You’re feeling overwhelmed. Your digital workspace is cluttered with dozens of tasks, notes, and deadlines, and the tool you’re currently using – a traditional task manager – seems to be adding to the chaos instead of solving it.
You spend more time managing your tasks than actually accomplishing them, and despite your best efforts, things continue to slip through the cracks.
You’re stuck in a cycle of underproductivity, and it’s starting to take a toll on your work-life balance.
That’s where many of us find ourselves in this digital era, tangled in a web of tasks and to-do lists, hoping to discover an organizing principle that works.
The impact of this disarray is not just limited to your professional life. The stress seeps into your time, affecting your peace of mind and overall well-being.
You know something needs to change, but what? Is there an alternative to these conventional task managers that only seem to add to the confusion?
This article explores the power of task manager alternatives, uncovering more intuitive and efficient ways to organize your work and personal life.
With the right tools and strategies, you can break free from the cycle of underproductivity, reclaim your time, and achieve the work-life balance you’ve always wanted.
So, let’s delve into the world of task manager alternatives and discover how you can streamline your workload, increase your productivity, and regain control over your day-to-day life.
Key Features to Look for in a Task Manager Alternative
When searching for a Task Manager alternative, it’s essential to consider the key features that can elevate your system management experience.
These features go beyond the basic functionalities offered by traditional Task Managers and provide advanced capabilities for enhanced control and efficiency.
Customization options are a crucial aspect to look for in a Task Manager alternative. The ability to tailor the software to your needs ensures a personalized experience and allows you to focus on the information that matters most.
An alternative with advanced process monitoring and management capabilities is invaluable. Look for real-time insights into resource usage, CPU performance, memory allocation, and network activity.
This level of visibility empowers you to identify resource-intensive tasks and optimize system responsiveness.
Another important feature is resource usage visualization. Clear and intuitive graphical representations of CPU, memory, and disk usage enable you to quickly grasp the system’s performance at a glance, making it easier to identify bottlenecks and allocate resources efficiently.
Efficient task organization and grouping capabilities streamline your workflow. Look for alternatives that allow you to easily categorize tasks, create task hierarchies, and manage complex processes.
Lastly, consider the accessibility and ease of use of the alternative. A user-friendly interface, intuitive navigation, and straightforward controls ensure a seamless experience.
In conclusion, when evaluating a Task Manager alternative, prioritize customization options, advanced process monitoring, resource usage visualization, task organization features, and overall accessibility.
These key features will empower you to manage your system and optimize its performance efficiently.
Here, we have prepared a list of some of the best ones for you –
Task Manager Alternatives To Take Charge of Your System👌
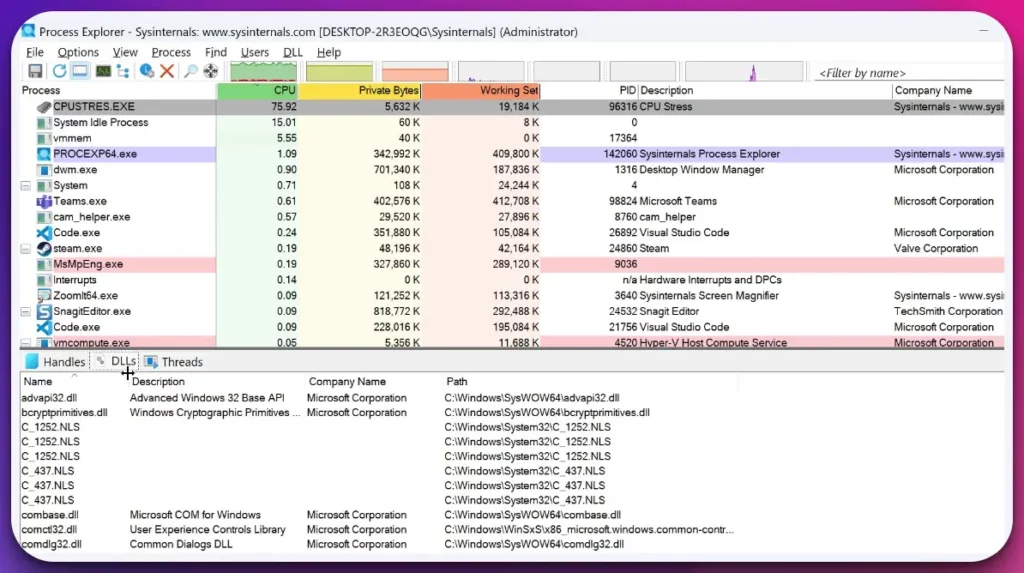
1. Process Explorer
Process Explorer is a compelling alternative to Windows Task Manager, providing users with advanced functionalities and in-depth insights into system processes and resource utilization.
With its comprehensive process monitoring capabilities, Process Explorer allows users to delve deep into the inner workings of their system.
Users can analyze individual processes, view their dependencies, and identify resource-intensive tasks that may impact system performance.
One key advantage of Process Explorer as an alternative to Windows Task Manager is its customizability. Users can configure the display to show the desired information, customize columns, and adjust settings to suit their needs and preferences.
Process Explorer’s user-friendly interface and intuitive navigation make it accessible to users of varying technical expertise.
It provides a more granular and detailed view of system processes, making it a valuable tool for system administrators and advanced users seeking a higher level of control.
