Many of us rely on the internet for work, play, or socialization purposes. So when something like “our internet is connected but not working” happens to us, it might cause a fair bit of apprehension.
Our fears can even grow further when we see that our connection to the WiFi Router is okay but the internet is still not working.
But the truth is, Wi-Fi is still basically a link between you and the internet connection. It isn’t the internet connection itself. So, sometimes your device may connect to the WiFi and you still won’t be able to access the Internet.
There are a few ways to get your internet connection working properly again and I will be explaining them below in steps that just about anybody can easily follow. It’s important that you don’t skip any step to ensure the fixes work out for you.
Trying To Find Out Where The Issue Is Most Likely Occurring From
Before I dive into explaining how to fix the internet connection, it is important I first explain how to narrow down where the fault lies. This can save you a lot of time, money, and effort.
You will just be able to apply fixes directly to the faulty part and you should get your internet connection up and running in no time.
Finding out where the fault is coming from isn’t an exact science though. But to a reliable extent, it can be done.
Figuring Out Whether The Problem Is From Your Device Or From Your WiFi Router
The first way to rule out your device as the problem is to connect with another device and try to see if you’ll be faced with the “internet is connected but not working” problem.
If you’re connecting using a PC, try using the same connection on a mobile device and see if you’re able to access the internet. If you can, then use fixes that are geared towards PCs.
If you can’t connect too on the mobile device, then you can assume that the problem is coming from the WiFi router side.
This first step, when done properly, will immediately help narrow down the fixes you can apply and it should help you get to the root of the problem faster and solve it.
Simple Steps You Should First Consider Taking To Get Your Internet Connection Working Again
There are other in-depth fixes below but these first few bits are the easy, very effective, and often overlooked fixes.
Some of them might come across as “stupid” but with tech, nothing is ever stupid. So, follow the simple steps first.
Even if the simple steps don’t work, they still help you rule out parts of the hardware that may be faulty and this helps overall in knowing which of the other fixes to use in trying to fix the “internet is connected but not working” problem.
- Try out several websites to ensure that the internet connection is really faulty and the problem isn’t coming from an offline website
- Look through your connection hardware (wires, lights, power cords). Check to see if everything’s in order
- Try restarting your device and then check to see if the problem still persists
- On your PC or mobile device, check to see if you’ve enabled the WiFi connection option. Even if you have, turn it off and turn it back on and then check to see if it works
- Check to see if you’ve not enabled Airplane Mode on your device. If you have, please disable it
- Try re-entering your router name (SSID) and your password. Incorrect details can cause your internet connection to not work
- Make sure your router and device are close to each other. Sometimes distance can play a role in causing internet connection problems
- Ensure you’ve paid your subscription and there’s nothing wrong with your account (like maybe your account is blocked)
Another reason why the above checks need to be done is to rule out false alarms.
I have seen situations where folks went out to get new hardware only to find out that they were entering the wrong details or that the power cord wasn’t connected properly.
So, after going through these checks and you still have “the internet is connected but not working” issues, use the advanced fixes below to fix the issue.
Ways to Fix the “Internet Is Connected but Not Working” Problem
Remember when I explained how to narrow down where the problem is coming from? Well, if you followed my explanation and you did so, here is where you’ll need that knowledge.
I have laid out the fixes for both devices and WiFi routers. Based on your own peculiar situation, use the fixes that pertain to where the problem seems to be coming from.
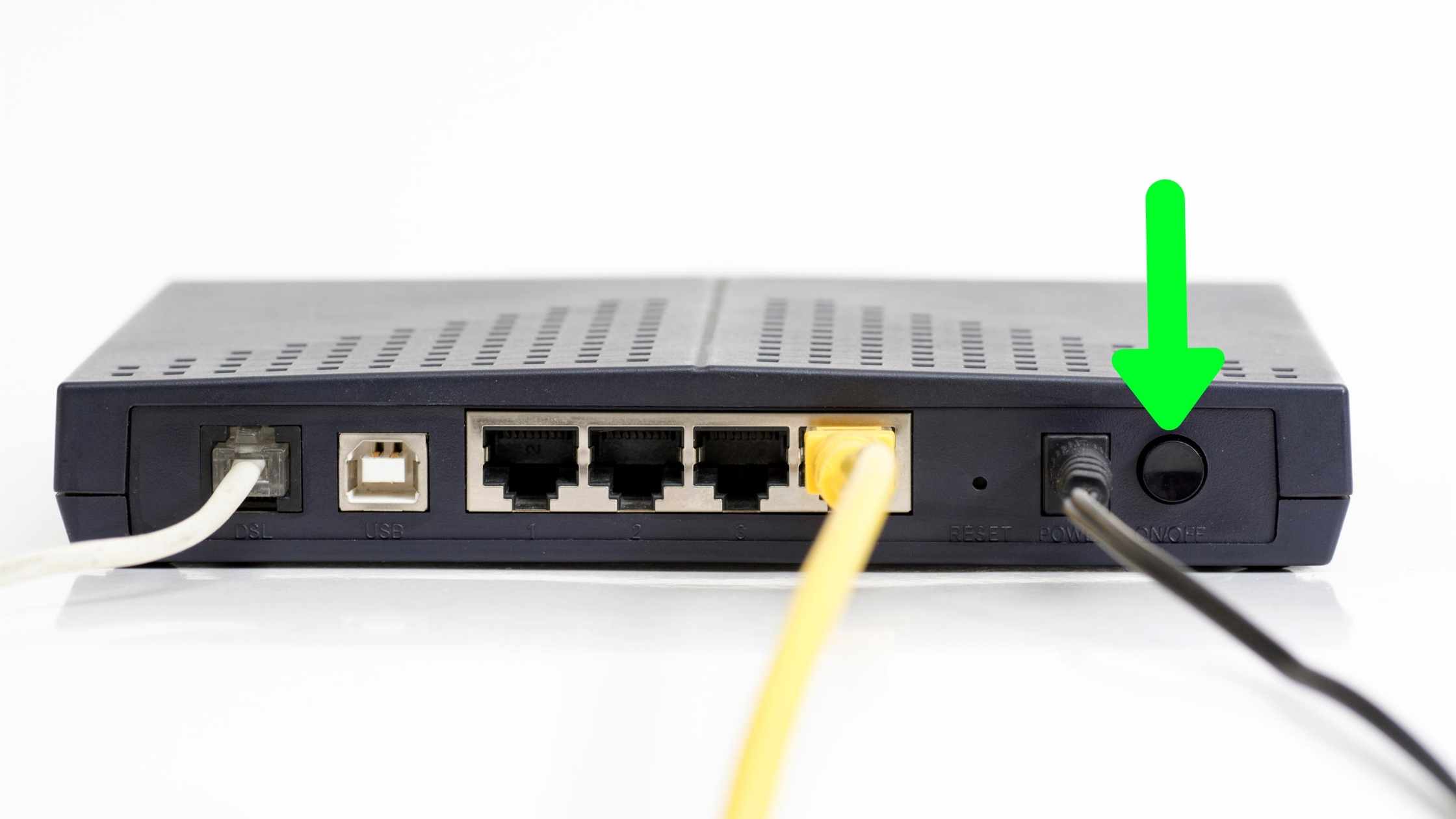
1. Checking Your Router Lights And Restarting Your Router & Modem
Routers have lights that indicate a lot of things depending on the model you’re using. The lights are usually labeled so that will help in trying to find out what’s wrong.
