Raspberry Pi is a fantastic tool that has unlocked a world of programming and computing possibilities for users around the globe. Its mini-sized power, affordability, and ease of use have made it a staple among DIYers, hobbyists, students, and professionals.
However, one common concern among users is that Raspberry Pi sometimes fails to process power, memory, and customization features despite its versatility. Additionally, availability issues and price hikes due to demand spikes have left many seeking other options.
Are you frustrated by the constraints of Raspberry Pi’s limited processing power when dealing with complex or power-hungry projects?
Have you ever encountered availability issues when you needed a Raspberry Pi urgently? Do you feel hindered by the lack of more customization features that could allow you to innovate freely?
Fear not; plenty of potent Raspberry Pi alternatives are ready to serve your specific needs. From mini-computers offering superior processing capabilities to those that provide advanced customization features, these alternatives offer intriguing possibilities for all levels of tech enthusiasts.
This comprehensive guide will explore the best Raspberry Pi alternatives, comparing their pros and cons, to help you make an informed decision for your next big project.
What is Raspberry Pi?🤷♂️
In DIY and maker communities, the Raspberry Pi has emerged as a quintessential tool for enthusiasts, tinkerers, and tech aficionados. Launched in 2012, the Raspberry Pi is a single-board computer (SBC) that has revolutionized the landscape of miniature computing.
The Raspberry Pi Foundation, a non-profit organization, spearheaded the development of this innovative device to promote computer science education and foster hands-on learning. With its compact size and affordable price, the Raspberry Pi has democratized access to powerful computing capabilities.
Its popularity stems from its versatility and immense potential for creative projects. The Raspberry Pi is a platform for various applications, including home automation, robotics, retro gaming consoles, media centers, and IoT devices.
Its GPIO pins enable connectivity to various electronic components, facilitating seamless integration with hardware projects. One of the key factors contributing to its success is the vibrant community surrounding Raspberry Pi.
Enthusiasts gather in online forums, sharing knowledge, exchanging ideas, and collaborating on open-source projects. The community’s dedication has led to extensive tutorials, projects, and software libraries, empowering users of all skill levels.
Moreover, the Raspberry Pi has fostered a culture of experimentation and innovation. It has inspired countless individuals to dive into coding, electronics, and engineering, igniting a passion for technology and fueling the next generation of inventors.
In conclusion, Raspberry Pi’s impact on the DIY and maker communities cannot be overstated. Its affordability, versatility, and robust community support have propelled it to the forefront of the miniature-computing revolution, empowering individuals to transform their ideas into reality.
Criteria For Evaluating Raspberry Pi Alternatives
When considering alternatives to the renowned Raspberry Pi, it is crucial to establish a set of criteria to help make an informed decision. Evaluating these alternatives requires a comprehensive analysis of various factors to ensure they meet your project requirements.
Here are some key criteria to consider:-
1. Performance and Processing Power:- Look for alternatives that offer comparable or superior computational capabilities to the Raspberry Pi. Assess the processor architecture, clock speed, number of cores, and GPU performance to determine their suitability for your use case.
2. Ease of Use and Compatibility:- Consider the user-friendly aspects of the alternative. Check for a well-designed interface, clear documentation, and compatibility with popular operating systems like Linux. Ensure that the alternative supports your project’s programming languages and libraries.
3. Community Support and Availability of Resources:- An active and supportive community is essential for troubleshooting, seeking guidance, and exploring new possibilities. Look for alternatives with a dedicated community with extensive online forums, tutorials, and documentation.
4. Connectivity Options and Expandability:- Consider the available input/output (I/O) options for connecting peripherals and external devices. Evaluate the presence of USB ports, HDMI or DisplayPort, Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth capabilities. Additionally, assess the expandability options, such as GPIO pins, to determine if the alternative can accommodate your project’s hardware requirements.
5. Price Range and Value for Money:- Assess the cost-effectiveness of the alternative. Compare the price point with the features and performance it offers. Consider the value for money in terms of the overall package, including performance, compatibility, community support, and expandability.
By evaluating Raspberry Pi alternatives based on these criteria, you can make a well-informed decision that aligns with your project’s requirements and ensures a successful implementation.
Here, we have prepared a list of some of the best ones for you –
Top Raspberry Pi Alternatives To Unleash Your Imagination😍
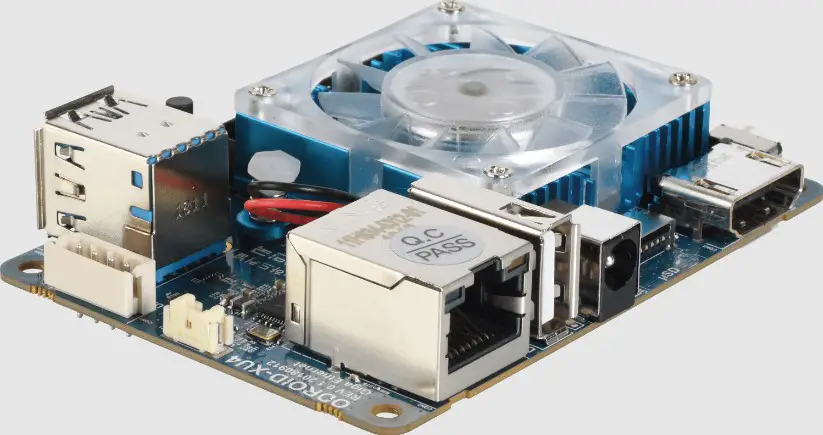
1. Odroid XU4
When it comes to finding a top-notch alternative to the Raspberry Pi, the Odroid XU4 stands out as a compelling choice. Packed with impressive features and powerful performance, the Odroid XU4 is a worthy competitor in single-board computers.
At the heart of the Odroid XU4 lies a robust Samsung Exynos 5422 processor featuring a big.LITTLE architecture that combines quad-core ARM Cortex-A15 and quad-core Cortex-A7 CPUs. This configuration allows optimal power efficiency and enhanced multitasking capabilities, making the Odroid XU4 excel in various computing tasks.
The Mali-T628 MP6 GPU offers remarkable visual processing power for graphics-intensive applications, enabling smooth and immersive experiences. This makes the Odroid XU4 ideal for projects that involve gaming, media streaming, and graphics-intensive applications.
Connectivity options are plentiful on the Odroid XU4, with Gigabit Ethernet ensuring high-speed networking and USB 3.0 ports providing fast data transfer. Additionally, it offers an HDMI port, microSD card slot, and 40 GPIO pins, ensuring extensive connectivity for various peripherals and expansion boards.
The active community surrounding the Odroid XU4 provides comprehensive support, with many tutorials, documentation, and forums available. This vibrant community fosters collaboration, knowledge sharing, and project inspiration.
In conclusion, the Odroid XU4 emerges as one of the best alternatives to the Raspberry Pi. Its impressive processing power, robust graphics capabilities, extensive connectivity options, and dedicated community support make it an exceptional choice for enthusiasts and professionals seeking a high-performance single-board computer.
Pros:-
Powerful Performance:- The Odroid XU4 boasts a powerful Samsung Exynos 5422 processor with a big.LITTLE architecture, delivering excellent performance for a wide range of computing tasks.
Impressive Graphics Capabilities:- With the Mali-T628 MP6 GPU, the Odroid XU4 excels in graphics-intensive applications, making it suitable for gaming, media streaming, and other visually demanding projects.
Extensive Connectivity:- The board offers Gigabit Ethernet, USB 3.0 ports, HDMI, microSD card slot, and GPIO pins, providing ample connectivity options for various peripherals and expansion boards.
Active Community Support: The Odroid XU4 has a dedicated and active community that provides extensive support, tutorials, documentation, and forums, fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing.
Robust and Reliable:- The Odroid XU4 is built with high-quality components and exhibits solid reliability, ensuring stable performance for long durations.
Cons:-
Higher Power Consumption: Compared to other alternatives, the Odroid XU4 can consume relatively more power, which may be a consideration for projects with strict power requirements or mobile applications.
Limited Availability of Accessories: While the Odroid XU4 has a decent selection of accessories, the options might not be as extensive as those for more widely adopted platforms like Raspberry Pi.
Less Extensive Software Ecosystem: Although the Odroid XU4 supports popular operating systems like Linux, the software ecosystem and community resources may not be as vast as those available for Raspberry Pi.
Learning Curve for Beginners: Due to its advanced features and powerful performance, the Odroid XU4 may have a steeper learning curve for beginners new to single-board computers.
Raspberry Pi vs Odroid XU4:-
The Raspberry Pi and Odroid XU4 are renowned single-board computers, each with strengths and capabilities.
Let’s compare these two powerhouses to help you make an informed decision for your next project.
In terms of performance, the Odroid XU4 takes the lead with its Samsung Exynos 5422 processor featuring a big.LITTLE architecture, offering a powerful combination of quad-core ARM Cortex-A15 and quad-core Cortex-A7 CPUs.
The Raspberry Pi, on the other hand, typically features ARM-based processors that vary in performance across different models. Graphics capabilities are another differentiating factor. The Odroid XU4’s Mali-T628 MP6 GPU delivers impressive visual processing power, making it suitable for graphics-intensive tasks like gaming and media streaming.