In conclusion, Process Explorer is a robust alternative to Windows Task Manager, offering advanced process monitoring, customization options, and a user-friendly interface.
Its comprehensive insights and enhanced control over system processes make it a powerful tool for efficient system management.
Pros:-
Comprehensive process monitoring: Process Explorer provides in-depth insights into system processes, resource utilization, and dependencies, allowing users to troubleshoot performance issues effectively.
Advanced features: With detailed information about DLLs, handles, and network connections, Process Explorer offers advanced functionalities for thorough system analysis.
Customization options: Users can personalize the display and data presented in Process Explorer, tailoring it to their specific needs and optimizing workflow efficiency.
User-friendly interface: Process Explorer’s intuitive interface and seamless integration with the Windows operating system make it accessible to users of all levels of expertise.
Cons:-
Learning curve: Due to its advanced features and functionalities, Process Explorer may have a steeper learning curve for users unfamiliar with system management tools.
Windows compatibility: Process Explorer is specifically designed for Windows systems, limiting its usability for users on other operating systems.
Overwhelming for casual users: The wealth of information provided by Process Explorer may be overwhelming for casual users who only require basic process management and monitoring.
Limited support: Process Explorer is a free tool provided by Microsoft, and while it offers extensive features, the support, and updates may not be as frequent or robust as with commercial alternatives.
Overall, Process Explorer remains a powerful Task Manager alternative for Windows, offering comprehensive insights and advanced features, albeit with a learning curve and limited support.
It is best suited for users who require in-depth system analysis and are comfortable navigating through detailed information about processes and resources.
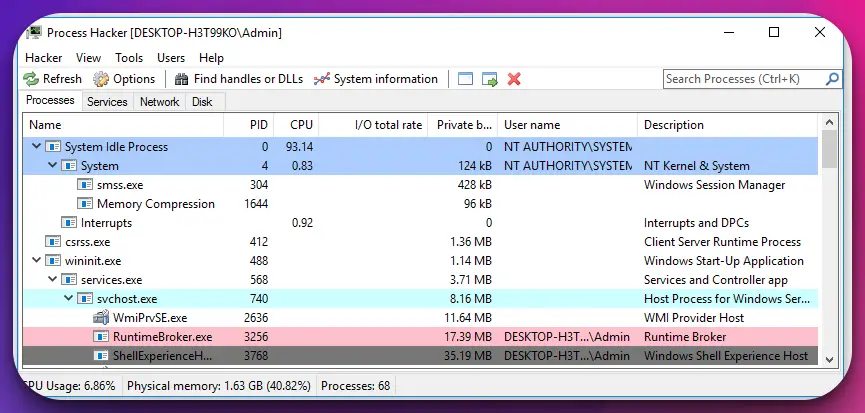
2. Process Hacker
Process Hacker is the epitome of a robust and feature-rich Windows task manager alternative.
With its comprehensive suite of advanced functionalities, Process Hacker empowers users to delve deep into the inner workings of their system, facilitating efficient management and troubleshooting.
Process Hacker offers a wealth of valuable insights and controls as a task manager alternative. Its real-time process monitoring capabilities provide users with a detailed overview of running processes, complete with resource utilization metrics.
Process Hacker equips users with a wealth of information to identify and address performance bottlenecks from CPU and memory usage to network activity.
One of the standout features of Process Hacker is its advanced process exploration functionality. Users can delve into the intricate details of process threads, modules, and memory regions, enabling in-depth analysis and troubleshooting.
With its meticulous attention to detail, Process Hacker allows for granular control over system operations, enhancing the overall management experience.
Furthermore, Process Hacker boasts a powerful process termination feature, enabling users to swiftly halt stubborn or malicious processes that may jeopardize system stability.
This capability grants users unparalleled control and the ability to mitigate potential security risks effectively.
In conclusion, for Windows users searching for a comprehensive and powerful task manager alternative, Process Hacker emerges as the prime choice.
Its robust feature set, real-time monitoring, advanced process exploration, and process termination capabilities make it an invaluable system management and optimization tool. Embrace Process Hacker and unlock the true potential of your Windows system.
Pros:-
Advanced Process Exploration: Process Hacker allows users to delve deep into process details, including threads, modules, and memory regions, providing extensive insights for troubleshooting and analysis.
Real-Time Monitoring: With real-time performance graphs, Process Hacker offers comprehensive monitoring of CPU, memory, and network usage, enabling users to identify performance bottlenecks and optimize system resources.
Powerful Process Termination: Process Hacker empowers users to terminate stubborn or malicious processes, enhancing system stability and security.
Resource Utilization Metrics: Process Hacker provides detailed information on resource utilization, allowing users to identify processes consuming excessive CPU, memory, or network resources.
Customizable Interface: Process Hacker offers a customizable interface with various viewing options and configurable columns, enabling users to tailor the display to their needs.
Cons:-
Steep Learning Curve: Process Hacker’s the extensive feature set and advanced functionalities may require a learning curve for users unfamiliar with task managers, making it less accessible for casual users.
Potentially Overwhelming: The abundance of information and advanced controls in Process Hacker may overwhelm users who only require basic process management, leading to unnecessary complexity.
Limited Official Support: Process Hacker is an open-source project, which means it may have limited official support compared to commercial alternatives.