There’s the Wireless light, the Ethernet light that indicates wired connections, the Send/Receive light (this is the light that blinks rapidly), and the Ready/Service/Connect light.
What you’re most likely concerned with is the Ready/Service/Connect light. If the light is blinking or out, then you’ve got a problem with the connection. You might want to consider restarting your modem and router.
Restarting Your Router/Modem
Sometimes there are some bugs in the router’s process causing the internet to fail that can be cleared by a simple reboot.
So, remove the power plug to your router and wait for a few minutes (three to five minutes) and then plug in the power cord back.
Wait for the router to load up, let the lights that indicate readiness to connect come up.
Then check if the “internet is connected but not working” problem has been solved. If it hasn’t been solved, try out another fix below.
2. Using The Windows Network Troubleshooting To Fix The Problem
This here is a fix you want to try out if you’ve already confirmed that the problem is with your device (using the steps I already outlined above).
If the problem is only with your device (PC), you might want to troubleshoot to solve the issue that’s probably in your network settings.
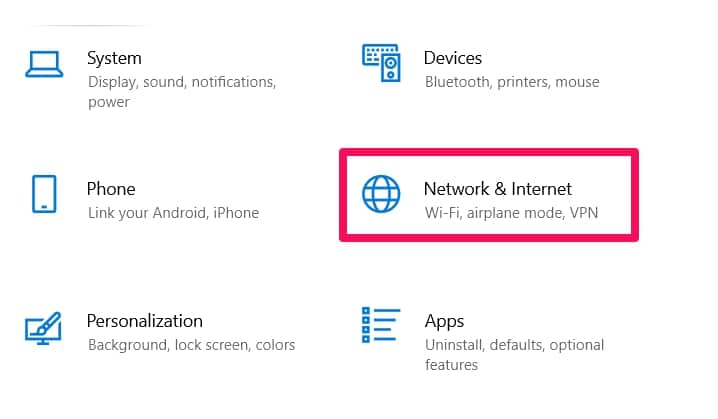
Navigate to Settings (Windows + I).
Then find and click on Network & Internet in the Settings menu.
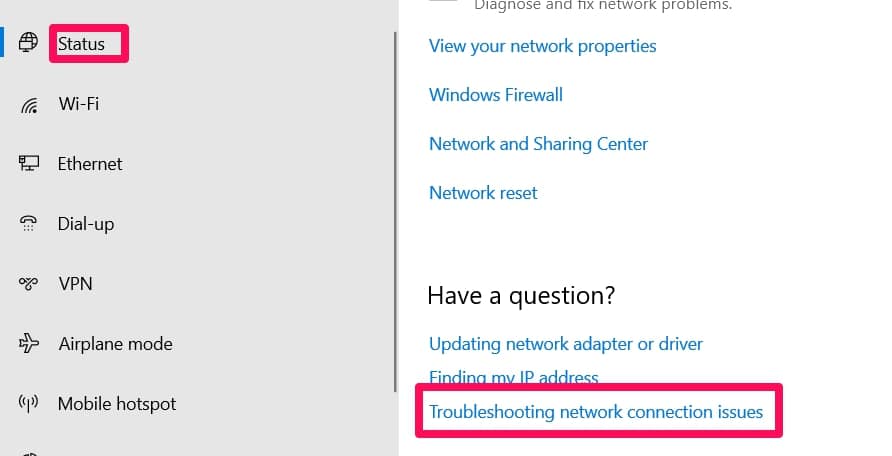
On the left-hand side of your screen, you’ll find a Status option in a pane. Click on it.
In the menu that appears, click on Network Troubleshooter.
Here, you’ll be given several options to troubleshoot. You’ll be asked what specific network connection problems you’ve been having.
If you’ve followed the advice about narrowing down the causes, you will be able to use the troubleshooting option that most likely resolves your issue.
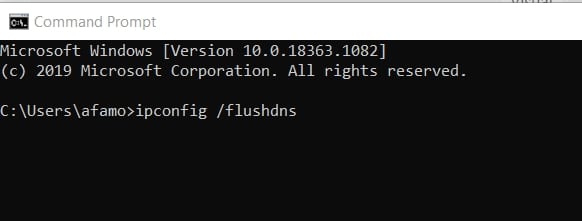
If that doesn’t fix the problem, type cmd into the Windows search box and press Enter to launch the Command Prompt window. Type the following commands, pressing Enter after each one:
netsh winsock reset
ipconfig /release
netsh int ip reset
ipconfig /renew
ipconfig /flushdns
3. Try Using An Ethernet Cable If WiFi Isn’t Working
This fix is a short-term fix and it also helps in figuring out where the problem lies. There are a few things you could find out using this fix.
