Have you ever been in the middle of an important task on your computer, only to be rudely interrupted by a blue screen with the frightening message “Kernel Security Check Failure”?🧐
This error, related to Microsoft Windows, can be a real headache, often leading to lost work and unexpected downtime.
The worst part about the Kernel Security Check Failure is its unpredictability and the potential damage it can cause.
It can happen at any moment, regardless of what you’re doing, and even repeatedly rebooting your computer might not fix the problem.
It’s frustrating, time-consuming, and could potentially risk your saved data. And, in some severe cases, it may even indicate a more serious underlying hardware issue.
But fear not, because help is at hand. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the causes of the Kernel Security Check Failure and provide a step-by-step guide to troubleshoot and resolve this issue.
Armed with this knowledge, you can address the problem confidently, safely, and effectively, putting you back in control of your digital world.
What Is The Kernel Security Check Failure?💁
You’re probably reading this article because you or someone you know has experienced the Kernel security check failure. The blue screen of death signals the error.
The error message comes suddenly and effectively shuts down the computer. This prevents further damage if the error isn’t fixed suddenly.
Some situations in which people have reported experiencing the Kernel security check failure include:
- After waking up from the computer from sleep
- After a RAM upgrade
- While playing a game, and
- While using a particular app.
So what exactly does the kernel security check failure mean? It means one or more files have failed a compatibility or integrity check. Though the error message does not point out what files are defective, your best bet at resolving the problem is by locating those files.
Causes Of The Kernel Security Check Failure
Many factors can lead to kernel security check failure. Some of the most common reasons for the blue screen of death are discussed briefly.
Incompatible drivers
This is the most common cause of kernel security check failure. If you recently upgraded from Windows 8 to 10 or Windows 10 to 11, some drivers may not be compatible with OS. The same also applies if you recently installed or upgraded drivers.
Outdated drivers
If your drivers need an upgrade, it can lead to kernel security check failure.
Corrupted Windows system files
This can also happen during upgrades. Duplicates or invalid files may be created that cause errors.
Memory problems
If you have a small memory size, it can cause the computer to misbehave. There are also problems with having RAM in need of an upgrade. This is also true if any hardware is damaged or improperly fixed.
Damaged or corrupted hard disk
If the hard disk is not fixed properly or is damaged, it can lead to serious problems.
Virus
This is also a common cause of problems with computers. Viruses can also lead to any of the problems on this list.
Security programs and Corrupted drivers
Troubleshooting Kernel Security Check Failure
Now we know what kernel security check failure is and what the major causes of the failure are, we can now dive into solving the problem.
These fixes work if the underlying problem they are meant to address is the cause of the kernel security check failure.
So a solution that involves you changing the hard disk only works of the hard disk is the cause of the kernel failure. With that in mind, let’s dive into the kernel security check failure fixes.
Here is a detailed chart on the common causes and solutions for the Kernel Security Check Failure error:-
| Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
| Corrupted system files | Run the System File Checker tool to repair any corrupted system files. Open Command Prompt as an administrator and run the command sfc /scannow. |
| Faulty hardware | Perform hardware diagnostics to identify any faulty hardware. This may involve running tests on your RAM, hard drive, and other components. |
| Outdated or corrupted drivers | Update or reinstall any outdated or corrupted drivers. You can do this through Device Manager or by downloading the latest drivers from the manufacturer’s website. |
| Malware or viruses | Run a virus scan using your preferred antivirus software. You may need to boot into Safe Mode to perform a thorough scan. |
| Overclocking | If you have overclocked your system, revert to the default clock speed settings. |
| Damaged or corrupted system files | Use the Deployment Image Servicing and Management tool (DISM) to repair any damaged or corrupted system files. Open Command Prompt as an administrator and run the command DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth. |
| Conflicting software | Uninstall any recently installed software or updates that may be conflicting with your system. |
| Insufficient disk space | Ensure that you have enough disk space available on your system drive. You can free up space by deleting unnecessary files or programs. |
| Hardware compatibility issues | Check for hardware compatibility issues, especially if you have recently installed new hardware. Ensure that all hardware components are compatible with your system and that you have installed the necessary drivers. |
| Windows update issues | Check for any Windows update issues, such as failed updates or missing updates. Run the Windows Update Troubleshooter to resolve any issues. |
1. Use System File Checker and Memory Diagnostic
This diagnostic tool helps you find out what specific files are defective and repair the damage. Here is how to go about using the file checker for diagnosis.