Windows Compatibility: While Process Hacker is primarily designed for Windows, it may not be compatible with all operating system versions, potentially limiting its usability for some users.
Lack of User-Friendly Interface: The user interface of Process Hacker may appear less intuitive and visually appealing compared to some commercial alternatives, which may deter users from seeking a more user-friendly experience.
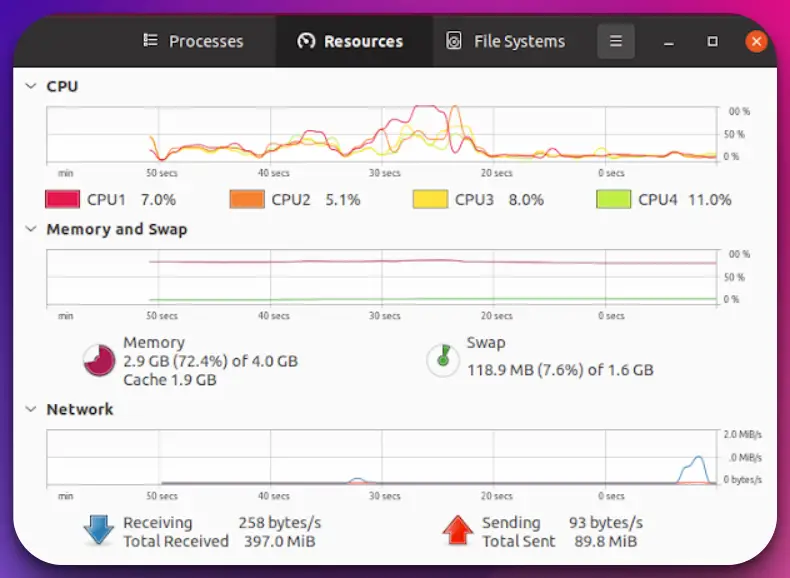
3. System Monitor
System Monitor is an exceptional task manager alternative for Ubuntu, offering a comprehensive suite of features that empower users to monitor and optimize their system performance.
With its versatility and robust functionality, System Monitor is the go-to tool for Ubuntu enthusiasts and administrators.
System Monitor provides valuable insights into system resource utilization and process management.
Its intuitive interface allows users to monitor CPU usage, memory consumption, disk activity, and network traffic effortlessly.
With real-time data and customizable views, System Monitor ensures users have a clear understanding of their system’s performance at all times.
One of the standout features of System Monitor is its ability to display detailed process information, enabling users to identify resource-intensive processes and address performance bottlenecks effectively.
The process prioritization feature allows users to allocate system resources optimally, ensuring critical processes receive the necessary attention.
Furthermore, System Monitor offers extensive historical data and reporting capabilities, allowing users to analyze system performance trends over time.
Users can make informed decisions for system optimization and resource allocation by identifying patterns and irregularities.
However, it’s important to note that System Monitor may have a steeper learning curve for novice Linux users due to its advanced features and terminology.
Additionally, while System Monitor provides comprehensive system monitoring capabilities, it may not offer the same level of process control as other alternatives on ubuntu.
In conclusion, System Monitor is a top-tier task manager alternative for ubuntu, offering features that empower users to monitor, analyze, and optimize their system performance.
With its user-friendly interface and comprehensive insights, System Monitor proves to be an invaluable tool for Ubuntu administrators and enthusiasts seeking to maximize their system’s potential.
Pros:-
Comprehensive System Monitoring: System Monitor provides a wide range of system monitoring features, including CPU usage, memory consumption, disk activity, and network traffic, offering users a holistic view of their system’s performance.
Detailed Process Information: System Monitor displays detailed process information, allowing users to identify resource-intensive processes and make informed decisions to optimize system performance.
Historical Data and Reporting: System Monitor offers the ability to track and analyze historical data, enabling users to identify performance trends, troubleshoot issues, and make data-driven optimizations.
Customizable Views: With customizable views and layouts, System Monitor allows users to personalize their monitoring experience, tailoring it to their needs and preferences.
Open Source: Being open source, System Monitor benefits from a community-driven development process, ensuring frequent updates, bug fixes, and improvements.
Cons:-
Steep Learning Curve: System Monitor’s extensive features and technical terminology may pose a learning curve for novice Linux users, requiring time and effort to grasp its functionalities fully.
Limited Process Control: While System Monitor provides comprehensive monitoring, it may lack advanced process control capabilities compared to other alternatives, limiting certain administrative actions.
Interface Complexity: The interface of System Monitor may appear overwhelming for users who prefer a simpler and more streamlined monitoring experience, potentially discouraging casual or non-technical users.
Compatibility: System Monitor is primarily designed for Linux, which means it may not be readily available or fully compatible with all Linux distributions, limiting its accessibility for some users.
Reliance on Desktop Environment: System Monitor’s functionality and availability may depend on the specific desktop environment used, potentially restricting its usage for users who prefer alternative desktop environments.