Raspberry Pi, although capable, may have limitations in handling complex graphics requirements. Connectivity options also vary. The Raspberry Pi typically offers a range of GPIO pins, USB ports, Ethernet, and HDMI, providing sufficient connectivity for most projects.
The Odroid XU4 goes further, with additional USB 3.0 ports and Gigabit Ethernet, ensuring faster data transfer rates and network speeds.
Both platforms have active communities that contribute to extensive support and resources. The Raspberry Pi community is larger and more established, resulting in a broader range of tutorials, projects, and software options. However, the Odroid XU4 community is growing and provides valuable assistance and expertise.
Ultimately, the choice between Raspberry Pi and Odroid XU4 depends on your project requirements.
If you prioritize raw performance, enhanced graphics capabilities, and expanded connectivity, the Odroid XU4 may be the ideal choice. However, if a larger community, extensive software ecosystem, and wider availability of accessories are essential, then Raspberry Pi might be the preferred option.
Here’s a comparison table highlighting some key differences between the Raspberry Pi and Odroid XU4:-
| Feature | Raspberry Pi | Odroid XU4 |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Broadcom BCM2837 or BCM2711 | Samsung Exynos 5422 (ARM Cortex-A15 Quad-core) |
| CPU Speed | Up to 1.4 GHz (Raspberry Pi 3B+) or 1.5 GHz (Pi 4) | Up to 2.0 GHz |
| RAM | Varies by model (1 GB, 2 GB, 4 GB, or 8 GB) | 2 GB LPDDR3 RAM |
| GPU | Broadcom VideoCore IV (Pi 3B+) or VideoCore VI (Pi 4) | Mali-T628 MP6 |
| Storage | MicroSD card | eMMC module or MicroSD card (Odroid XU4 with Cloudshell2) |
| Ethernet | 10/100 Ethernet (Raspberry Pi 3B+) or Gigabit Ethernet (Pi 4) | Gigabit Ethernet |
| USB Ports | USB 2.0 (Pi 3B+) or USB 3.0 (Pi 4) | 2 x USB 3.0, 1 x USB 2.0, 1 x USB OTG |
| Video Output | HDMI | HDMI, DisplayPort, and MIPI-DSI |
| Audio Output | 3.5mm jack | HDMI, 3.5mm jack, SPDIF |
| Operating System Support | Raspbian, Ubuntu, Windows 10 IoT Core, and more | Ubuntu, Android, Arch Linux, and more |
| GPIO Pins | 40 (Raspberry Pi Model B+) or 40/26 (Pi 4) | 30 GPIO pins |
| Price Range | $10 to $75+ | $59 to $79 (Odroid XU4) |
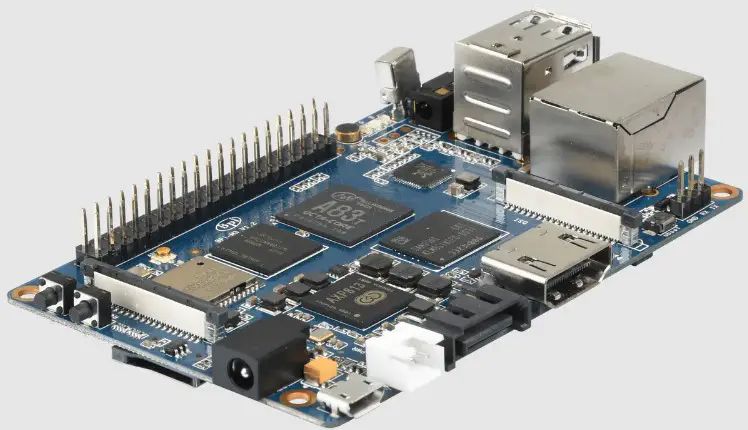
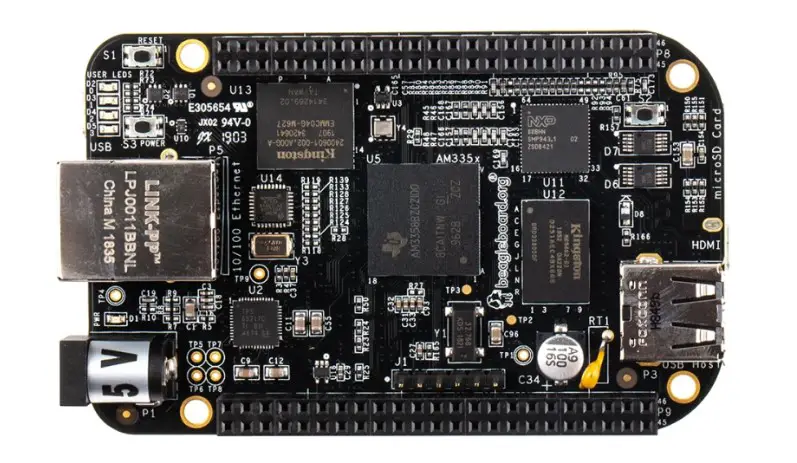
2. BeagleBone Black
The BeagleBone Black emerges as a compelling contender in single-board computers, positioned as a worthy alternative to the renowned Raspberry Pi. With its robust feature set and exceptional versatility, the BeagleBone Black offers an intriguing proposition to tech enthusiasts and DIY aficionados.
At the heart of the BeagleBone Black lies an ARM Cortex-A8 processor, which packs a punch with impressive processing capabilities. This, coupled with 512MB of DDR3 RAM, ensures snappy performance even when tackling resource-intensive tasks. Its onboard eMMC storage and support for microSD cards provide ample space for data storage and expansion.
One notable differentiator of the BeagleBone Black is its focus on real-time computing. Equipped with two Programmable Real-Time Units (PRUs), it enables precise control and synchronization of time-critical processes.
This makes it an ideal choice for applications such as robotics, industrial automation, and Internet of Things (IoT) projects that demand deterministic behavior.
Connectivity options abound on the BeagleBone Black, featuring an Ethernet port for reliable network connectivity and a USB host for peripheral expansion. Its HDMI output and audio jack also facilitate multimedia applications and audio processing.
Moreover, the BeagleBone Black boasts an array of general-purpose input/output (GPIO) pins, allowing seamless interaction with external devices and sensors. This opens up possibilities for hardware interfacing and custom electronics projects.
The BeagleBone Black presents a compelling Raspberry Pi alternative, offering potent computational power, real-time capabilities, and extensive connectivity options. Whether you’re a hobbyist, a developer, or a professional seeking a versatile single-board computer, the BeagleBone Black is worth considering.
Pros:-
Powerful Performance:- The BeagleBone Black excels in processing power thanks to its ARM Cortex-A8 processor and 512MB of DDR3 RAM. It delivers snappy performance, making it suitable for various applications.
Real-Time Computing:- Including two Programmable Real-Time Units (PRUs) sets the BeagleBone Black apart. It enables precise control and synchronization of time-critical processes, making it ideal for robotics, industrial automation, and IoT projects.
Versatile Connectivity:- The BeagleBone Black offers a variety of connectivity options, including Ethernet, USB host, HDMI output, and audio jack. These features facilitate networking, peripheral expansion, multimedia applications, and audio processing.
GPIO Pins:- With its extensive array of general-purpose input/output (GPIO) pins, the BeagleBone Black provides flexibility for hardware interfacing and custom electronics projects. It allows seamless interaction with external devices and sensors.
Cons:-
Limited RAM:- While the BeagleBone Black offers 512MB of DDR3 RAM, it may fall short for memory-intensive applications or those requiring significant multitasking capabilities. Users with such requirements may find the available memory insufficient.
Less Community Support:- Compared to the Raspberry Pi, the BeagleBone Black has a smaller community of users. As a result, finding extensive online resources, tutorials, and community support specific to the BeagleBone Black may be relatively more challenging.
Price:- The BeagleBone Black tends to have a slightly higher price tag than some Raspberry Pi models. This can be a factor for users on a tight budget or those looking for a cost-effective solution.
Limited Software Compatibility: The BeagleBone Black supports popular operating systems such as Linux, but it may have slightly fewer software options and community-developed projects than the Raspberry Pi. This could impact the availability of pre-built software and tools.
Raspberry Pi vs BeagleBone Black:-
The battle of Raspberry Pi vs BeagleBone Black sparks a captivating debate among tech enthusiasts, as both single-board computers offer unique features and cater to diverse project requirements.
Raspberry Pi, renowned for its accessibility and extensive community support, is a versatile platform for various applications. Its Broadcom ARM-based processor delivers commendable performance, and with 1GB or 2GB of RAM, it easily handles multitasking.
The Raspberry Pi boasts a rich ecosystem of expansion boards and accessories, enabling seamless integration into numerous projects. Its GPIO pins provide extensive options for hardware interfacing, allowing users to connect sensors, actuators, and other devices effortlessly.
On the other side, the BeagleBone Black shines with its emphasis on real-time computing. Powered by an ARM Cortex-A8 processor, it offers robust performance for demanding tasks.
Equipped with two Programmable Real-Time Units (PRUs), the BeagleBone Black delivers precise control and synchronization of time-critical processes, making it an ideal choice for robotics and industrial automation projects. Its GPIO pins provide ample flexibility for hardware interfacing, catering to complex electronics applications.
While the Raspberry Pi benefits from a vast and supportive community, the BeagleBone Black offers a more specialized approach with its real-time capabilities. However, it is essential to consider cost, software compatibility, and community resources when choosing between the two.