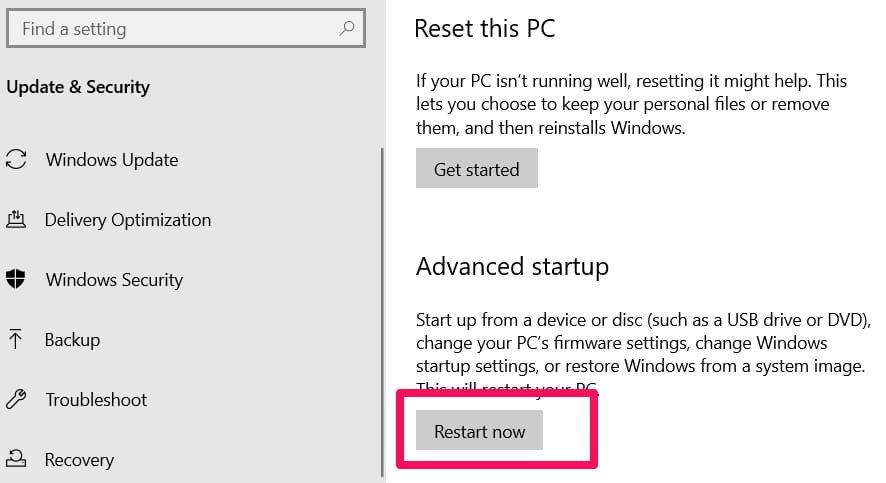
Go to Settings, go to Advanced option, then select Startup settings
Click the restart button on the lower right side of the screen. This will make the OS startup with minimal system requirements
When the computer boots hover the mouse around the upper right side of the window.
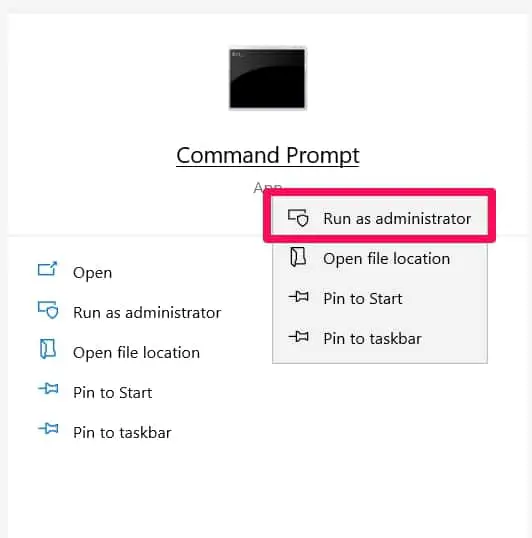
Click the search feature from the menu and type cmd to open the command prompt.
Right-click on the command prompt and select run as administrator.
Type the command: sfc /scannow and press enter.
After the scan, type exit in the command prompt to exit the window. Move the cursor over the right side of the screen again.
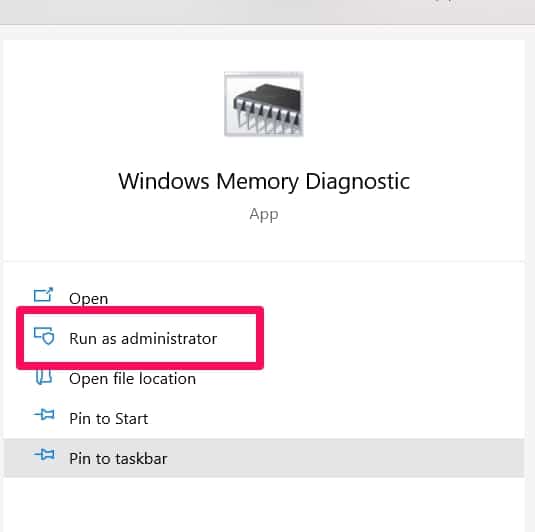
Go to the search feature and find Windows memory diagnostic.