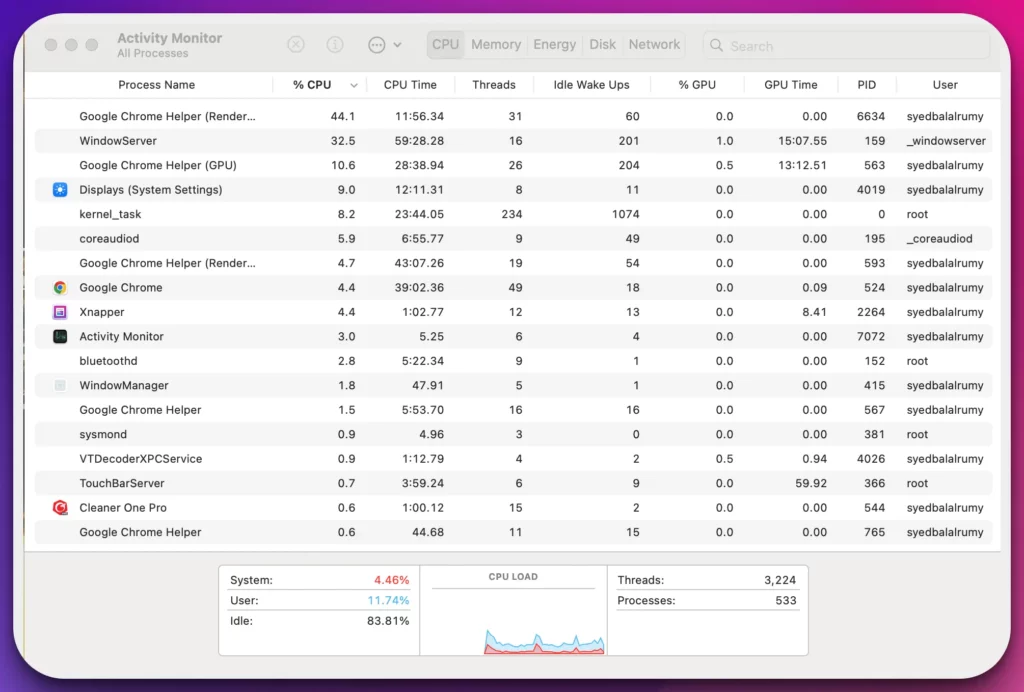
4. Activity Monitor
Activity Monitor shines as Mac’s ultimate task manager alternative, providing users with a comprehensive set of tools to monitor and manage system processes efficiently.
With its rich feature set and user-friendly interface, Activity Monitor is an invaluable asset for Mac users seeking detailed insights into their system performance.
Activity Monitor offers valuable information, allowing users to monitor CPU usage, memory utilization, disk activity, and network performance.
Its real-time monitoring capabilities provide users with up-to-date data, enabling them to promptly identify resource-intensive processes and address performance issues.
One of the standout features of Activity Monitor is its detailed process analysis, empowering users to delve deep into process information, including CPU usage, energy impact, and memory footprint. This level of granularity allows for effective troubleshooting and optimization of system resources.
Moreover, Activity Monitor offers process management functionalities such as force quitting applications and monitoring energy consumption, enabling users to maximize efficiency and prioritize critical tasks.
However, it’s worth noting that while Activity Monitor excels at system monitoring and process analysis, it may lack advanced features for in-depth system optimization and customization.
Users seeking more advanced controls and customization options may need to explore additional tools or utilities.
In conclusion, Activity Monitor emerges as Mac’s best task manager alternative, providing users with a comprehensive range of monitoring and process management capabilities.
Its intuitive interface and detailed insights empower users to make informed decisions, optimize system performance, and ensure a smooth computing experience on their Mac systems.
Pros:-
Comprehensive System Monitoring: Activity Monitor offers a wide range of monitoring capabilities, including CPU usage, memory utilization, disk activity, and network performance, providing users with a holistic view of their system’s health and performance.
Detailed Process Analysis: Activity Monitor provides detailed information about running processes, such as CPU usage, energy impact, and memory footprint, enabling users to identify resource-intensive applications and troubleshoot performance issues effectively.
User-Friendly Interface: With its intuitive and visually appealing interface, Activity Monitor allows users to navigate and understand system metrics easily, making it accessible even to non-technical users.
Process Management Functions: Activity Monitor allows users to manage processes by force quitting applications, tracking energy consumption, and monitoring system responsiveness, giving users control over system resources.
Native Integration: As a built-in utility in macOS, Activity Monitor seamlessly integrates with the operating system, ensuring reliability, stability, and compatibility with other macOS features.
Cons:-
Limited Advanced Features: Activity Monitor primarily focuses on monitoring and basic process management, lacking some advanced features in third-party alternatives.
Lack of Customization: While Activity Monitor provides essential monitoring tools, it may have limited customization options compared to more specialized third-party tools, which can be a drawback for advanced users seeking extensive control and customization.
Limited Historical Data: Activity Monitor doesn’t offer extensive historical data or advanced reporting features, limiting the ability to analyze long-term system performance trends.
Dependency on macOS: Since Activity Monitor is specific to macOS, it may not be accessible to users on other operating systems, restricting its usability for multi-platform environments.
Learning Curve for Novice Users: Despite its user-friendly interface, Activity Monitor can still present a learning curve for novice users unfamiliar with system monitoring and performance metrics.
Consider these pros and cons based on your specific needs and requirements when considering Activity Monitor as a task manager alternative for your Mac.
5. Htop
htop emerges as an exceptional task manager alternative for Linux, offering a wealth of advanced features and a user-friendly interface that sets it apart from traditional task managers.
It’s powerful functionalities and intuitive design, htop provides users unparalleled control and insight into their system processes.
htop surpasses the standard features found in traditional task managers, providing a dynamic real-time view of system resource utilization, including CPU usage, memory consumption, and network activity.