Ultimately, the choice between Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone Black depends on the specific project requirements and the desired balance between general-purpose capabilities and real-time performance.
Here’s a comparison table highlighting some key differences between the Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone Black:-
| Feature | Raspberry Pi | BeagleBone Black |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Broadcom ARM Cortex-A72 or A53 (varies by model) | Texas Instruments Sitara AM335x ARM Cortex-A8 |
| CPU Speed | Up to 1.5 GHz (varies by model) | 1 GHz |
| RAM | Varies by model (typically 1 GB to 8 GB) | 512 MB to 1 GB |
| Storage | MicroSD card slot for external storage | 4 GB eMMC onboard storage |
| GPU | Broadcom VideoCore IV (RPi 2/3) or Videocore VI (RPi 4) | PowerVR SGX530 |
| GPIO Pins | 26 to 40 (varies by model) | 65 (including analog inputs) |
| Ethernet | 10/100 Mbps Ethernet | 10/100 Mbps Ethernet |
| Wireless Connectivity | Wi-Fi (varies by model) and Bluetooth | Optional Wi-Fi/Bluetooth via expansion board |
| USB Ports | USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 (RPi 4) | USB 2.0 |
| HDMI Ports | 1 to 2 (varies by model) | 1 |
| Audio Output | 3.5 mm audio jack and HDMI | 3.5 mm audio jack and HDMI |
| Operating System Support | Raspbian (Linux-based), various Linux distributions | Debian Linux, various Linux distributions |
| Price Range | $10 to $75+ (varies by model) | $45 to $60 |
| Community Support | Large and active community with extensive online resources | Active community with good online resources |
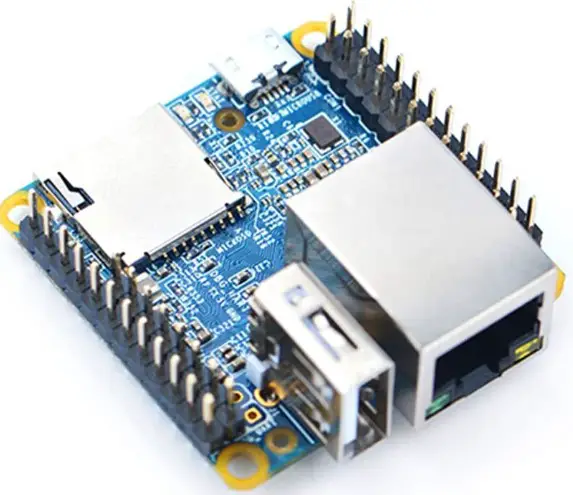
3. NanoPi NEO
The NanoPi NEO is an intriguing contender in single-board computers, offering a compelling alternative to the ubiquitous Raspberry Pi. Despite its diminutive size, this tiny powerhouse packs a punch, delivering impressive performance and versatility.
At the core of the NanoPi NEO lies a powerful quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 processor, enabling it to handle demanding tasks easily. Its 512MB of DDR3 RAM ensures smooth multitasking capabilities, while the MicroSD card slot provides ample storage space for data and applications.
Don’t let its size fool you – the NanoPi NEO offers an array of expansion interfaces, including GPIO pins, USB ports, and Ethernet connectivity. These features empower users to connect various peripherals and extend the board’s functionality for various projects.
One standout feature of the NanoPi NEO is its built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities. This allows for seamless wireless connectivity, opening doors to IoT applications, remote control, and wireless data transfer.
Furthermore, the NanoPi NEO offers an extensive software ecosystem compatible with popular operating systems such as Ubuntu and Debian. This facilitates rapid development and enables access to various software tools and libraries.
In conclusion, the NanoPi NEO is a powerful alternative to the Raspberry Pi, boasting impressive performance, versatile expansion options, built-in wireless connectivity, and a rich software ecosystem. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional seeking a compact yet capable single-board computer, the NanoPi NEO will captivate and empower your projects.
Pros:-
Impressive Performance: Despite its small size, the NanoPi NEO packs a powerful punch with its quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 processor. This enables it to handle demanding tasks and deliver smooth performance.
Versatile Expansion Options: The NanoPi NEO offers a range of expansion interfaces, including GPIO pins, USB ports, and Ethernet connectivity.
This allows seamless integration with various peripherals and extends the board’s functionality for diverse projects.
Built-in Wireless Connectivity: The NanoPi NEO provides convenient wireless connectivity with built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities.
This opens possibilities for IoT applications, remote control, and wireless data transfer.
Extensive Software Ecosystem:- The NanoPi NEO supports popular operating systems such as Ubuntu and Debian, offering access to a rich software ecosystem. This facilitates rapid development and provides various software tools and libraries.
Cons:-
Limited RAM: The NanoPi NEO comes with 512MB of DDR3 RAM, which may be insufficient for memory-intensive applications or extensive multitasking scenarios. Users with such requirements may find the available memory limiting.
Smaller Community: Compared to the Raspberry Pi, the NanoPi NEO has a smaller user community. As a result, finding extensive online resources, tutorials, and community support specific to the NanoPi NEO may be relatively more challenging.
Availability and Compatibility: The NanoPi NEO may have limited availability and compatibility with certain peripherals or accessories compared to the more popular Raspberry Pi. Users may need to ensure compatibility before integrating specific hardware components.
Price: Depending on the specific model and features, the NanoPi NEO’s price may be slightly higher than some Raspberry Pi alternatives. This can be a consideration for users on a tight budget or those seeking a cost-effective solution.
Raspberry Pi vs NanoPi NEO
The battle between Raspberry Pi vs NanoPi NEO fuels a captivating discussion among tech enthusiasts, as these single-board computers offer unique features and cater to diverse project requirements.
Raspberry Pi, a household name in the SBC world, boasts a large and supportive community. With its Broadcom ARM-based processor, it delivers a commendable performance.
The Raspberry Pi’s versatility shines through its GPIO pins, enabling seamless hardware interfacing. It also offers a range of expansion boards and accessories, enhancing its functionality for various projects.
On the other hand, the NanoPi NEO presents a more compact alternative with its powerful features. Its quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 processor delivers impressive performance, ideal for demanding tasks.
The NanoPi NEO offers diverse expansion interfaces, including GPIO pins, USB ports, and Ethernet connectivity, enabling seamless integration with peripherals. Its built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities provide convenient wireless connectivity.
While the Raspberry Pi benefits from a larger community and extensive software support, the NanoPi NEO’s compact size and impressive performance make it an attractive choice for specific projects. However, it is important to consider factors such as RAM capacity, availability of resources, and compatibility with peripherals when selecting the two.
Ultimately, the choice between Raspberry Pi and NanoPi NEO depends on the project’s specific requirements and the desired balance between community support and compact yet powerful performance.
Here’s a comparison table between Raspberry Pi and NanoPi NEO:-
| Feature | Raspberry Pi | NanoPi NEO |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Broadcom ARM Cortex-A72 (64-bit) | Allwinner H3 ARM Cortex-A7 (32-bit) |
| CPU Speed | Up to 1.5 GHz | Up to 1.2 GHz |
| GPU | VideoCore IV | Mali-400MP2 |
| RAM | 1 GB, 2 GB, 4 GB (model dependent) | 256 MB, 512 MB, 1 GB |
| Storage | MicroSD card | MicroSD card |
| Ethernet | Gigabit | 10/100Mbps |
| Wi-Fi | 2.4 GHz 802.11b/g/n/ac | 2.4 GHz 802.11b/g/n |
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth 5.0 | Bluetooth 4.0 |
| USB Ports | USB 3.0, USB 2.0 | USB 2.0 |
| GPIO Pins | 40 | 26 |
| Display Output | HDMI, DSI | HDMI, DVP |
| Operating System | Raspberry Pi OS (Linux-based) | Various Linux distributions |
| Dimensions | 85.6 mm × 56.5 mm × 17 mm | 40 mm × 40 mm |
| Price (approximate) | $10 – $75 (model dependent) | $7 – $25 (model dependent) |
4. Orange Pi PC
The Orange Pi PC stands out as a compelling alternative to the widely popular Raspberry Pi in the ever-evolving landscape of single-board computers. Packed with powerful features and diverse capabilities, the Orange Pi PC offers an intriguing proposition for tech and DIY enthusiasts.
At the heart of the Orange Pi PC lies a quad-core ARM Cortex-A7 processor, ensuring robust performance for various computing tasks. With 1GB of DDR3 RAM, it easily handles multitasking, making it suitable for lightweight and resource-intensive applications.
The Orange Pi PC offers expansion options through its TF card slot and onboard eMMC storage. Connectivity options are abundant on the Orange Pi PC, including Ethernet, USB ports, and HDMI output.
These features facilitate seamless networking, peripheral connectivity, and multimedia applications. The Orange Pi PC also supports Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, enhancing its wireless capabilities.
One notable aspect of the Orange Pi PC is its GPIO pins, which allow for extensive hardware interfacing and custom electronics projects. This flexibility empowers users to connect various external devices and sensors, expanding the possibilities for experimentation and innovation.
While the Raspberry Pi enjoys a larger community and extensive software support, the Orange Pi PC presents itself as a viable alternative with its powerful processing capabilities, versatile connectivity options, and GPIO pin expansion.