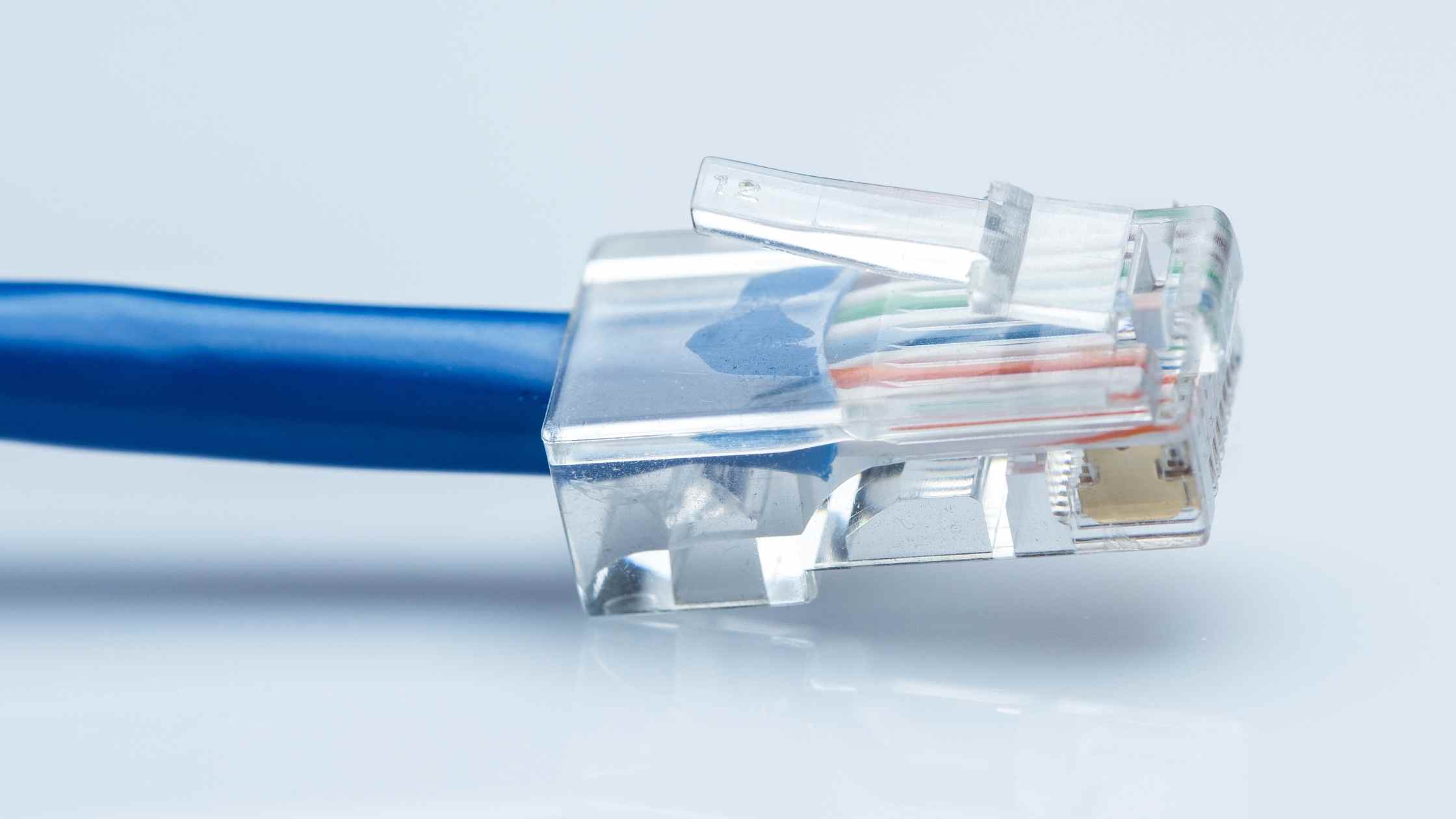

You could find out if the “internet is connected but not working” problem is related to only WiFi issues.
You could also find out if the problem is from a specific device (it’s WiFi settings) or if the problem is affecting all devices.
If the problem is affecting all devices, you’ll know that your router is the problem and you can use any of the fixes in this article that specifically targets routers.
The plus in using this fix is if the Ethernet cable option works out, you now at least have your internet connection working back albeit wired. You can use this option until you figure out what’s wrong with the WiFi part and how to fix it.
4. Disabling Your Security Software
Sometimes Antivirus software can conflict with system processes and this can cause problems for your system.
This is a fix geared towards the fact that you’re sure the problem is with your device.
All you have to do is disable the antivirus software and then check to see if it helps restore the connection.
If it does, then remove that software and find a much more compatible security option.
5. Updating Your Wireless Drivers (And Your Network Adapter Driver)
This is also more like the above option. A fix that means the problem is from your device.
Outdated drivers can cause all sorts of problems, so it is advisable to update them to see if it solved your “internet is connected but not working” problem.
Follow this navigation to update your drivers.
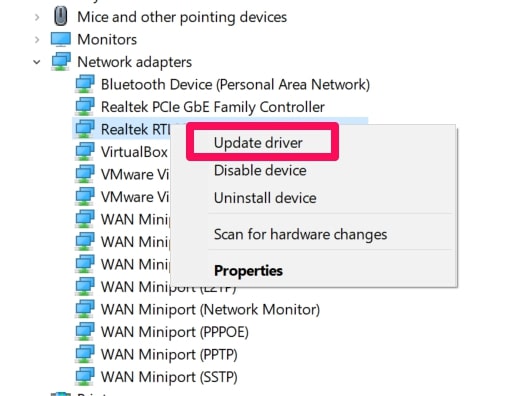
Right-click the Start Menu, then choose Device Manager.
Then right-click on your Wireless Driver, choose the Update Driver option.
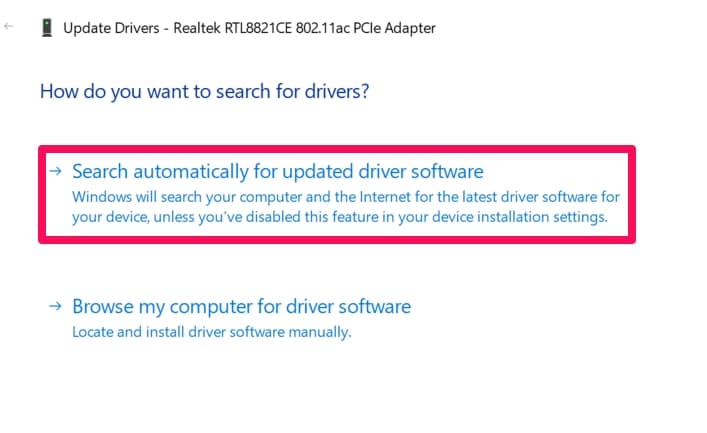
Choose the preferred way of searching for updates (automatically or browse your computer for the software needed) and update the driver.