Its color-coded display enables users to quickly identify resource-intensive processes and monitor system performance.
One of the standout features of htop is its ability to display processes in a hierarchical tree structure, allowing users to visualize process dependencies and resource allocation.
This feature enhances the understanding of system behavior and aids in identifying troublesome processes.
Moreover, htop offers interactive process management, enabling users to terminate processes selectively, change process priorities, and monitor threads. This level of control empowers users to optimize system resources and troubleshoot performance issues efficiently.
However, it’s important to note that htop may have a steeper learning curve for novice users, as it presents a more advanced and technical interface than traditional task managers.
Additionally, while htop excels in process management, it may lack extended features such as historical data analysis and reporting.
In conclusion, htop is a top-tier task manager alternative for Linux, combining powerful functionalities with an intuitive interface.
Its real-time monitoring, hierarchical process display, and interactive process management make it invaluable for system administrators, power users, and those seeking in-depth insights and control over their Linux systems.
To use htop in Linux, follow these steps:-
Open a terminal: Launch a terminal window by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T or searching for “Terminal” in your Linux desktop environment.
Install htop (if not already installed): Type the following command in the terminal and press Enter to install htop:
Sudo apt-get install htop
Note: The installation command may vary depending on your Linux distribution. You can use package managers like apt, yum, or dnf to install htop.
Launch htop: Once htop is installed, simply type htop in the terminal and press Enter. The htop interface will appear, displaying real-time system information.
Navigate the htop interface: htop provides a dynamic and interactive display. Here are some key controls:
- Use the arrow keys to navigate through processes.
- Press Enter to expand/collapse the process tree.
- Press F1 or h to access the htop help menu, which lists available commands and their functions.
Monitor system resources: htop displays system metrics, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and network activity, in real-time. Processes are color-coded, making it easier to identify resource-intensive ones.
Interact with processes: To manage processes, you can use htop’s built-in functions. For example:
- Press F9 or k to send a signal to a selected process (e.g., to terminate or kill a process).
- Press F7 or n to change the nice value of a process and adjust its priority.
Exit htop: To exit htop, press the q key.
Remember that htop provides a wealth of features and customization options, which you can explore further by referring to the htop documentation or using the help menu within the application.
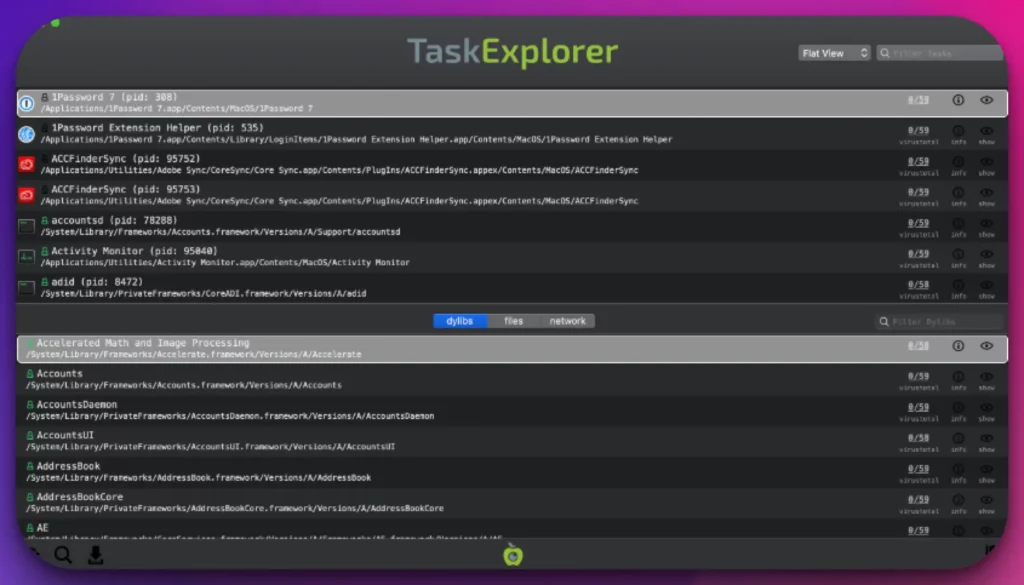
6. TaskExplorer
TaskExplorer is a cutting-edge and feature-rich task manager alternative on your Mac, offering a wealth of functionalities and a sleek interface for efficient system management.
With its comprehensive tools and intuitive design, TaskExplorer is an indispensable asset for users seeking enhanced control over their processes.
TaskExplorer provides a real-time view of running processes, allowing users to monitor CPU usage, memory consumption, and other critical system metrics.
Its advanced filtering and sorting options enable users to identify resource-intensive processes and prioritize tasks effectively and quickly.
One of the standout features of TaskExplorer is its process tree visualization, which provides a hierarchical view of process dependencies and relationships.
This feature enhances the understanding of system behavior and aids in troubleshooting complex process interactions.
Moreover, TaskExplorer offers process termination, process suspension, and priority adjustment capabilities, empowering users to take control of system resources and optimize performance.
Furthermore, TaskExplorer boasts a user-friendly interface with customizable layouts and a sleek design. Its modern and intuitive visuals make navigating and comprehending process information easy.