Whether you’re a hobbyist, developer, or professional seeking a single-board computer, the Orange Pi PC offers a compelling platform to explore and bring your ideas to life.
Pros:-
Powerful Performance:- The Orange Pi PC has a quad-core ARM Cortex-A7 processor, delivering robust performance for various computing tasks.
Ample RAM:- With 1GB of DDR3 RAM, the Orange Pi PC provides sufficient memory for smooth multitasking and resource-intensive applications.
Versatile Connectivity:- The Orange Pi PC offers a variety of connectivity options, including Ethernet, USB ports, HDMI output, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. This enables seamless networking, peripheral integration, multimedia applications, and wireless connectivity.
GPIO Pins:- Including GPIO pins on the Orange Pi PC allows for extensive hardware interfacing, providing flexibility for custom electronics projects and the connection of external devices and sensors.
Cons:-
Limited Community Support:- Compared to the Raspberry Pi, the Orange Pi PC has a smaller community of users, resulting in relatively fewer online resources, tutorials, and community-driven projects.
Software Compatibility:- While the Orange Pi PC supports various operating systems, it may have slightly fewer software options and community-developed projects than Raspberry Pi. This can affect the availability of pre-built software and tools.
Availability and Compatibility:- Some peripherals and accessories designed specifically for the Raspberry Pi may not be compatible with the Orange Pi PC. Users should ensure compatibility before integrating specific hardware components.
Learning Curve:- As the Orange Pi PC may have a different architecture and software environment than the Raspberry Pi, users transitioning from Raspberry Pi to the Pi Pi PC might need to familiarize themselves with its unique features and configuration.
Raspberry Pi vs Orange Pi PC:-
While the Raspberry Pi benefits from a larger and more established community, the Orange Pi PC stands out with its powerful processing capabilities and comprehensive connectivity options.
However, it is important to consider factors such as community support, software compatibility, and availability of resources when choosing between the two.
Ultimately, the choice between the Raspberry Pi and Orange Pi PC depends on the specific project requirements, desired level of community support, and the balance between established capabilities and innovative features.
Here’s a comparison table highlighting some key features and specifications of the Raspberry Pi and Orange Pi PC:-
| Feature | Raspberry Pi | Orange Pi PC |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Broadcom BCM2711 | Allwinner H3 |
| CPU | Quad-core ARM Cortex-A72 | Quad-core ARM Cortex-A7 |
| Clock Speed | 1.5 GHz (overclocking possible) | 1.2 GHz (overclocking possible) |
| GPU | VideoCore VI | Mali-400MP2 |
| RAM | 2GB/4GB LPDDR4 | 1GB DDR3 |
| Storage | microSD card slot | microSD card slot |
| Ethernet | Gigabit Ethernet | 10/100 Ethernet |
| Wi-Fi | Dual-band 802.11ac | 802.11 b/g/n |
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth 5.0 | No |
| USB Ports | 2 x USB 3.0, 2 x USB 2.0 | 3 x USB 2.0, 1 x USB OTG |
| Video Output | 2 x micro HDMI (up to 4K 60Hz) | HDMI, CVBS |
| Audio Output | 3.5mm audio jack, HDMI | 3.5mm audio jack, HDMI |
| GPIO Pins | 40-pin GPIO header | 40-pin GPIO header |
| Operating System | Raspbian, various Linux distributions | Armbian, various Linux distributions |
| Price (approx.) | $35 (for Raspberry Pi 4 Model B 2GB) | $15 (may vary based on seller) |
5. Banana Pi M3
When seeking a worthy alternative to the iconic Raspberry Pi, the Banana Pi M3 shines as a compelling contender. Packed with powerful features and diverse capabilities, it offers an intriguing proposition for tech and DIY enthusiasts.
At the heart of the Banana Pi M3 lies a powerful octa-core ARM Cortex-A7 processor, ensuring robust performance for various computing tasks.
Its 2GB of DDR3 RAM allows smooth multitasking and resource-intensive applications, making it suitable for lightweight and demanding projects. The Banana Pi M3 provides ample storage options, including eMMC, SATA, and MicroSD card slots, allowing for flexible data storage and expansion.
The Banana Pi M3 has abundant connectivity options, including Gigabit Ethernet, USB ports, HDMI output, and Wi-Fi. These features facilitate seamless networking, peripheral integration, multimedia applications, and wireless connectivity.
One standout feature of the Banana Pi M3 is its GPIO header, enabling hardware interfacing and customization. This opens up possibilities for connecting external devices, sensors, and other components, expanding the scope of projects and experimentation.
While the Raspberry Pi enjoys a larger community and extensive software support, the Banana Pi M3 presents a versatile alternative with its powerful processing capabilities, ample RAM, versatile connectivity options, and GPIO header.
Whether you’re a hobbyist, developer, or professional seeking a single-board computer, the Banana Pi M3 offers a compelling platform to explore and realize your creative ideas.
Pros:-
Powerful Performance: With its octa-core ARM Cortex-A7 processor, the Banana Pi M3 delivers impressive processing power, allowing for smooth performance and handling of demanding tasks.
Ample RAM: The Banana Pi M3’s 2GB of DDR3 RAM provides sufficient memory for multitasking and resource-intensive applications, enabling seamless operation.
Versatile Connectivity: The Banana Pi M3 offers a range of connectivity options, including Gigabit Ethernet, USB ports, HDMI output, and Wi-Fi. This allows for seamless networking, peripheral integration, multimedia applications, and wireless connectivity.
Storage Expansion: With options for eMMC, SATA, and MicroSD card slots, the Banana Pi M3 offers flexibility in storage expansion, accommodating diverse data storage needs.
Cons:-
Limited Community Support: Compared to the Raspberry Pi, the Banana Pi M3 has a smaller community of users. As a result, finding extensive online resources, tutorials, and community support specific to the Banana Pi M3 may be more challenging.
Software Compatibility: The Banana Pi M3 may have slightly fewer software options and community-developed projects than the Raspberry Pi. Users may need to ensure the compatibility and availability of desired software tools and libraries.
Availability and Compatibility of Peripherals: Some peripherals and accessories designed specifically for the Raspberry Pi may not be compatible with the Banana Pi M3. Users should verify compatibility before integrating specific hardware components.
Learning Curve: As the Banana Pi M3 may have a different architecture and software environment than the Raspberry Pi, users transitioning from Raspberry Pi to the Banana Pi M3 may need to familiarize themselves with its unique features and configuration.
Raspberry Pi vs Banana Pi M3
Banana Pi M3 stands out with its powerful hardware configuration. Equipped with an octa-core ARM Cortex-A7 processor, it delivers impressive processing power, making it suitable for demanding tasks.
The Banana Pi M3 also offers ample RAM and storage expansion options, providing room for multitasking and data storage flexibility.
Regarding connectivity, both boards offer Ethernet, USB ports, and HDMI output options. However, the Banana Pi M3 may have an advantage with its support for Gigabit Ethernet and additional storage interfaces. While the Raspberry Pi benefits from a larger and more established community, the Banana Pi M3 excels in raw processing power.
When choosing between the two, it is important to consider factors such as community support, software compatibility, and specific project requirements.
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the differences between the Raspberry Pi and the Banana Pi M3:-
| Feature | Raspberry Pi | Banana Pi M3 |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Broadcom BCM2837 (ARM Cortex-A53) | Allwinner A83T (ARM Cortex-A7) |
| CPU Speed | 1.2 GHz (Quad-core) | 1.8 GHz (Octa-core) |
| GPU | VideoCore IV | PowerVR SGX544MP1 |
| RAM | 1 GB / 2 GB / 4 GB LPDDR4 | 2 GB DDR3 SDRAM |
| Storage | microSD card slot | microSD card slot, SATA interface |
| Ethernet | 10/100 Mbps Ethernet | Gigabit Ethernet |
| Wireless Connectivity | 802.11 b/g/n Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 4.2 | 802.11 b/g/n Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 4.0 |
| USB Ports | 4 x USB 2.0 | 2 x USB 2.0, 1 x USB OTG |
| Video Output | HDMI, MIPI DSI, MIPI CSI | HDMI, LVDS |
| Audio Output | 3.5mm jack, HDMI | 3.5mm jack, HDMI |
| GPIO Pins | 40 GPIO pins | 40 GPIO pins |
| Operating System | Supports various Linux distributions | Supports various Linux distributions |
| Power Supply | Micro USB or GPIO header | DC power jack, Micro USB |
| Dimensions | 85.60 mm x 56.5 mm x 17.0 mm | 92 mm x 60 mm x 19 mm |
| Price | Varies based on model and configuration | Varies based on model and configuration |
6. Pine64
One finds a powerful contender in single-board computers when considering Pine64 as a Raspberry Pi alternative. With its distinct features and capabilities, the Pine64 offers an intriguing proposition for tech enthusiasts and DIY aficionados.
At the core of the Pine64 lies a robust ARM-based processor, delivering commendable performance for various computing tasks.
With options ranging from quad-core to hexa-core configurations, the Pine64 caters to different project requirements, ensuring smooth multitasking and efficient processing power.
The Pine64 boasts generous memory options, with models available offering 2GB, 3GB, or even 4GB of DDR3 RAM. This ample memory capacity allows for seamless operation and resource-intensive applications.
