM configuration is generally better for more demanding applications and overclocking. However, a simpler VRM setup may be sufficient for basic computing tasks.
What are the symptoms of VRM failure?
Symptoms of VRM failure can include instability, crashes, and even damage to the CPU. In extreme cases, it can also lead to the motherboard failing to boot or even becoming permanently damaged.
Does VRM affect CPU temp?
The VRM can indirectly affect CPU temperature, as a poorly functioning VRM can result in unstable power delivery, which can cause the CPU to heat up more than normal. A well-functioning VRM can help to stabilize power delivery and maintain consistent temperatures.
What is the benefit of VRM?
The primary benefit of VRM is that it helps to regulate and stabilize the power supply to the CPU. This ensures that the CPU receives a consistent and safe power level, which helps improve overall system stability and performance.
Does VRM affect GPU?
The VRM in a motherboard is primarily responsible for regulating and stabilizing the voltage supply to the CPU, not the GPU. However, a poorly functioning VRM can result in instability and crashes in the system, impacting GPU performance.
Does VRM need cooling?
The VRM can generate significant heat, especially under heavy loads or when overclocking. As such, it is generally a good idea to have some form of cooling, such as a heatsink or fan, to help dissipate the heat and maintain stable performance.
Do you need a VRM heatsink?
A VRM heatsink can help dissipate the heat generated by the VRM, which can help maintain stable performance and extend the motherboard’s lifespan.
While it may not be strictly necessary in all cases, having one installed is generally a good idea, especially when overclocking or using a higher-end CPU.
What happens if VRM overheats?
If the VRM overheats, it can result in instability, crashes, and even damage to the CPU or other components.
In extreme cases, it can also lead to the motherboard failing to boot or becoming permanently damaged. It is important to keep the VRM cool to ensure stable and consistent performance.
Does VRM need cooling?
VRM works as a voltage regulator for your processor. This keeps everything under check and ensures your system works smoothly, even during heavy tasks.
In this case, VRM often heats up to 120°C, which might cause it to malfunction. Therefore, VRM also needs a cooling mechanism to keep everything under control.
What are the VRM power phases?
VRM Power phase consists of a choke, capacitor, and MOSFETS. Modern systems now need multiple such phases to enable better voltage distribution.
This, in turn, reduces the components’ load and spreads the power. Hence, it is believed that the more phases your motherboard has, the better performance you will get.
Is more power phase better?
Not always. However, it is the most common notion that more power phases only keep the system stable by reducing the power of each phase. But that should not be the only factor in determining the outcome. It is sometimes better to have four phases than right, considering your system’s condition.
Do VRMs matter if not overclocking?
VRMs matter in every situation, whether you are overclocking or not. The ultimate goal is to keep the voltage regulated, keeping the system cooler and smoother.
VRMs take part in the normal functioning of the system as well so that the processor can work smoothly even in lesser load situations.
Where is the VRM on a motherboard?
You will generally find VRM on the processor socket. It has three main components known as the power phase. This power phase has MOSFETs, chokes, and Capacitors that keep the voltage in check together.
Final Note:-
VRM is very vital for your high-end computers. As without VRM, your computer’s delicate components such as Graphic cad, processor will be damaged due to overclocking.
While going for VRM try opting for a Multi-phase VRM system as because of it being parallelly cascaded the switching will happen more often and hence, the transient voltage drop-off time will be less.