In conclusion, TaskExplorer sets itself apart from other alternatives with its comprehensive features, process visualization, and user-friendly interface.
Whether you’re a power user, system administrator, or simply seeking more control over your processes, TaskExplorer provides the tools and insights necessary to manage and optimize your system’s performance effectively.
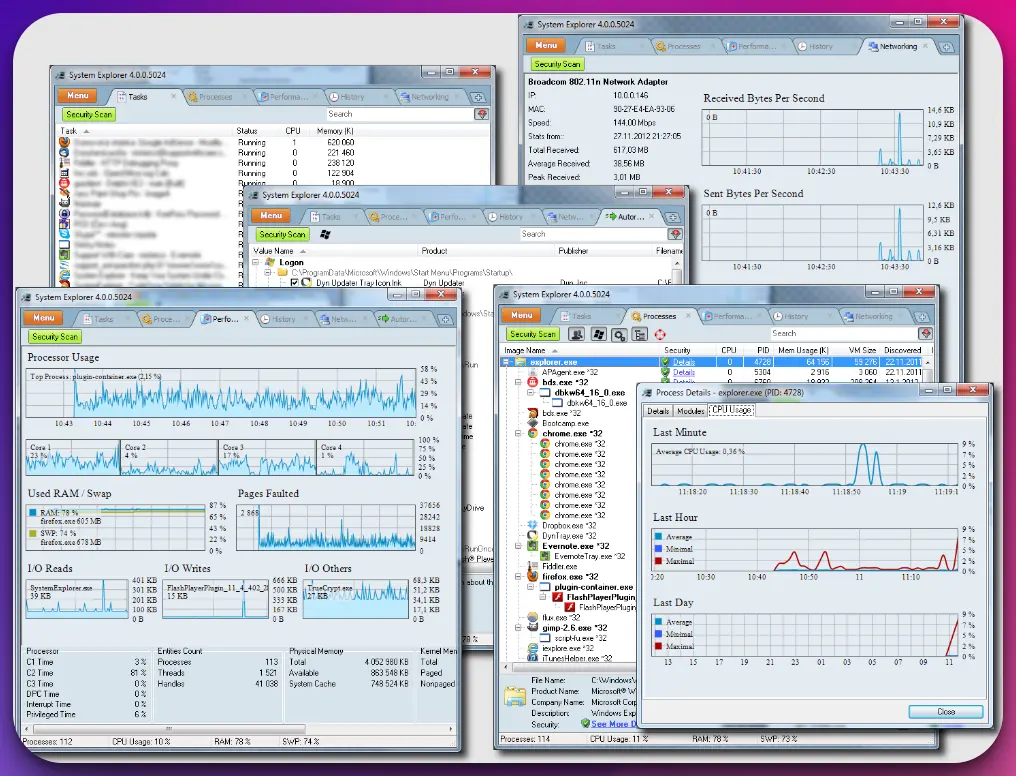
7. System Explorer
System Explorer is an exceptional system management tool, offering many advanced features and a user-friendly interface for comprehensive system analysis.
Its extensive functionality and intuitive design make System Explorer invaluable for users seeking deep insights and control over their systems.
As a robust system management tool, System Explorer provides a multifaceted approach to system analysis, allowing users to monitor processes, services, startup programs, and system performance metrics.
Its real-time monitoring capabilities offer a dynamic view of CPU usage, memory consumption, network activity, and more, ensuring users stay informed about their system’s health.
One of the standout features of System Explorer is its detailed process exploration, providing users with in-depth information about running processes, including file associations, network connections, and loaded modules. This level of detail enables users to identify and address potential issues efficiently.
Moreover, System Explorer offers advanced tools such as a registry editor and a file analyzer, allowing users to delve into the intricacies of their system’s configuration and file structure.
Furthermore, System Explorer facilitates process management, enabling users to terminate or suspend processes, adjust process priorities, and manage startup programs, empowering them to optimize system resources effectively.
In conclusion, System Explorer is a powerful system management tool combining advanced features, real-time monitoring, and process exploration.
Its user-friendly interface and comprehensive insights make it an indispensable tool for users seeking to easily analyze, optimize, and maintain their systems.
Pros of System Explorer:-
Comprehensive System Analysis: System Explorer offers a wide range of system analysis features, including process monitoring, service management, startup program control, and performance metrics, providing users with a holistic view of their system’s health and performance.
Real-Time Monitoring: System Explorer monitors critical system metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and network activity, allowing users to stay updated on their system’s performance in real-time.
Detailed Process Exploration: System Explorer allows users to dive deep into process details, including file associations, network connections, and loaded modules, enabling thorough analysis and troubleshooting of running processes.
Advanced Tools: With features like a registry editor and file analyzer, System Explorer provides advanced tools for system configuration, file management, and analysis, empowering users to delve into the intricacies of their system.
User-Friendly Interface: System Explorer offers a user-friendly interface with intuitive navigation and well-organized information, making it accessible and easy for users of all technical levels.
Cons of System Explorer:-
Platform Limitation: System Explorer is primarily designed for Windows systems, limiting its usability for users on other operating systems.
Limited Compatibility: System Explorer may not be compatible with all versions of Windows or specialized system configurations, potentially restricting its usage for some users.
Learning Curve for Novice Users: System Explorer’s advanced features and terminology may present a learning curve for novice users unfamiliar with system analysis tools.