Connectivity is a highlight of the Pine64, featuring Ethernet, USB ports, HDMI output, and Wi-Fi/Bluetooth capabilities. These features facilitate networking, peripheral integration, multimedia applications, and wireless connectivity.
One distinctive aspect of the Pine64 is its modularity, offering various expansion modules for specific applications. These modules cater to diverse needs such as additional storage, LCD screens, camera interfaces, etc.
While the Raspberry Pi enjoys a larger community and extensive software support, the Pine64 presents itself as a viable alternative with its powerful processing capabilities, generous memory options, versatile connectivity, and modular expansion possibilities.
Whether you’re a hobbyist, a developer, or a professional seeking a single-board computer, the Pine64 offers an attractive platform to explore and bring your innovative projects to life.
Pros:-
Powerful Processing:- The Pine64 offers a range of ARM-based processors, including quad-core and hexa-core configurations, providing powerful processing capabilities for various computing tasks.
Ample Memory:- With options for 2GB, 3GB, or 4GB of DDR3 RAM, the Pine64 offers generous memory capacity, ensuring smooth multitasking and efficient operation.
Versatile Connectivity:- The Pine64 features Ethernet, USB ports, HDMI output, and Wi-Fi/Bluetooth capabilities, providing versatile connectivity options for networking, peripheral integration, multimedia applications, and wireless connectivity.
Modularity and Expansion:- The Pine64 supports various expansion modules, enabling customization and catering to specific project requirements. These modules offer additional storage, LCD screens, camera interfaces, and more.
Cons:-
Community Support:- While the Pine64 has a growing community, it may have a smaller user base than the Raspberry Pi. This can result in fewer online resources, tutorials, and community-driven projects specific to Pine64.
Software Compatibility:- The Pine64 may have slightly fewer software options and community-developed projects than the Raspberry Pi. Users may need to ensure software compatibility and availability for their project needs.
Availability of Accessories:- Some accessories and peripherals designed specifically for the Raspberry Pi may not be readily available or compatible with the Pine64. Users should verify compatibility before integrating specific hardware components.
Learning Curve:- As the Pine64 may have a different architecture and software environment than the Raspberry Pi, users transitioning from Raspberry Pi to the Pine64 may need to familiarize themselves with its unique features and configuration.
7. ASUS Tinker Board
As tech enthusiasts seek alternatives to the popular Raspberry Pi, the ASUS Tinker Board is a compelling choice in single-board computers. With its impressive features and capabilities, the Tinker Board offers a powerful platform for various projects.
At the heart of the ASUS Tinker Board lies a Rockchip RK3288 quad-core processor, delivering robust performance for various computing tasks. Its 2GB of DDR3 RAM ensures smooth multitasking and efficient operation, surpassing the memory capacity of many Raspberry Pi models.
Connectivity options on the Tinker Board are extensive, featuring Gigabit Ethernet, USB ports, HDMI output, and Wi-Fi/Bluetooth capabilities. These features enable seamless networking, peripheral integration, multimedia applications, and wireless connectivity.
One standout feature of the Tinker Board is its enhanced audio capabilities, including a dedicated audio jack and 192kHz/24-bit audio support. This makes it an excellent choice for audio-centric projects and high-quality sound output.
The ASUS Tinker Board also offers an impressive array of GPIO pins, providing extensive options for hardware interfacing and custom electronics projects. This flexibility allows users to connect sensors, actuators, and other devices effortlessly.
While the Raspberry Pi enjoys a larger community and extensive software support, the ASUS Tinker Board presents itself as a formidable alternative with its powerful processing capabilities, generous memory, versatile connectivity, enhanced audio features, and GPIO pin expansion.
Whether you’re a hobbyist, a developer, or a professional seeking a single-board computer, the ASUS Tinker Board offers a compelling platform to explore and bring your projects to life.
Pros:-
Powerful Processing:- The ASUS Tinker Board features a Rockchip RK3288 quad-core processor, providing robust processing power for various computing tasks.
Generous Memory:- With 2GB of DDR3 RAM, the Tinker Board offers ample memory capacity, allowing for smooth multitasking and efficient operation.
Versatile Connectivity:- The Tinker Board includes Gigabit Ethernet, USB ports, HDMI output, and Wi-Fi/Bluetooth capabilities, offering versatile options for networking, peripheral integration, multimedia applications, and wireless connectivity.
Enhanced Audio Features:- The Tinker Board boasts enhanced audio capabilities, including a dedicated audio jack and support for 192kHz/24-bit audio, making it an excellent choice for audio-centric projects and high-quality sound output.
Cons:-
Community Support:- Compared to the Raspberry Pi, the Tinker Board may have a smaller community of users. This could result in fewer online resources, tutorials, and community-driven projects tailored to the Tinker Board.
Software Compatibility: While the Tinker Board supports popular operating systems like Linux, it may have slightly fewer software options and community-developed projects than Raspberry Pi. Users should ensure software compatibility for their specific project needs.
Availability of Accessories: Some accessories and peripherals designed specifically for the Raspberry Pi may not be readily available or compatible with the Tinker Board. Users should verify compatibility before integrating specific hardware components.
Learning Curve: As the Tinker Board may have a different architecture and software environment than the Raspberry Pi, users transitioning from Raspberry Pi to the Tinker Board may need to familiarize themselves with its unique features and configuration.
Best Raspberry Pi 4 Alternatives
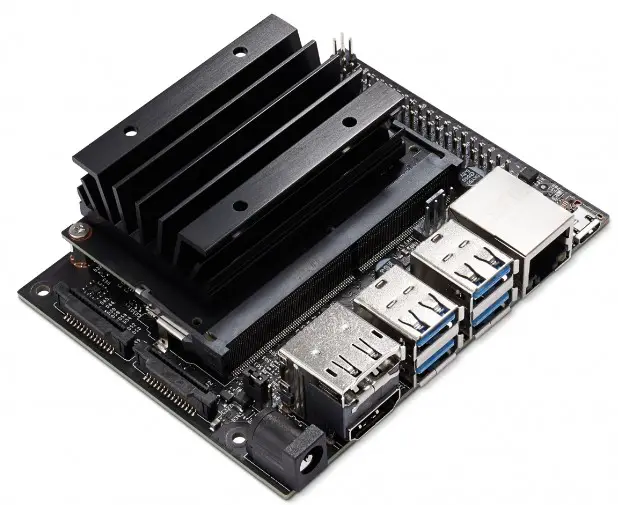
1. Nvidia Jetson Nano
Regarding alternative options to the ever-popular Raspberry Pi 4, the Nvidia Jetson Nano is a compelling choice for tech enthusiasts and professionals alike. Combining impressive performance with advanced capabilities, the Jetson Nano offers a unique experience in single-board computers.
One of the standout features of the Jetson Nano is its AI focus. Powered by Nvidia’s cutting-edge GPU architecture, it delivers exceptional performance for machine learning and deep learning tasks.
Whether you’re working on computer vision projects, robotics, or autonomous systems, the Jetson Nano’s AI capabilities give it a clear edge over its counterparts. With its quad-core ARM Cortex-A57 CPU and 128-core Nvidia Maxwell GPU, the Jetson Nano delivers powerful processing that rivals the Raspberry Pi 4.
This makes it ideal for resource-intensive applications like real-time data processing and high-definition video analysis. Furthermore, the Jetson Nano offers extensive I/O options, including USB 3.0, HDMI, Ethernet, and GPIO, ensuring seamless connectivity with a wide range of peripherals.
Its compact form factor and low power consumption make it an excellent choice for embedded systems and edge computing applications.
In conclusion, the Nvidia Jetson Nano is a top-notch alternative to the Raspberry Pi 4. Its AI-focused capabilities, impressive performance, and versatile I/O options make it a go-to solution for enthusiasts and professionals seeking a powerful single-board computer.
Whether diving into AI projects or exploring the frontiers of embedded computing, the Jetson Nano is a remarkable choice that won’t disappoint.
Pros:-
AI-Focused Performance: The Nvidia Jetson Nano excels in AI tasks, thanks to its powerful GPU architecture and dedicated AI capabilities. It offers superior performance for machine learning and deep learning projects.
Impressive Processing Power: With its quad-core ARM Cortex-A57 CPU and 128-core Nvidia Maxwell GPU, the Jetson Nano delivers robust processing power, making it suitable for resource-intensive applications and real-time data processing.
Versatile I/O Options: The Jetson Nano offers a wide range of I/O options, including USB 3.0, HDMI, Ethernet, and GPIO, ensuring seamless connectivity with various peripherals and devices.
Compact Form Factor: Its compact size allows for easy integration into projects with space constraints, making it an excellent choice for embedded systems and edge computing applications.
Extensive Community Support: The Jetson Nano benefits from a vibrant and active community of developers and enthusiasts. This ensures ample resources, tutorials, and support for troubleshooting and expanding its capabilities.
Cons:-
Higher Cost:- Compared to the Raspberry Pi 4, the Jetson Nano has a higher price tag, primarily due to its specialized AI capabilities and advanced hardware components.
Limited Availability:- The Jetson Nano may not be as widely available as the Raspberry Pi 4, which could make it slightly more challenging to purchase, especially in certain regions.