When the update process is completed, check to see if the internet connection problem is still there.
6. Problem With Your Router’s DNS (Domain Name System)
The DNS server plays a huge role in accessing websites because it transforms the website name you inputted into your search box into IP addresses that the system can understand and search for.
It can also improve browsing time by making sure that information about sites you visit often is stored and used to speed up the loading times when you revisit the sites.
But there are problems that can occur with your DNS server. There are two you should look into.
- Problems With Your DNS Cache
- Problems With The Router’s Preassigned DNS Server
Overview On The DNS Server Fix For Network Connection Problems
This fix is definitely the most complex or longest to try. So it is important you exhaust all the other options in this article first before you try out this one.
It definitely works, but only if the DNS server is what’s causing the “internet is connected but not working” problem to occur.
Here’s how to solve the problem and get rid of your “internet is connected but not working” issue.
Deleting Your DNS Cache
Because DNS servers save info to make loading times of sites you revisit faster, their cache is really important. But that can also cause problems when there are bugs in the cache.
These bugs may be limiting or blocking the DNS server from carrying out its process. If the DNS server doesn’t work, then there’s no way you’ll be able to access websites.
So, you might have to lose that cache (and the loading times speed for now) to ensure your network connection starts working properly.
To delete your DNS cache, navigate to your Start Menu and type in cmd.
When the search results come back, choose, and run the Command Prompt option.
Input the command below into the Command Prompt and press the Enter key.
ipconfig /flushdns
Remember to press Enter after inputting the command.
Now try out your internet connection to see if it’s working.
6. Changing Your Private DNS To A Much Better/Faster Public DNS
It is now common knowledge that the private DNS servers that our service providers provide us with are quite slower than some free to use public DNS servers out there.
Changing your DNS server is not something that can really hurt your system (it can definitely help it though). If it doesn’t work out, you can always just go back to the private DNS you were using before.
Sometimes the “internet is connected but not working” problem might be occurring because the private DNS server you’re using is down, changing the DNS server and your internet connection should be back to normal working conditions.
You have two options here. You can change your Router’s DNS server which automatically affects all the devices (in a good way) or you can override your Router’s DNS server by inputting a custom DNS server in your device (say PC).
Changing Your Router’s DNS Server
This is the option I’ll suggest folks go for. Especially when the public DNS server you use turns out to be really good and faster than the private DNS servers you were using before.
This way, you can always change the DNS settings in one place that also affects all devices and if you choose to revert to your private DNS server, you can easily do so here too.
To be able to change your Router’s DNS server, you will need to be able to get to your router’s web interface.
There is no set way because of differences in routers. So I’ll just ask folks to google how to access their web interface based on the router manufacturer and model.
Also, add to the search terms how to get to your DNS server settings. The answer will most likely be found on your manufacturer’s website.
When you can access the web interface and you’re in your router’s DNS server settings menu, change the DNS server (it is a bunch of numbers) to other public DNS servers like Google or Cloudflare.
Note Google’s Public DNS server below
- Server1 – 8. 8. 8. 8
- Server2 – 8. 8. 4. 4
You should Google search beforehand the best free public DNS servers you can use and choose one. Google is just an option( a good option though), you don’t have to use it.
Changing Your PC’s DNS Server
I’m working under the assumption that you’re using Windows OS.
You might choose to change only your PC’s DNS server if you’re not totally sold on the whole public DNS server idea.
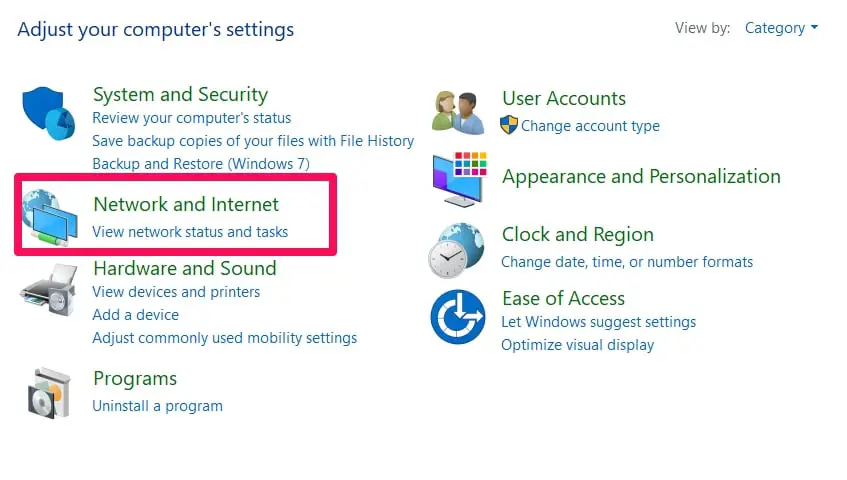
Navigate to your Control Panel.
Then select the Network & Internet option.
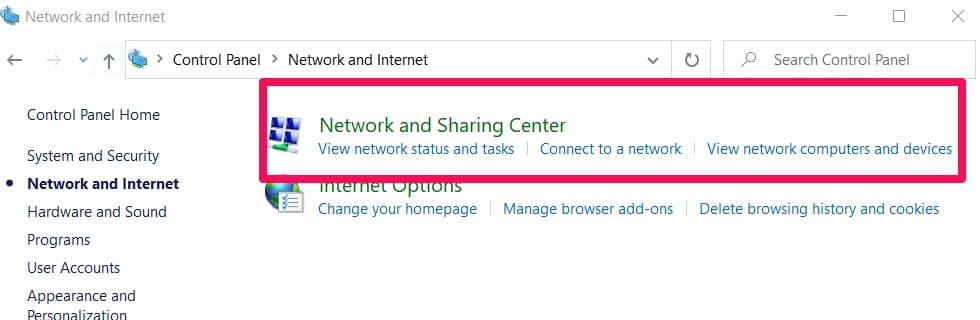
In the Network & Internet menu, search for and click on Network and Sharing Center.