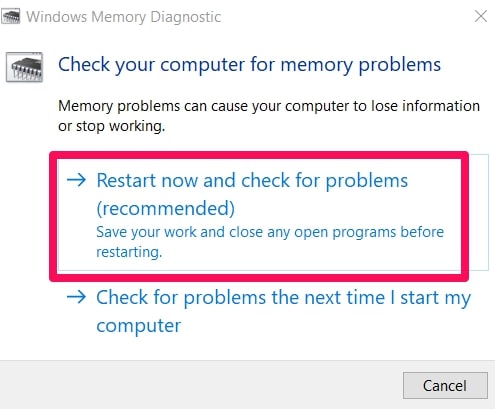
Run as administrator and select Restart now and check for problems.
After a reboot, the OS will check the RAM and display the possible reasons for the error. Once the diagnostics are completed, reboot the PC normally
2. Enable Legacy Advanced Boot Menu
Enabling the advanced boot menu is another fix to the problem. You do this using the command prompt. Follow these steps to enable the legacy advanced boot menu. For this, you’ll need Windows bootable media.
Restart the computer and insert Windows 10 bootable media optical media drive.
Click next on the displayed Windows setup box, then click Repair your computer.
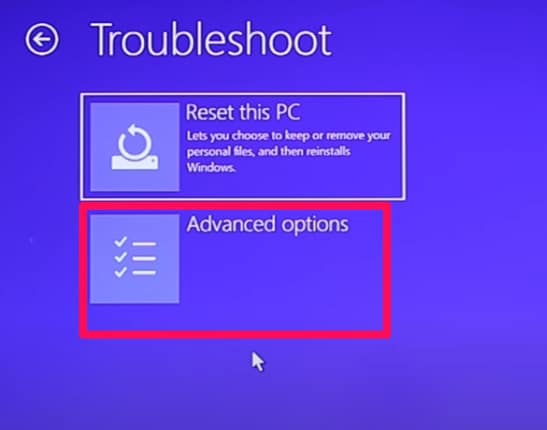
In the Choose an option screen click Troubleshoot, then click Advanced options>>command prompt.
On command prompt type C and press Enter. On C type the command: BCDEDIT/SET {DEFAULT} BOOTMENUPOLICY LEGACY
After the command executes exit the command prompt by typing exit and hitting Enter.
Return to the Choose an option screen, click continue and start the computer normally.
3. Run System Restore
System restore aims to restore the system to a condition it was before it developed any problem. If you had enabled System restore previously, the computer would automatically choose to restore points that can be used whenever you want to restore the system. To try this method follow these steps.
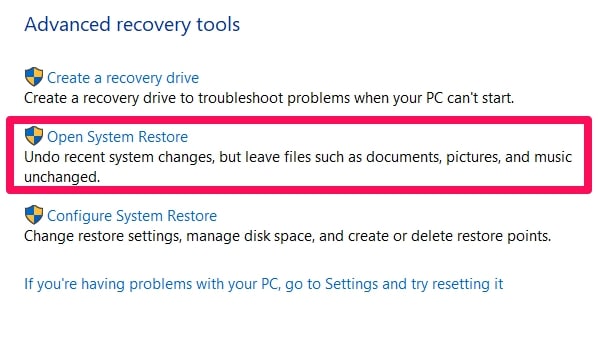
Go to the Control panel and select Recovery. Under Advanced Recovery tools, choose Open System Restore.