Steeper Learning Curve:- While the Jetson Nano offers impressive capabilities, it may require a deeper understanding of AI and GPU computing concepts to utilize its potential fully. This might pose a challenge for beginners or those unfamiliar with these technologies.
Power Consumption:- The Jetson Nano consumes more power than the Raspberry Pi 4, which is worth considering if energy efficiency is critical for your project.
Compatibility Limitations: As an alternative to the Raspberry Pi 4, software and peripheral support might have some compatibility differences. It’s essential to ensure that the Jetson Nano meets your requirements before deciding.
Raspberry Pi 4 vs Nvidia Jetson Nano:-
The Raspberry Pi 4 and the Nvidia Jetson Nano are popular single-board computers catering to diverse technical needs. While both boards offer impressive capabilities, they target different use cases, making it crucial to understand their unique strengths and limitations.
The Raspberry Pi 4 is a versatile and affordable option for various projects. Its quad-core ARM Cortex-A72 CPU and VideoCore VI GPU deliver solid performance for everyday computing tasks.
With 1GB, 2GB, 4GB, or 8GB of RAM options, the Raspberry Pi 4 provides flexibility to meet varying memory requirements.
On the other hand, the Nvidia Jetson Nano focuses on AI and machine learning applications. Powered by a quad-core ARM Cortex-A57 CPU and a 128-core Nvidia Maxwell GPU, it offers exceptional computational power for complex AI algorithms. Its AI-focused architecture enables accelerated inferencing and deep learning capabilities.
Regarding I/O options, both boards offer a variety of ports, including USB, HDMI, and Ethernet. However, the Jetson Nano provides additional GPIO pins, enabling seamless integration with various hardware peripherals.
While the Raspberry Pi 4 excels in general-purpose computing, the Jetson Nano shines in AI-centric tasks. However, it’s worth noting that the Jetson Nano’s higher cost and steeper learning curve might make it less accessible for beginners or those on a tight budget.
Choosing between the Raspberry Pi 4 and the Nvidia Jetson Nano depends on your project requirements. If you’re looking for a cost-effective, versatile solution for various applications, the Raspberry Pi 4 is an excellent choice.
However, if you prioritize AI and machine learning capabilities and are willing to invest in enhanced computational power, the Nvidia Jetson Nano stands as the preferred option.
Here’s a comparison table between the Raspberry Pi 4 and Nvidia Jetson Nano:-
| Feature | Raspberry Pi 4 | Nvidia Jetson Nano |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Broadcom BCM2711, Quad-core Cortex-A72 | Nvidia Tegra X1, Quad-core Cortex-A57 |
| CPU Speed | 1.5 GHz | 1.43 GHz |
| GPU | VideoCore VI | Nvidia Maxwell GPU |
| RAM | 2GB, 4GB, or 8GB LPDDR4-3200 SDRAM | 4GB LPDDR4-3200 SDRAM |
| Storage Options | microSD card slot | microSD card slot |
| USB Ports | 2x USB 3.0, 2x USB 2.0 | 4x USB 3.0, USB 2.0 Micro-B |
| Ethernet | Gigabit Ethernet | Gigabit Ethernet |
| Wireless Connectivity | 802.11ac Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 5.0 | 802.11ac Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 5.0 |
| Video Output | 2x micro HDMI (up to 4Kp60) | HDMI 2.0 (up to 4Kp60) |
| GPIO Pins | 40-pin GPIO header | 40-pin GPIO header |
| Camera Interface | CSI (Camera Serial Interface) connector | MIPI CSI-2 |
| AI Acceleration | None | Nvidia CUDA, Tensor Cores |
| Operating System Support | Linux (Raspbian, Ubuntu, etc.) | Linux (JetPack SDK) |
| Price | Starting from $35 | Starting from $59 |
2. Intel NUC
In single-board computers (SBCs), the Intel NUC stands tall as one of the best alternatives to the Raspberry Pi 4. While the Raspberry Pi 4 has garnered immense popularity, the Intel NUC offers compelling features that make it a worthy contender.
At the heart of the Intel NUC lies its robust performance. Powered by Intel processors that boast high clock speeds and multiple cores, the NUC outshines the Raspberry Pi 4 in raw computing power.
Whether you’re engaged in resource-intensive tasks or running demanding applications, the NUC delivers unrivaled processing capabilities.
Furthermore, the Intel NUC shines in its expandability and connectivity options. With multiple USB 3.0 and USB-C ports, you can effortlessly connect various peripherals and devices. Its NVMe storage support ensures lightning-fast data transfer speeds, providing a seamless computing experience.
One aspect where the Intel NUC truly excels is graphics performance. Equipped with powerful integrated GPUs or even the option to add a dedicated graphics card, the NUC offers superior graphical capabilities compared to the Raspberry Pi 4.
This makes it an excellent choice for graphics-intensive tasks such as video editing, 3D rendering, and gaming.
While the Raspberry Pi 4 caters to the maker and hobbyist community with its affordability and extensive GPIO support, the Intel NUC targets users seeking enterprise-level performance and a desktop-like experience in a compact form factor.
In conclusion, if you require a high-performance SBC with extensive expandability, connectivity, and graphics capabilities, the Intel NUC is the best Raspberry Pi 4 alternative. Its powerful processors, versatile connectivity options, and impressive graphics performance make it a compelling choice for various applications.
Pros:-
Powerful Performance:- The Intel NUC boasts high-performance Intel processors with multiple cores and high clock speeds, providing superior processing power for demanding tasks.
Expandability:- With a range of USB ports and support for NVMe storage, the Intel NUC offers excellent expandability options, allowing you to connect various peripherals and achieve fast data transfer speeds.
Graphics Capabilities:- The NUC excels in graphics performance, with powerful integrated GPUs and the option to add dedicated graphics cards, making it ideal for graphics-intensive applications like gaming and video editing.
Enterprise-level Performance:- Designed for professional and enterprise use, the Intel NUC delivers desktop-like performance in a compact form factor, making it suitable for various business applications.
Reliability:- Intel is a well-established and trusted brand known for producing reliable and high-quality hardware, ensuring a stable and dependable computing experience.
Cons:-
Higher Cost: The Intel NUC tends to be more expensive than the Raspberry Pi 4, making it less accessible for budget-conscious users or hobbyists.
Limited GPIO Support: Unlike the Raspberry Pi 4, which offers extensive GPIO support for interacting with external devices, the Intel NUC has limited GPIO capabilities, which may not be ideal for certain DIY or maker projects.
Power Consumption: The powerful processors and graphics capabilities of the Intel NUC result in higher power consumption compared to the energy-efficient Raspberry Pi 4.
Less Community Support: The Raspberry Pi has a large and active community, offering extensive online resources, tutorials, and community support.
While still supported, the Intel NUC may have a comparatively smaller community and fewer dedicated resources.
Raspberry Pi 4 vs Intel NUC:-
The decision between the Intel NUC and Raspberry Pi 4 depends on your specific requirements, budget, and the nature of your project. The Intel NUC is a compelling alternative for high-performance computing, expandability, and superior graphics capabilities.
However, if you prioritize affordability, extensive GPIO support, and a thriving community, the Raspberry Pi 4 may be the better choice.
Here’s a comparison table highlighting some key differences between the Raspberry Pi 4 and Intel NUC:-
| Specification | Raspberry Pi 4 | Intel NUC |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Broadcom BCM2711, Quad-core ARM Cortex-A72 @ 1.5GHz | Intel Core i3/i5/i7 processors |
| GPU | VideoCore VI GPU | Intel HD Graphics |
| RAM | 2GB, 4GB, or 8GB LPDDR4 RAM | Various configurations up to 64GB DDR4 |
| Storage Options | MicroSD card | M.2 SSD, SATA, NVMe |
| USB Ports | 2 x USB 3.0, 2 x USB 2.0 | Multiple USB 3.0 and USB 2.0 ports |
| Ethernet | Gigabit Ethernet | Gigabit Ethernet |
| Wireless Connectivity | 802.11ac Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 5.0 | Wi-Fi and Bluetooth options available |
| Video Output | 2 x micro HDMI (up to 4Kp60) | HDMI, DisplayPort, or Thunderbolt |
| Operating System | Supports various Linux distributions and other OS options | Supports various operating systems |
| Price | Affordable, ranging from $35 to $75 depending on the model | Higher price range depending on the model |
The Most Powerful Raspberry Pi Alternatives: A Deep Dive
The world of single-board computers (SBCs) is a vast, uncharted expanse. The Raspberry Pi undoubtedly occupies the zenith among its myriad intriguing specimens, owing to its versatility and ease of use. However, we present the most powerful Raspberry Pi alternatives for tech aficionados yearning for extra dynamism.
BeagleBone Black is a veritable paradigm of high-octane performance. Heralded for its robust Processing Unit and Debian Linux OS, it embodies a potent Raspberry Pi alternative. It facilitates Micro HDMI output and has an inbuilt storage of 4GB, substantially outstripping Raspberry Pi’s SD Card dependency.
Next, we tread into the dominion of Odroid-XU4, an SBC that’s a marvel in raw computational power. It comes equipped with an 8-core processor and 2GB LPDDR3 RAM, which makes it an attractive proposition for computationally intensive tasks. Its other attractive features include a USB 3.0 port and a Gigabit Ethernet, which foster high-speed data transfer.