Dependency on Third-Party Software: System Explorer may rely on additional software or libraries to provide certain functionalities, which could sometimes introduce compatibility or dependency issues.
Lack of Additional Features: While System Explorer offers comprehensive system analysis capabilities, it may lack some additional features in similar tools, such as detailed historical data analysis or performance benchmarking.
Consider these pros and cons based on your specific needs and requirements when considering System Explorer as a system management tool for your Windows system.
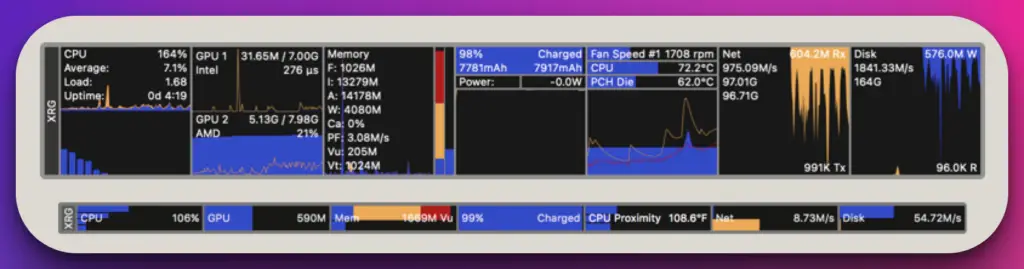
8. XRG
XRG is an innovative and feature-rich system monitoring tool that provides Mac users with an insightful and visually appealing interface to monitor and analyze their system performance.
With its advanced functionalities and intuitive design, XRG proves to be an indispensable tool for those seeking detailed insights into their Mac systems.
As a powerful system monitoring tool, XRG offers a comprehensive view of crucial system metrics, including CPU usage, memory consumption, network activity, and disk utilization.
Its real-time monitoring capabilities provide users with accurate and up-to-date information, allowing them to track system performance precisely.
One of the standout features of XRG is its customizable dashboard, which allows users to configure and arrange the display of system metrics according to their preferences. This flexibility empowers users to focus on the metrics most matter to them.
Moreover, XRG provides graphical representations of system metrics, enabling users to visualize trends and patterns in their system performance over time. This feature aids in identifying anomalies and making informed decisions for system optimization.
Furthermore, XRG offers customizable notifications and alerts based on user-defined thresholds, ensuring users stay informed about critical system conditions and potential issues.
In conclusion, XRG stands out as a top-tier system monitoring tool for Mac users, providing rich features, real-time monitoring, customizable dashboards, and graphical representations of system metrics.
With its user-friendly interface and insightful visualizations, XRG empowers users to effectively monitor, analyze, and optimize the performance of their Mac systems.
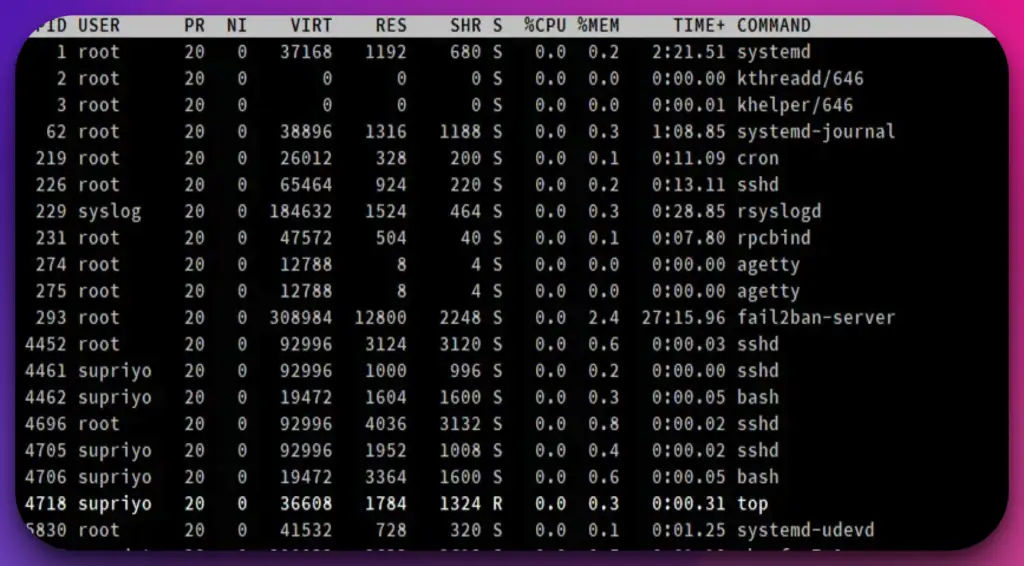
9. top
The top command is a powerful and versatile utility in Linux, offering users real-time insights into system processes and resource utilization.
As a command-line tool, the top provides a comprehensive overview of system performance, allowing users to monitor running processes, CPU usage, memory consumption, and more.
When executed, the top command displays a dynamic and interactive interface that updates in real time.
It presents a sortable list of processes, sorted by default based on CPU usage. Users can easily navigate through the process list, obtaining vital information such as process ID, user, CPU utilization, memory usage, and running time.
One of the standout features of the top command is its ability to highlight resource-intensive processes. Users can promptly identify processes consuming excessive CPU or memory resources, enabling them to prioritize troubleshooting efforts or terminate problematic processes.