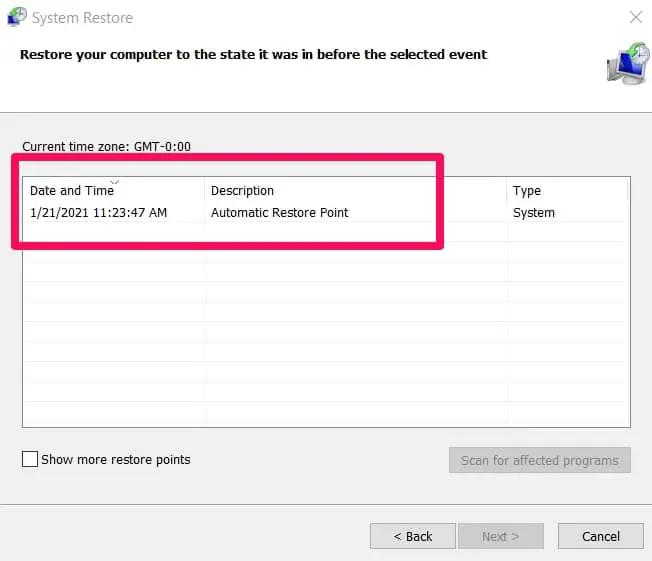
In the Restore system files and settings, click next, then select the restore point you want to use. Scan for affected programs and drivers. Click OK to proceed.
Click Next, then Finish. Wait while system restore takes place. Restart the computer once it is completed.
4. Restart Computer In Safe Mode
Restarting your computer in safe mode is another useful technique for solving the problem of kernel security check failure. It helps you identify the software or apps causing the problem. Follow these steps to restart the computer in safe mode.
Open the Start menu, and select the power button option to look through the different power options.
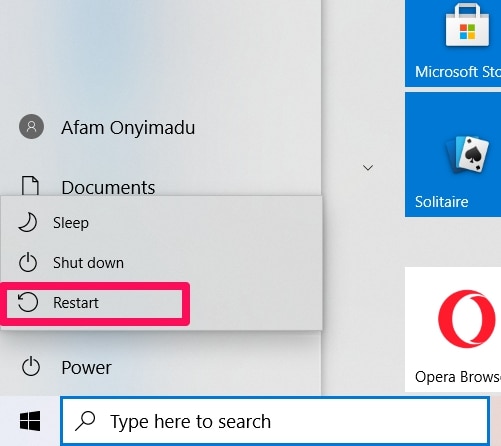
Click the reboot button while pressing the SHIFT key. So, reboot button + SHIFT key simultaneously.
Click Troubleshoot and select Startup Settings. Select the Advanced tab.
Select the Restart option when it appears on the screen. Select Enable safe mode with network.
5. Check Disk For Error
Using the command prompt you can check the hard disk for errors. This helps you identify where exactly the source of the error is. These are the steps involved in checking the disk for errors.
Open the start menu and use the search feature to search for the command prompt.
Right-click on the command prompt and select Run as administrator.
When the command prompt interface opens, type the command: chkdsk C:/f, and press enter.
Note that the letter C should be changed to the letter of the hard drive partition on your computer.
Run the command chkdsk C:/r also.
This is a time-consuming process that can take between 30 minutes and two hours depending on the size of the disk.
Note also that the /f makes sure the file is fixed. If it isn’t added the message will be displayed that the file needs to be fixed without actually fixing it.
/f resolves logical issues with the drive while /r resolves physical issues.
6. Check Memory Slots
Memory problems also cause the kernel security check failure. If the memory slots are not properly fixed or connected, it can lead to this error. Check if the memory slot is properly placed in the socket.
If the slot is damaged, you can replace the memory slot or change the slot in which it is plugged into the motherboard. After checking the memory slots, restart the computer.
7. Check Hard Drive
Check if the hard drive is plugged correctly. If you are sure it is plugged correctly, restart your computer and see if the error persists. If the error persists it is also possible the hard drive needs to be changed.