Unveiling yet another titan, the Asus Tinker Board is a dynamic Raspberry Pi alternative. Adorned with a Rockchip Quad-Core RK3288 processor, it maintains an edge in GPU performance and memory speed. Its proficient Realtek ALC4040 codec supports high-definition audio, which enhances the immersive multimedia experience.
The Banana Pi M4 can’t be sidelined in this exploration of Raspberry Pi alternatives. This powerful SBC boasts an efficient Quad Core A53 CPU and Dual-core MALI 450 MP3 GPU. With onboard Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n AC and Bluetooth 4.2, it is a competent contender for IoT projects requiring superior connectivity.
For the seekers of a budget-friendly powerhouse, PINE A64 makes an irresistible proposition. It features a Quad-Core ARM Cortex A53 64-Bit Processor and a Dual-Core MALI 400 MP2 GPU. Including a high-speed Gigabit Ethernet port, coupled with a 64-bit DDR2/DDR3 Memory Bus width, indeed makes it a potent Raspberry Pi substitute.
Transcending into the arena of top-tier SBCs, we encounter the formidable Jetson Nano Developer Kit from NVIDIA. Revered for its GPU capabilities, it flaunts a 128-core NVIDIA Maxwell GPU and a Quad-core ARM A57 CPU. An enticing pick for AI development and machine learning, it revolutionizes the concept of edge computing.
Next in line is the LattePanda Alpha 864s, an SBC par excellence. Equipped with an Intel 7th gen Core m3 processor and an integrated Arduino co-processor, it blends a laptop’s power with a microcontroller’s ecosystem. This gem of a device enables running a full version of Windows 10, thereby presenting a powerful Raspberry Pi alternative.
Lastly, we have the Khadas VIM3, a potent contender in the SBC landscape. It is powered by an Amlogic S922X Hexa-core processor, complemented by a Neural Processing Unit (NPU) for AI and machine learning applications. Its M.2 slot for NVMe SSDs, switchable PCIe, and USB 3.0 interfaces elevate it to a higher pedestal of power and versatility.
The arena of SBCs is a pulsating galaxy of endless possibilities. While Raspberry Pi continues to reign supreme in popularity and versatility, the most powerful Raspberry Pi alternatives discussed herein possess unique strengths that can cater to specific requirements and projects.
Whether it is raw power, superior connectivity, or prowess in specialized applications like AI and machine learning, these alternatives represent the frontier of innovation in single-board computers.
Best Cheap Raspberry Pi Alternatives
The Raspberry Pi, a remarkable single-board computer (SBC), has enjoyed a well-deserved spotlight in budget-friendly and high-performance computing. Nonetheless, several other players in SBCs offer immense value at a reduced price point. Let’s delve into these best cheap Raspberry Pi alternatives.
Orange Pi Lite, a compact yet potent SBC, heads our list. Bearing a striking semblance to the Raspberry Pi regarding GPIO pin configuration, it incorporates a Quad-Core Cortex A7 processor. With a virtually unbeatable price point, it is an affordable choice for beginners dipping their toes into the SBC universe.
Another robust contender is the PINE64 Rock64. It furnishes a Rockchip RK3328 Quad-Core ARM Cortex A53 processor, complemented by up to 4GB of LPDDR3 RAM. Notably, it sports a USB 3.0 port, an attractive feature in pricier models. This SBC strikes an impressive balance between cost and performance, making it a splendid Raspberry Pi alternative.
Then, we introduce the NanoPi NEO, an SBC that does not skimp on power despite its low cost. Equipped with a Quad-Core Cortex-A7 processor and up to 512MB DDR3 RAM, it is a formidable contender in budget SBCs. Its minuscule size and the flexibility of power options cement its position in the list of best cheap Raspberry Pi alternatives.
The ODROID-C2 is a different beast altogether. Despite being competitively priced, it packs a punch with its Amlogic ARM Cortex-A53 Quad-core 1.5Ghz processor. Coupled with 2GB DDR3 SDRAM and a Gigabit Ethernet, it embodies both affordability and power, an uncommon combination in the SBC market.
The C.H.I.P is another SBC that deserves a mention. Donning a 1GHz Allwinner R8 Cortex A8 processor with a Mali400 GPU and 512MB of RAM, it is a capable device for various IoT applications. Its built-in WiFi and Bluetooth connectivity provide further value, reinforcing its status as a cheap Raspberry Pi alternative.
The ASUS Tinker Board S is an embodiment of power and affordability. It features a Rockchip RK3288 Quad-Core SOC with 2GB DDR3 RAM and Gigabit LAN. Additionally, it has onboard storage of 16GB eMMC, a feature conspicuously absent in the Raspberry Pi. Its robust community support ensures a smooth transition for Raspberry Pi enthusiasts.
On our list, we also have the Banana Pi M2 Zero. It comes equipped with a Quad-core H2+ processor and 512MB DDR3 SDRAM. Its compact form factor and compatibility with the Raspberry Pi’s GPIO make it an attractive and cost-effective Raspberry Pi alternative.
Lastly, we have the Libre Computer Board AML-S905X-CC (Le Potato). This budget SBC flaunts an Amlogic S905X SoC, 2GB DDR3 SDRAM, and Gigabit Ethernet. Its compatibility with both Linux and Android operating systems makes it versatile and budget-friendly.
Unquestionably, the Raspberry Pi has set a high benchmark in the SBC realm. However, the best cheap Raspberry Pi alternatives we’ve explored above offer substantial competition. Whether you are a hobbyist, a developer, or a tech enthusiast, these affordable SBCs provide an incredible value proposition, marrying affordability with diverse functionality.
This catalog of alternatives ensures that cost never becomes a hurdle in pursuing creativity and innovation in the ever-expanding universe of single-board computers.
📗FAQ’s
What is the best alternative to Raspberry Pi 4?
Regarding alternatives to the Raspberry Pi 4, one standout option is the NVIDIA Jetson Nano.
The Jetson Nano is a powerful single-board computer designed for AI and machine learning applications. It features a quad-core ARM Cortex-A57 CPU and a 128-core NVIDIA Maxwell GPU, providing exceptional performance for AI workloads.
The Jetson Nano also supports various AI frameworks and libraries, making it an ideal choice for developers and enthusiasts working on AI projects.
Is there a Windows equivalent to Raspberry Pi?
Yes, there is a Windows equivalent to the Raspberry Pi called the LattePanda. The LattePanda is a single-board computer that runs on a Windows operating system, providing compatibility with a wide range of Windows applications and software.
It features an Intel Atom quad-core processor, Intel HD graphics, and ample RAM, making it capable of handling various tasks and applications.
The LattePanda is an excellent choice for those who prefer the familiarity and ecosystem of Windows while enjoying the flexibility of a single-board computer.
How are Raspberry Pi so cheap?
One of the reasons why Raspberry Pi is so affordable is its foundation’s goal to provide an affordable and accessible computer for educational purposes.
The Raspberry Pi Foundation focuses on cost optimization by utilizing components and manufacturing techniques that keep production costs low.
The Raspberry Pi’s design also follows a modular approach, allowing users to choose and add peripherals based on their requirements, reducing the overall cost.
By targeting a specific price range and utilizing cost-effective manufacturing methods, the Raspberry Pi Foundation has created an affordable single-board computer.
What is the fastest single-board computer?
The Odroid N2+ is considered one of the fastest single-board computers available. It features a powerful Amlogic S922X chipset with a quad-core Cortex-A73 CPU and a dual-core Cortex-A53 CPU.
The board also includes a Mali-G52 GPU, making it well-suited for multimedia and gaming applications. With its high-performance hardware, the Odroid N2+ offers impressive processing power and can handle resource-intensive tasks and applications.
Do professionals use Raspberry Pi?
Yes, professionals from various fields utilize Raspberry Pi in their work. Its affordability, versatility, and wide range of capabilities make it attractive for robotics, automation, IoT, and software development professionals.
Raspberry Pi’s ability to run Linux-based operating systems and its GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) pins allows professionals to create custom solutions, prototypes, and proofs-of-concept efficiently.
Is Raspberry Pi better than Arduino?
Raspberry Pi and Arduino serve different purposes, so it’s not a matter of being better. Raspberry Pi is a full-fledged single-board computer that runs on various operating systems, running complex software and handling multiple tasks simultaneously.
On the other hand, Arduino is a microcontroller platform designed for physical computing and controlling simple electronics.
Arduino is best suited for projects that require precise control and real-time interaction with sensors and actuators. The choice between Raspberry Pi and Arduino depends on the specific requirements of the project at hand.
Can Raspberry Pi run Android?
Yes, Raspberry Pi can run Android. There are versions of the Android operating system specifically optimized for Raspberry Pi, such as the official Android Things OS or third-party solutions like LineageOS.
These versions provide compatibility with Raspberry Pi hardware and allow users to run Android applications on their Raspberry Pi devices.
What is Banana Pi?
Banana Pi is another single-board computer that offers a Raspberry Pi alternative. It is designed to be compatible with Raspberry Pi’s form factor and pin layout, making it a suitable option for those familiar with Raspberry Pi.
Banana Pi offers various models with different features and specifications catering to different needs. Like Raspberry Pi, Banana Pi supports different operating systems and offers GPIO pins for hardware interfacing.