Moreover, top provides interactive controls, allowing users to dynamically adjust the displayed information. They can customize the update frequency, sort processes based on various criteria, and filter processes by user or process name.
While the top command excels in real-time process monitoring, it may have a steep learning curve for novice users due to its extensive features and specialized terminology.
However, once users become familiar with its capabilities, they can leverage top to effectively monitor and manage system performance in Linux, ensuring optimal resource utilization and troubleshooting efficiency.
To use the top command in Linux, follow these steps:-
Open a terminal: Launch a terminal window by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T or searching for “Terminal” in your Linux desktop environment.
Execute the top command: In the terminal, type top and press Enter. The top interface will display real-time information about system processes and resource utilization.
Understand the top interface: The top command presents a dynamic and interactive interface with multiple sections. The most significant sections include the summary information at the top and the process list below.
Navigate the process list: Use the arrow keys to scroll through the process list. The highlighted line represents the currently selected process.
Sort processes: By default, the processes are sorted by CPU usage. You can change the sorting order by pressing the corresponding keys. For example, pressing M will sort processes by memory usage.
Monitor system metrics: The top command displays various system metrics, such as CPU usage, memory usage, load average, and uptime, at the top of the interface. These metrics update in real-time.
Interact with processes: While in the top interface, you can perform certain actions on processes. For example, you can press k to send a signal to a process, r to renice a process, or q to quit a process.
Customize the display: Top provides various interactive commands to customize the display. Press h to access the help screen and view available commands.
Exit top: To exit the top command, simply press q.
Remember, the top command offers extensive functionality, and the available options and key commands may vary slightly depending on the specific Linux distribution and version you are using.
You can refer to the top command’s man page (man top) for more detailed information and a comprehensive list of options.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Task Manager Alternative
When seeking a Task Manager alternative, it is vital to consider several factors that can significantly impact your choice and ensure the alternative aligns with your system management needs.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision and select the most suitable alternative.
One of the primary factors to consider when choosing a Task Manager alternative is compatibility. Ensure that the alternative is compatible with your operating system, taking into account both the version and architecture.
Resource utilization is another crucial consideration. Analyze the resource requirements of the alternative, including CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk space, to ensure it doesn’t strain your system or affect overall performance.
The functionality and features offered by the alternative are paramount. Evaluate whether it provides advanced process monitoring, customizable views, resource usage visualization, and additional tools for efficient task management.
Consider the user interface and user experience of the alternative. A clean, intuitive interface with easy navigation and well-organized information enhances usability and productivity.
Security is a vital aspect to contemplate. Ensure the alternative prioritizes security measures to protect sensitive system data and offers features like process integrity checking and malware detection.
Ongoing developer support is crucial for long-term usability. Evaluate the developer’s responsiveness regarding updates, bug fixes, and community engagement to ensure the alternative remains reliable and up-to-date.
In conclusion, consider factors such as compatibility, resource requirements, functionality, user interface, security, and developer support when choosing a an alternative.
By carefully assessing these factors, you can select an alternative that effectively meets your system management needs and enhances your overall experience.
📗FAQ’s
Is there a better alternative to Task Manager?
The answer lies in the specific needs and preferences of the user. While the built-in Task Manager in Windows provides basic process management functionality, some users may seek a more robust solution with advanced features and capabilities.
Fortunately, the software market offers several alternatives that can be considered superior to Task Manager.
One such alternative is Process Explorer. With its extensive process monitoring and management features, Process Explorer provides deeper insight into system processes, resource utilization, and dependencies.
It offers a customizable interface, detailed information about DLLs and network connections, and the ability to troubleshoot performance issues effectively.
Another notable alternative is Process Hacker, which goes beyond the capabilities of Task Manager by providing advanced features like process injection detection, customizable graphs, and detailed system information.
It also offers power user capabilities and customization options, making it attractive for users seeking more control and flexibility.
Additionally, System Explorer is a comprehensive Task Manager alternative, offering process management, system information, and network monitoring in one unified interface. With its extensive set of features and intuitive user interface, it provides an enhanced user experience for effective system management.
In conclusion, while Task Manager serves its purpose of basic process management, users seeking more advanced features and capabilities can explore alternatives like Process Explorer, Process Hacker, and System Explorer.
These alternatives offer a range of advanced functionalities and customization options, making them potentially better alternatives to Task Manager for users with specific system management needs.
Summing up
Throughout this article, we have unpacked the potential of various task manager alternatives and highlighted how they could revolutionize your approach to managing your workload.
From enhancing organization to improving efficiency, the right task management tool can transform chaos into a harmonious flow of productivity.
Remember, feeling overwhelmed with your tasks isn’t a sign of incompetence; it’s often a sign that your current tool is not serving your needs effectively. Traditional task managers can often create more clutter.
Still, the right alternative can become an extension of your mind, helping you navigate the jungle of tasks easily and precisely.
Choosing a task manager alternative may seem daunting, but the benefits of switching far outweigh any initial discomfort.
Start by assessing your needs, explore your options, and don’t be afraid to experiment until you find what works best for you. Remember, the goal is to find a tool that works for you, not vice versa.
In the end, pursuing productivity is more than just getting things done – finding balance, satisfaction, and joy in our work.
A task manager alternative might be the missing piece in your productivity puzzle. So, why wait? Begin your journey towards a more organized and efficient life today.