If you have a spare replace it and see if it solves the problem of kernel security check failure.
8. Update Windows
A Windows update usually solves many problems. During the update, many bugs and defects in the previous version are repaired. Furthermore, software and system applications that have problems are automatically repaired.
Search for Updates on the search bar and follow all the prompts to update Windows.
9. Scan For Virus
Running a virus scan is a good way to find defective files and applications. The antivirus also helps to repair or delete files that are a threat.
10. Delete Software
Deleting software is particularly useful if the problem started after a recent software installation. Instead of a full system reset, you delete the recently installed software.
📗FAQ
How do I fix kernel security check failure?
Kernel security check failure is a common issue in Windows 10 that can be caused by various factors, such as outdated drivers, corrupted system files, or hardware issues.
To fix this issue, you can try updating your device drivers, running a system file checker scan, or running a memory diagnostic test to check for any RAM issues. You may also need to disable any third-party antivirus software temporarily to see if it’s causing the problem.
What is a kernel security check failure?
Kernel security check failure is an error message that appears on a blue screen of death in Windows 10. It usually indicates a problem with the operating system’s kernel, the core component that manages system resources and hardware devices. This error can be caused by various factors, including software conflicts, outdated drivers, or hardware issues.
How to fix Windows 10 stop code kernel Security Check failure?
To fix the Windows 10 stop code kernel Security Check failure, you can try updating your device drivers, running a system file checker scan, or running a memory diagnostic test to check for any RAM issues.
You may also need to temporarily disable any third-party antivirus software to see if it’s causing the problem. If none of these solutions work, you may need to install Windows 10 cleanly.
What is kernel security check failure due to RAM?
RAM issues, such as faulty memory modules or incorrect configurations, can sometimes cause kernel security check failure.
To check if RAM is the cause of the problem, you can run a memory diagnostic test using Windows’ built-in memory diagnostic tool or third-party software. If the test detects any errors, you may need to replace the faulty RAM module.
How to reset the Windows kernel?
To reset the Windows kernel, perform a system restore or reset the Windows installation to its default settings.
Both options will remove any software changes or modifications you’ve made to the system and restore it to its previous state, before resetting the system, back up any important data to avoid losing it during the process.
Is blue screen of death fixable?
Yes, the blue screen of death errors is usually fixable. The causes of these errors can vary widely, but many solutions involve updating or reinstalling device drivers, repairing or replacing faulty hardware components, or performing a system restore or reset.
Some blue screen of death errors can be more difficult to fix than others, but most issues can be resolved with the right tools and resources.
How do I fix kernel mode?
Various factors, including outdated drivers, software conflicts, or hardware issues, can cause kernel mode errors.
To fix kernel mode errors, you can try updating your device drivers, running a system file checker scan, or performing a memory diagnostic test. If none of these solutions work, you may need to perform a clean install of Windows.
What happens if kernel fails?
If the kernel fails, the system will no longer be able to manage system resources or hardware devices, causing the system to crash or become unresponsive.
In most cases, the system will display a blue screen of death error message or freeze up, requiring a hard reset to restart the system.
How do I reboot into Safe Mode?
To reboot into Safe Mode on a Windows 10 device, press and hold the Shift key while clicking the Restart button in the Start menu.
This will bring up the Windows Recovery Environment, where you can select the Troubleshoot option, Advanced options, Startup Settings, and finally, the Restart button. Once the device restarts, you can choose the Safe Mode option from the Startup Settings menu.
How to boot Windows 10 in Safe Mode?
You can use one of several methods to boot Windows 10 in Safe Mode. One way is to press and hold the Shift key while clicking the Restart button in the Start menu, then select the Safe Mode option from the Startup Settings menu.
Another way is to use the System Configuration tool to enable Safe Mode from within Windows. You can also use the Advanced Startup options to boot into Safe Mode, which can be accessed by pressing the F11 key during startup or by using the Windows Recovery Environment.