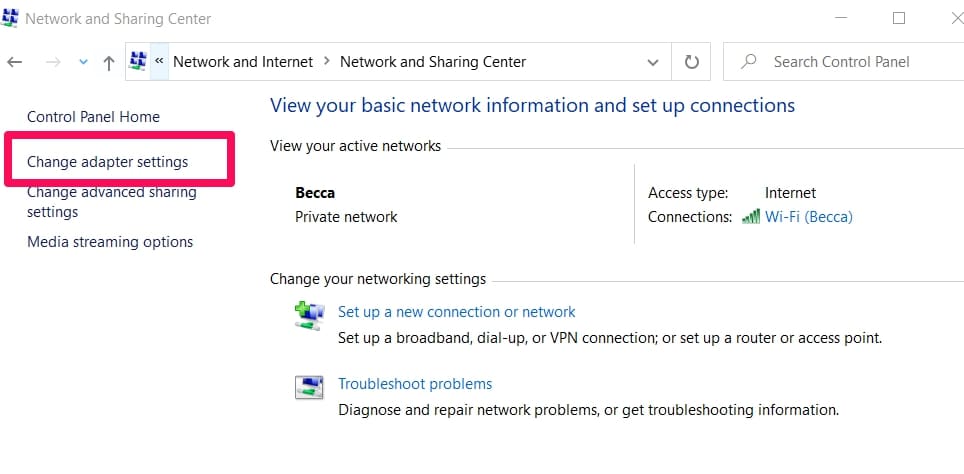
When a menu opens, select the Change Adapter Settings.
You will have to change the DNS for both your WiFi and your Ethernet connection if you want to try it out using both network connections.
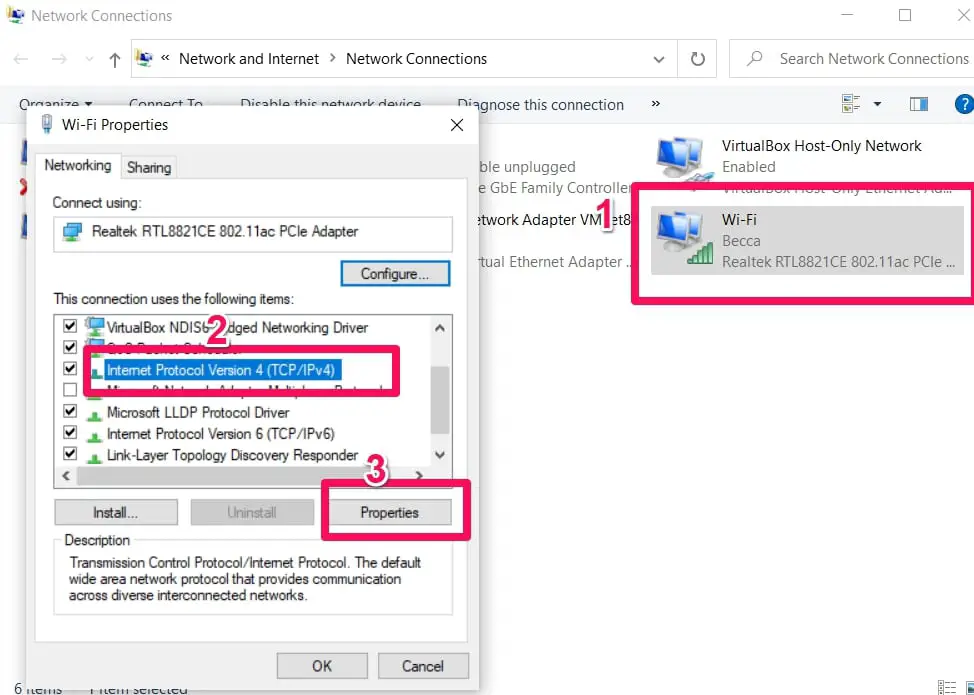
All you need to do is right-click on the network connection you’re trying to configure and select Properties from the pop-up menu that appears.
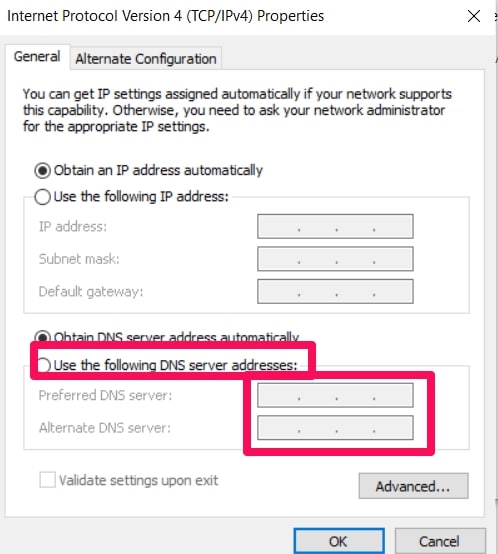
Click on the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCIP/IPv4) option and choose Properties.
Select the Use The Following DNS Server Addresses option and you’ll be given the space to input your preferred DNS server.
Input the new public DNS server you want to try out and then click on OK.
You can also do the same changes for the IPv6 connection too. Just follow the same process above but click on IPv6 instead of IPv4.
Note: Always remember to flush your DNS server cache after changing your DNS server, this helps ensure the new DNS server isn’t using the same cache that the old DNS server used (to avoid the same problems affecting the new server).
7. Calling Your Internet Service Provider Or Router Helpdesk
If any of the steps above didn’t work out, you might want to call for some assistance.
Especially if you’ve ruled out that individual devices aren’t the problem.
The ISP or router manufacturers should be able to find out what the problem is and offer solutions.
Fix All Your WiFi Problems
1. Windows can’t connect to your network
If Windows reports that it can’t connect to your wireless network, the solution is to uninstall the network adapter driver and let Windows reinstall it. This isn’t as risky as it sounds and is relatively easy to do.