Can Raspberry Pi run other OS?
Yes, Raspberry Pi can run a variety of operating systems. The most popular choice is Raspbian, a Linux-based operating system optimized for Raspberry Pi.
However, several other operating systems are available, such as Ubuntu, Arch Linux, Fedora, and even Windows 10 IoT Core.
These operating systems provide different functionalities and compatibility, allowing users to tailor their Raspberry Pi experience based on their specific requirements.
What is Raspberry Pi’s disadvantage?
While Raspberry Pi is a versatile and affordable single-board computer, it does have a few limitations. One disadvantage is its relatively limited processing power compared to full-fledged desktop computers.
This can impact performance for resource-intensive applications. Additionally, Raspberry Pi’s built-in storage is an SD card, which may be slower than traditional hard drives or solid-state drives.
Finally, Raspberry Pi lacks a real-time clock, which means it relies on an internet connection or external hardware for accurate timekeeping.
Which Raspberry Pi is the most powerful?
The Raspberry Pi 4 Model B is the most powerful Raspberry Pi available. It features a quad-core ARM Cortex-A72 CPU, up to 8GB of RAM, and supports dual 4K displays.
The Raspberry Pi 4 Model B significantly improves processing power, multimedia capabilities, and connectivity options compared to its predecessors.
Does NASA use Raspberry Pi?
Yes, NASA has utilized Raspberry Pi for various projects and experiments. The affordability, compactness, and versatility of Raspberry Pi make it suitable for applications in space exploration and research.
NASA has deployed Raspberry Pi devices for monitoring environmental conditions, controlling cameras and sensors, and educational outreach programs.
Do hackers use Raspberry Pi?
Raspberry Pi can be used for both ethical and unethical purposes, and it has been utilized by individuals involved in hacking activities.
However, it is important to note that the Raspberry Pi itself is just a tool, and the intent and actions of the user determine its usage.
Raspberry Pi’s accessibility, small form factor, and GPIO pins make it an attractive platform for various hacking and cybersecurity projects and for learning about computer security and ethical hacking.
What language is Raspberry Pi best for?
Raspberry Pi supports various programming languages, and the choice of language depends on the specific requirements and familiarity of the user. Python is often recommended for beginners due to its simplicity and readability.
It has extensive support within the Raspberry Pi community and is commonly used for tasks such as automation, data analysis, and web development.
However, other languages like C, C++, Java, and JavaScript are compatible with Raspberry Pi and provide different functionalities and advantages.
Should I learn Arduino or Raspberry Pi first?
The choice between learning Arduino or Raspberry Pi first depends on your interests and project goals.
If you are more interested in physical computing, building electronic circuits, and controlling sensors and actuators, learning Arduino might be a good starting point. Arduino’s simplicity and focus on physical computing make it an excellent platform for learning electronics and basic programming concepts.
On the other hand, if you want to explore a broader range of projects, run a full operating system, and work with a more powerful computer, starting with Raspberry Pi may be a better fit.
Can Arduino run Python?
While Arduino is primarily programmed using the Arduino programming language, a subset of C++, it is possible to interface Arduino with Python.
Python can communicate with Arduino boards using libraries such as PySerial or Firmata. This allows you to write Python code to control and interact with Arduino’s sensors, actuators, and other components.
Can Arduino replace Raspberry Pi?
Arduino and Raspberry Pi serve different purposes, so they are not direct replacements.
Arduino excels in physical computing, where precise control and real-time interactions with sensors and actuators are required.
Raspberry Pi, on the other hand, offers the capabilities of a full-fledged computer, including running operating systems, executing complex software, and providing graphical interfaces.
Depending on your project requirements, you may choose Arduino for hardware-focused projects or Raspberry Pi for broader computing applications.
Can I run Netflix on Raspberry Pi?
Running Netflix on Raspberry Pi can be challenging due to the Digital Rights Management (DRM) used by Netflix. Netflix requires DRM support, which is unavailable by default on Raspberry Pi’s operating systems like Raspbian.
However, workarounds and third-party projects, such as Kodi with the Netflix add-on, can enable Netflix streaming on Raspberry Pi. These solutions may require additional configuration and might not provide the same seamless experience as running Netflix on a dedicated streaming device.
How long will a Raspberry Pi last?
The lifespan of a Raspberry Pi depends on various factors, including usage patterns, environmental conditions, and component quality. When properly maintained, a Raspberry Pi board can last for several years.
However, it is important to note that Raspberry Pi’s SD card, which serves as the primary storage, may have limited durability compared to traditional hard or solid-state drives. Regular backups and a proper power supply can help prolong the lifespan of a Raspberry Pi.
Is Raspberry Pi powerful enough for AI?
While Raspberry Pi has limited processing power compared to high-end computers, it can still run AI applications and machine learning models.
Raspberry Pi’s GPU capabilities and optimized frameworks like TensorFlow Lite allow for AI inference tasks on the board. However, more powerful hardware may be required for resource-intensive AI training or complex deep learning models.
Can Banana Pi replace Raspberry Pi?
Banana Pi is an alternative to Raspberry Pi, offering similar capabilities and compatibility with Raspberry Pi’s form factor and GPIO layout.
While Banana Pi can be a suitable replacement for certain projects, it is important to consider compatibility with software, community support, and specific project requirements before deciding.
What is a Rock Pi?
Rock Pi is another single-board computer that provides an alternative to Raspberry Pi. It is based on Rockchip’s system-on-chip (SoC) and offers various models with different specifications.
Rock Pi supports Linux distributions and offers connectivity options like USB, Ethernet, and HDMI, making it suitable for various applications.
What OS does Arduino use?
Arduino uses a programming language and integrated development environment (IDE) specifically designed for the platform.
The Arduino IDE provides a simplified interface for writing, compiling, and uploading code to Arduino boards. It is compatible with various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Is Raspberry Pi Linux-based?
Yes, Raspberry Pi is Linux-based. The official operating system for Raspberry Pi, Raspbian (now known as Raspberry Pi OS), is based on the Debian Linux distribution.
Raspberry Pi OS provides a user-friendly interface and a range of pre-installed software optimized for Raspberry Pi’s hardware.
Can Raspberry Pi run 64-bit OS?
Yes, Raspberry Pi can run a 64-bit operating system. While the earlier models of Raspberry Pi (prior to the Raspberry Pi 3) were limited to 32-bit operating systems, the Raspberry Pi 3 and later models support 32-bit and 64-bit operating systems. Raspberry Pi OS offers a 32-bit version and an experimental 64-bit version.
Why is Raspberry Pi not used in industry?
While Raspberry Pi is widely used in educational, hobbyist, and prototyping contexts, it is not as prevalent in industrial settings.
This is primarily due to limited processing power compared to dedicated industrial computers, concerns about long-term reliability and support, and the need for certifications and industrial-grade components.
Industrial applications often require more robust and specialized hardware to withstand harsh environments and meet specific industry standards.
Is it safe to touch Raspberry Pi?
It is generally safe to touch a Raspberry Pi board when powered off and not connected to any power source. However, handling the board carefully is important to avoid damaging any sensitive components.
When the Raspberry Pi is powered on, there is a risk of electric shock if you touch certain parts, especially if you are unfamiliar with electronics.
Following proper safety precautions, such as avoiding contact with exposed pins or connectors and consulting relevant documentation and guides for safe handling practices is recommended.
Why is Raspberry Pi so slow?
Raspberry Pi’s processing power and performance can be considered relatively modest compared to high-end computers due to its emphasis on affordability and energy efficiency.
While newer models have seen significant performance improvements, Raspberry Pi’s ARM-based processors and limited RAM can impact its overall speed and responsiveness, especially when running resource-intensive tasks or operating system features.
Managing expectations and optimizing software and applications for Raspberry Pi’s hardware limitations is important.
Can Raspberry Pi run for years?
Raspberry Pi boards are designed to be reliable and can run continuously for extended periods.
However, the lifespan of a Raspberry Pi board can depend on various factors, including operating conditions, power supply quality, and usage patterns.
Regular maintenance, proper cooling, and reliable power sources can help ensure the longevity of a Raspberry Pi board.
Is Raspberry Pi faster than a phone?
Raspberry Pi’s processing power can vary depending on the model, but high-end smartphones generally tend to have more powerful processors and better performance than Raspberry Pi boards.
Smartphones are designed to handle various tasks and applications efficiently, while Raspberry Pi boards prioritize affordability, versatility, and power efficiency.
However, considering its price point, Raspberry Pi can still provide sufficient performance for many projects and applications.
Conclusion
Exploring Raspberry Pi alternatives doesn’t mean you’re leaving behind a trusted tool; rather, you’re expanding your horizon, ready to embrace other potential game-changers.
The alternatives we’ve explored in this guide provide various choices, each with unique strengths and capabilities to cater to your diverse project needs.
Whether you seek superior processing power, enhanced memory capabilities, advanced customization features, or perhaps an all-rounder, these Raspberry Pi alternatives stand tall as competent competitors.
Remember, choosing the right device depends on your unique project requirements and personal preferences.
Considering these Raspberry Pi alternatives enriches your toolkit and paves the way for more innovative and complex projects.
It’s time to step into a broader realm of possibilities and unleash your creativity like never before. After all, the world of DIY computing is about exploring, learning, and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.