Can RAM cause kernel power?
RAM issues can sometimes cause kernel power problems in Windows, such as random system shutdowns or restarts. This can be caused by faulty or improperly configured RAM modules, which can cause data corruption or other system errors.
To check if RAM is the cause of the problem, you can run a memory diagnostic test using Windows’ built-in memory diagnostic tool or third-party software.
Is kernel always in RAM?
The kernel is loaded into RAM when the system boots up and remains there as long as the system is running. This is because the kernel needs to be constantly accessible to manage system resources and hardware devices.
However, the kernel code is stored on the hard drive or other storage device and loaded into RAM as needed.
How do I check my RAM health?
To check the health of your RAM, you can use Windows’ built-in memory diagnostic tool or third-party software.
To use the Windows memory diagnostic tool, search for “Windows Memory Diagnostic” in the Start menu, then select the “Restart now and check for problems” option. The tool will run a diagnostic test on your system’s memory and report any errors.
What causes kernel security check failure Windows 10?
Kernel security check failure in Windows 10 can be caused by various factors, including outdated or incompatible drivers, corrupted system files, or hardware issues.
Software conflicts, such as incompatible antivirus software or third-party system optimization tools can also cause it.
How do I force a factory reset on Windows 10?
To force a factory reset on Windows 10, you can use the Windows Recovery Environment to reset the system to its default settings.
To access the Windows Recovery Environment, restart your device and hold down the Shift key while clicking the Restart button in the Start menu. This will bring up the Advanced Startup options, where you can select the Troubleshoot option, then Reset this PC, and finally, the option to remove all files and settings.
Can I reinstall Windows without losing data?
Reinstalling Windows without losing data is possible by using the “Keep my files” option in the Windows Reset process.
This will reinstall Windows while preserving your files and data, but it will remove all installed applications and settings. It’s still recommended to back up your data before reinstalling Windows, as unexpected errors can occur during the process.
Can viruses cause blue screens?
Yes, viruses and other malware can cause blue screen of death errors by corrupting system files or modifying critical system components.
It’s important to keep your antivirus software up to date and regularly scan your system for malware to prevent these issues.
What is the root cause of blue screen of death?
The root cause of blue screen of death errors can vary widely, but they are typically caused by software or hardware issues that prevent the operating system from functioning properly. Common causes include faulty or outdated device drivers, corrupted system files, or hardware failures.
Will factory reset remove blue screen of death?
A factory reset may resolve blue screen of death errors caused by software issues or corrupted system files.
However, if a hardware problem causes the issue, a factory reset will not fix the problem. It’s always recommended to back up your data before performing a factory reset.
How does the kernel mode get triggered?
The kernel mode is triggered when a user-mode application or hardware device makes a system call or interrupt request.
The kernel then switches to kernel mode to perform the necessary operations, such as managing system resources or communicating with hardware devices.
Can a computer work without a kernel?
No, a computer cannot function without a kernel. The kernel is the core component of the operating system that manages system resources and hardware devices; without it, the system would be unable to function.
Can a kernel damage hardware?
In most cases, a kernel cannot damage hardware directly. However, faulty or outdated device drivers or software issues can cause hardware problems, such as overheating or component failures.
It’s important to keep your device drivers up to date and to scan for software issues to prevent hardware problems regularly.
Is kernel power serious?
Kernel power errors in Windows can be serious, as they can cause system crashes or other issues that can result in data loss or other problems. These errors can be caused by various factors, including hardware failures, software conflicts, or power management issues.
Why can’t I boot into Safe Mode?
You may be unable to boot into Safe Mode on a Windows device for several reasons, including hardware failures, driver conflicts, or corrupted system files.
To troubleshoot the issue, you can try running a system file checker scan, disabling unnecessary hardware devices, or performing a clean boot to identify and resolve the problem.
How do I boot into BIOS?