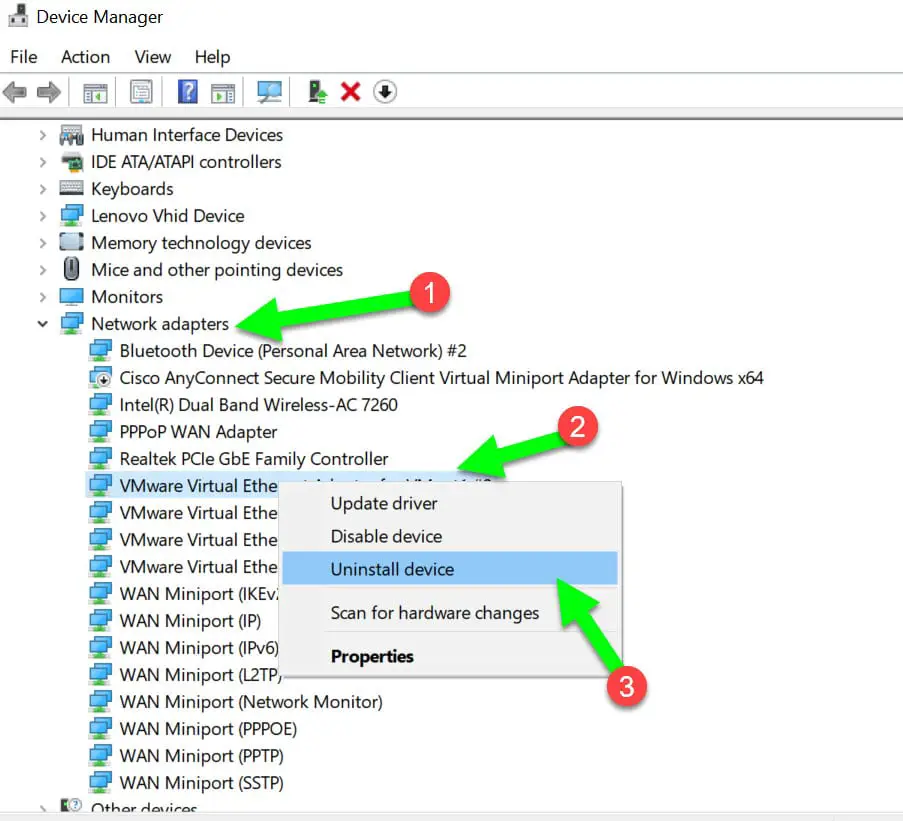
Right-click (not left-click) the Start menu or press Win+X on your keyboard, then select Device Manager. When the Device Manager window opens, expand the Network Adapters section by clicking the little down arrow and find your adapter.
There may be several listed, especially if you use a VPN or have virtualization software such as VirtualBox installed. Right-click the correct adapter and select the ‘Uninstall device’. Confirm that you want to do this if prompted.
Once the driver has been uninstalled, restart your PC. When Windows loads, it will automatically reinstall the driver and that should solve the problem.
If you have to keep doing this, it’s worth seeing if there’s a different driver on the manufacturer’s support site that you can install, or consider buying a new adapter.
2. No wireless networks shown
An apparent absence of networks to connect to may seem like a serious problem, but it’s usually easy to solve. Make sure you’re in range of your network and click the Network icon on the right of your taskbar.
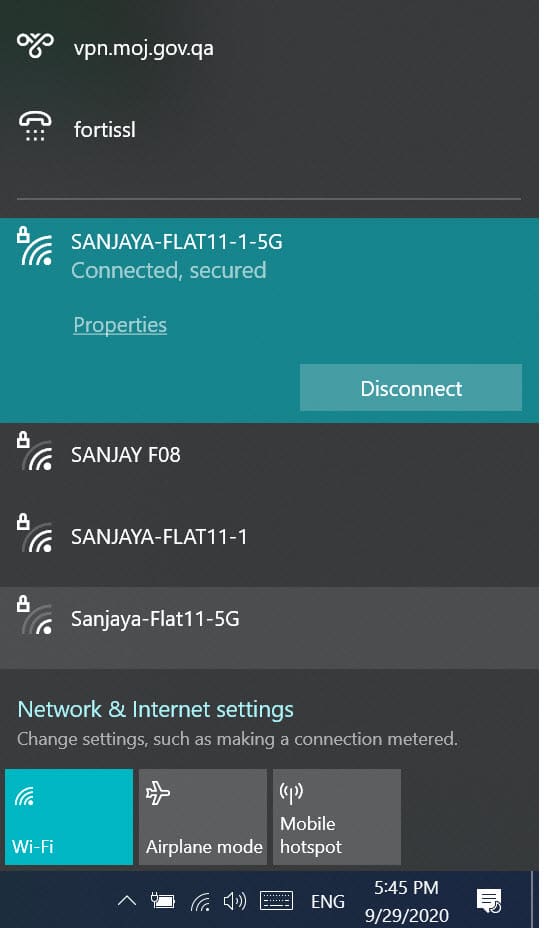
is switched on if no networks appear to be available
If the Wi-Fi quick action in the bottom-left of the Network window is off, click it to turn Wi-Fi back on. Alternatively, if you see your device is in Flight mode, select this option to turn it off. Another approach is to simply restart your router and/or Windows.
In most cases, these steps should be enough to get the missing network to appear. If not, try updating or removing and reinstalling your network adapter as explained previously.
If you desperately need to get online, you can try turning on your phone’s hotspot (usually under Network & Internet settings in Android or iOS) and connect to that.
If none of this works, try changing your wireless adapter’s region. Open Device Manager (see the previous tip, left) and expand the Network Adapters section, then right-click your network adapter and select Properties.
Click the Advanced tab, select ‘Country and Region’, and set your location. If you don’t see ‘Country and Region’ in the list, this option may not be available for your adapter.
3. Wi-Fi is slower than it should be
If your wireless connection seems slow, and speed tests bear this out, try connecting a desktop PC or laptop to your router using an Ethernet cable, then compare the speeds to identify whether the problem is with your router or your ISP.
If there’s a big difference in the speed results, install the excellent free tool WinFi Lite (www.helge-keck.com) to carry out some troubleshooting.
The software’s Channel Utilisation column shows you which channels in your vicinity are the most congested (as well as other interesting information about your neighbors’ Wi-Fi, such as their network names and connection speeds).