To boot into the BIOS on a Windows device, restart the system and press the key designated to enter the BIOS setup utility.
This key can vary depending on the device, but it’s often F2 or Del. Once you’re in the BIOS setup utility, you can change system settings or configure hardware devices.
How do I start fail safe hard reset mode?
To start the fail safe hard reset mode on a Windows device, restart the system and hold down the F8 key until the Advanced Boot Options menu appears. From there, select the option for “Repair Your Computer,” then Troubleshoot, Advanced options, and finally, the Reset this PC option.
Does Windows 10 have F8 Safe Mode?
Windows 10 does not have the F8 Safe Mode option by default. However, you can still access Safe Mode using the Shift + Restart method or the Advanced Startup options to boot into Safe Mode.
What happens if F8 doesn’t work?
If the F8 key doesn’t work to access Safe Mode, you can use the Shift + Restart method or the Advanced Startup options to boot into Safe Mode.
If none of these methods work, you may need a recovery drive or installation media to access the Windows Recovery Environment and troubleshoot the issue.
How do I fix startup repair in Windows 10?
To fix startup repair in Windows 10, try running a system file checker scan, restoring your system to a previous restore point, or performing a clean boot to identify and resolve software conflicts. If none of these methods work, you may need to perform a clean install of Windows.
Is the kernel in the motherboard?
No, the kernel is not stored on the motherboard. It is loaded into RAM when the system boots up and remains there as long as it runs.
Can RAM cause Windows corruption?
Yes, faulty or improperly configured RAM can cause Windows corruption by causing data corruption or other system errors.
To check if RAM is the cause of the problem, you can run a memory diagnostic test using Windows’ built-in memory diagnostic tool or third-party software.
What happens when RAM loses its power?
When RAM loses power, any stored data is lost, and the system cannot access it until power is restored. This can cause system crashes or other issues like corrupted files or data loss.
It’s important to ensure that your system’s power supply is stable and to check your RAM for any issues to prevent them regularly.
Where is the kernel located?
The kernel code is stored on the hard drive or other storage device and is loaded into RAM when the system boots up. Once it’s loaded into RAM, it remains there as long as the system is running.
Does the BIOS have a kernel?
No, the BIOS does not have a kernel. It is a firmware component that initializes and configures hardware devices during the boot process.
What runs in kernel mode?
The kernel mode runs the operating system’s core components, such as device drivers, system services, and security protocols. It manages system resources and hardware devices and provides a secure environment for applications to run in.
How do I know if my RAM is corrupted?
To check if your RAM is corrupted, you can run a memory diagnostic test using Windows’ built-in memory diagnostic tool or third-party software. The test will scan your system’s memory for errors and report any issues.
How to repair damaged RAM?
If your RAM is damaged, it will need to be replaced. There is no way to repair a damaged RAM module, as it is a physical component that cannot be repaired.
How to check RAM health from BIOS?
To check the health of your RAM from the BIOS, you can usually find a memory diagnostic tool in the BIOS setup utility.
This tool will allow you to perform a memory test to check for errors or issues with your system’s RAM. If you’re unsure how to access the memory diagnostic tool in your BIOS, you can refer to your device’s user manual or manufacturer’s website for instructions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, experiencing a Kernel Security Check Failure can feel like a daunting experience. However, with the understanding and troubleshooting strategies discussed in this article, it doesn’t have to be a cause for panic.
Diagnosing the problem, applying the right solutions, and even taking preventative measures can minimize your computer’s downtime and protect your precious data.
Remember, while this issue can be a nuisance, it often highlights areas of our computer system that need attention.
Seeing it as an opportunity to improve your system’s health rather than a mere setback can change your perspective and help you easily navigate these issues.
Hopefully, this guide has helped demystify the Kernel Security Check Failure and given you the tools to tackle it head-on.
However, if you continue to experience problems, don’t hesitate to consult a professional or contact the Microsoft support community.
With a little patience and the right resources, you can overcome any computer challenge that comes your way.