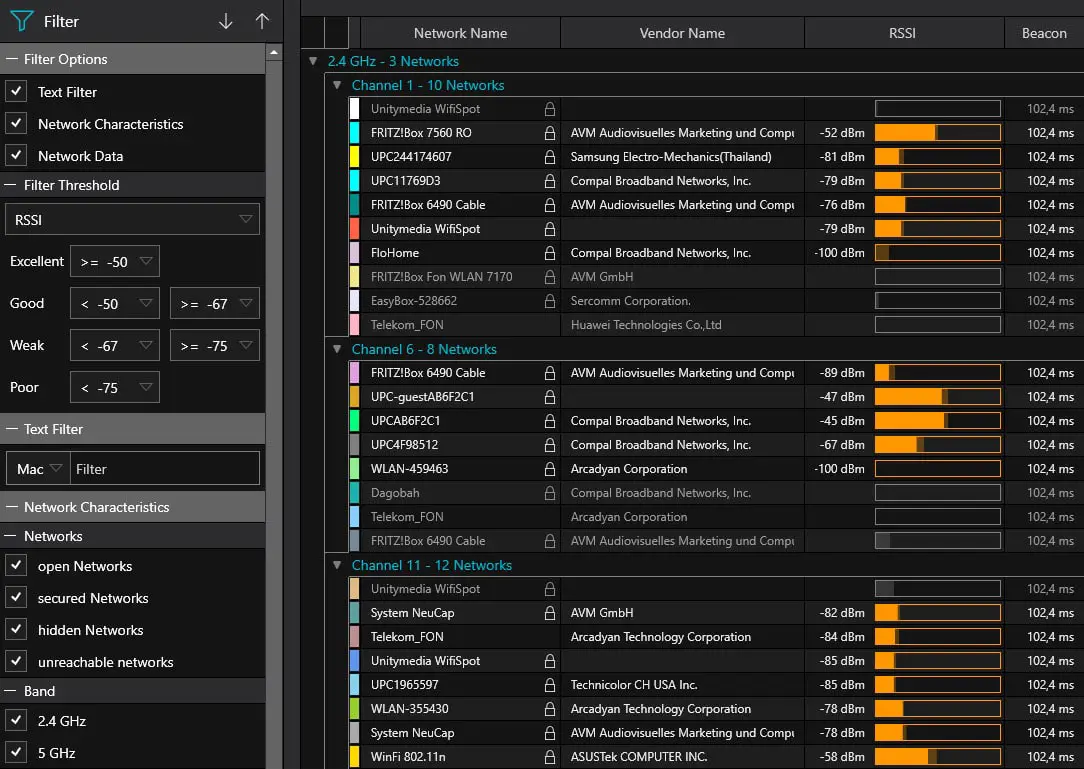
Switching to a less busy option through your router settings could make a big difference to your speed.
You should also check the signal strength at different times of the day, to see if there are any noticeable changes. If there’s no obvious cause, your router may have a problem and need replacing.
4. Wi-Fi connection keeps dropping
If you’re connected to the internet one moment but not the next, the problem could be caused either by your adapter trying to switch to a different network or a problem driver. It could also be a problem with your network adapter’s power-management settings.
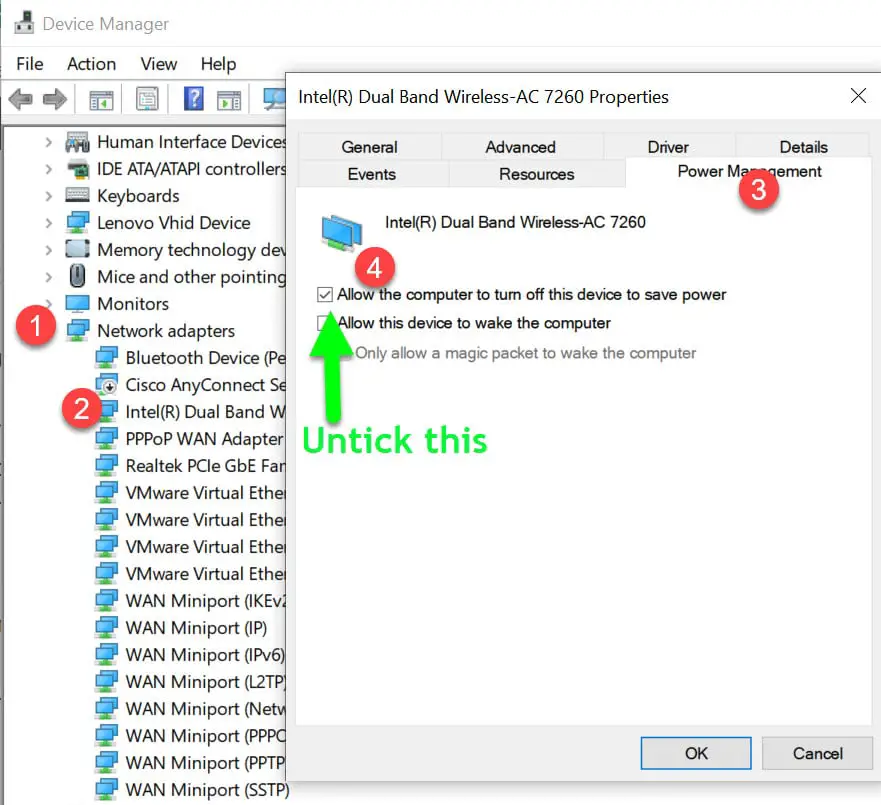
To fix this, open Device Manager, expand the Network Adapters section, right-click your network adapter, select Properties and go into the Power Management tab.
Untick the option to ‘Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power’. That might solve the problem.

5. Your firewall is blocking your connection
A firewall is designed to keep your PC safe from malicious activity by blocking or allowing incoming and outgoing traffic. Windows Security comes with its own firewall, or you can install one from a third party.
The Windows Firewall offers a useful degree of protection, but occasionally it can get overzealous and block all web access.
If that happens, you can fix the problem by typing cmd into the Windows search box, right-clicking the Command Prompt entry, and selecting ‘Run as administrator’. At the command prompt, type:
netsh advfirewall set all profiles state off
Press Enter. This will disable the firewall and you will hopefully be able to get online once more.
When you want to enable the firewall again, repeat the process but type:
netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state on
6. Your antivirus is blocking your Wi-Fi
Antivirus software is designed to keep you safe, but sometimes – as with the firewall – it can inadvertently kill your internet access. If you’re not sure which antivirus software you have running, or you have more than one installed, Windows 10 can reveal the details.
Type Windows Defender Security Centre into the Windows search bar and press Enter. Click the ‘Virus & threat protection’ entry on the left.
This displays all the currently active security software on your PC and lets you open each program so you can disable it and try to get back online.
7. Wi-Fi stopped working after an update
Microsoft rolls out major feature updates for Windows 10 twice a year, along with numerous other smaller updates designed to fix bugs and boost security.
Unfortunately, as we explain in our feature on the opposite page, updates can sometimes introduce problems of their own. If you’re sure a rogue update is responsible for your woes, try removing it or rolling back to a previous version.
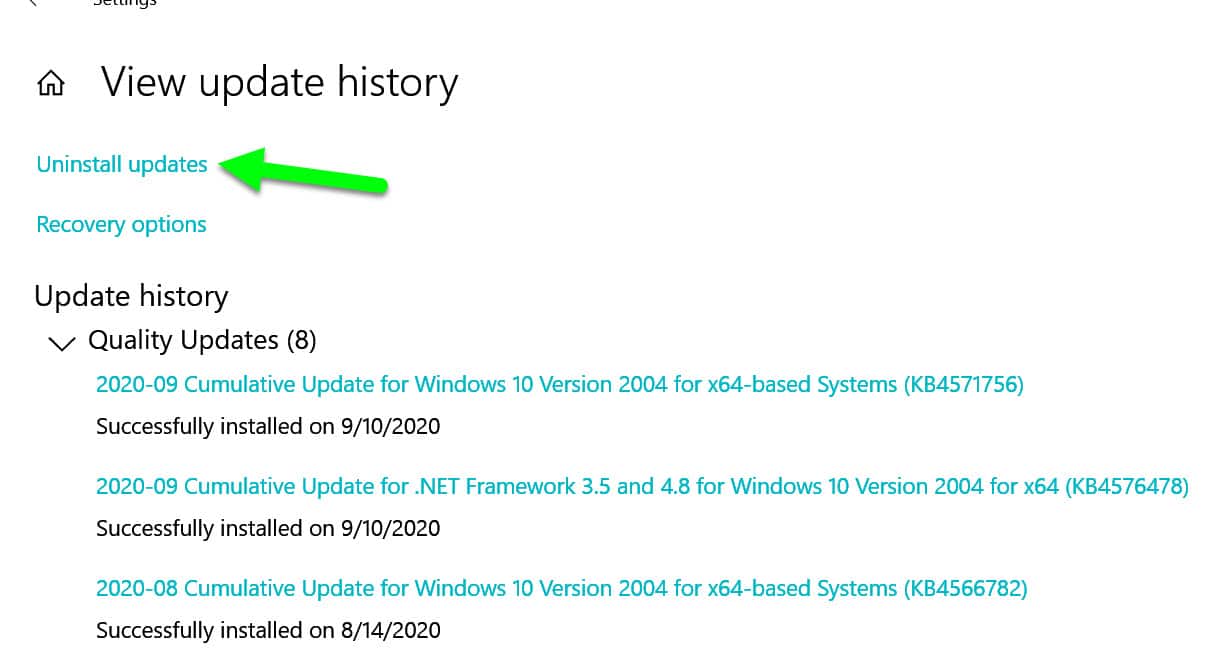
To uninstall the update, open Settings, click ‘Update & security’, then ‘View update history’. This displays all the updates on your PC. Click the ‘Uninstall updates’ link and, in the new window that opens, select the suspected culprit and click Uninstall.
8. Google Wifi can’t connect
Google Wifi is a mesh system that provides blanket home Wi-Fi using a series of nodes. When you move about with a connected device – such as a phone or laptop – from one room to another, it will seamlessly switch wireless points to ensure you have the best connection at all times.
But if one of these nodes stops working, you won’t have the speedy internet coverage you’d normally enjoy.
To fix this problem, open the Google Wifi app on your phone and check to make sure all the Wi-Fi points are active.
Tap the Shortcuts button in the top-right corner and run a Network check This will ensure you’re connected to the internet, compare the connection quality between points, and test the Wi-Fi. If there’s a problem, open Network & General on the Shortcuts screen, tap Wifi Points, and select Restart network.
9. Forgotten Wi-Fi password
New wireless routers come with a default network name (SSID) and password that you use to get connected quickly. For security purposes, you should change this to something unique.
If you forget your login details (or have lost the piece of paper you wrote them down on), there are two options available to you. You could simply reset the router by pressing down on the reset button or by poking a paperclip into the reset hole for 30 seconds or so.
However, this is quite a drastic step to take and you may be able to recover the missing Forgotten Wi-Fi password
New wireless routers come with a default network name (SSID) and password that you use to get connected quickly. For security purposes, you should change this to something unique.
If you forget your login details (or have lost the piece of paper you wrote them down on), there are two options available to you. You could simply reset the router by pressing down on the reset button or by poking a paperclip into the reset hole for 30 seconds or so.
However, this is quite a drastic step to take and you may be able to recover the missing details directly in Windows.
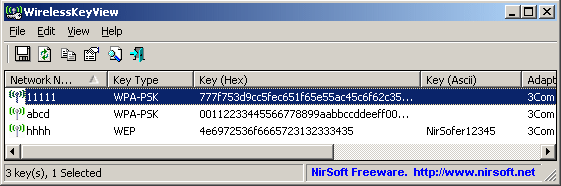
This can be done manually through the Network Internet Settings, but a quicker solution is to use WirelessKeyView from Nirsoft (www.nirsoft.net).
You need to go online to download this in the first place (it’s worth keeping it stored on a USB stick), then run it on the target machine and it will display all the networks stored on that PC.
Details revealed include Network Name, security type, password and adapter name. Right-clicking a password lets you copy it in ASCII (text) format. While you’re using WirelessKeyView, you can delete any networks that are no longer relevant.
10. Your password is incorrect
If you think you have the correct password, but Windows disagrees and displays an error message saying ‘The network security key isn’t correct’,do as suggested and try entering it again, making sure you haven’t accidentally pressed the Caps Lock button.
Wireless passwords are case-sensitive and often use a mix of upper- and lower-case letters and numbers, so make sure you type it correctly and haven’t muddled up any Os and Os (zeros) or lowercase ‘L’s, capital Ts or number 1s.
Conclusion
Most times, the “internet is connected but not working” problem occurs from simple causes that can be solved using the simple fixes or the more complex ones.
Narrowing down where the fault lies is important. Don’t skip that step and go straight to the fixes, you might be wasting your time using fixes that aren’t needed.
Is there any fix that worked for you but isn’t on this list? Please share with everybody using the comments section below. If you also have problems with any of the steps, you can ask for help too.