Every PC user has been there: you open multiple applications, flipping back and forth between them.
You admire the live thumbnails on your taskbar and relish the smooth transitions, but do you ever stop to think about what makes this possible?🤷♂️
You might not realize it, but a hidden hero is at work: the Desktop Window Manager. It’s an integral part of your operating system, yet many users aren’t aware of its existence or importance.
When your computer seems to freeze momentarily, the graphics lag or you get an error message related to your graphical interface.
The frustration is real, and the Desktop Window Manager is often having a hard time. But what can you do if you don’t understand what it is or how it works?
In this comprehensive guide, we will pull back the curtain on the Desktop Window Manager, breaking down its functionalities, its role in your everyday computing, and how to troubleshoot common issues.
By understanding this essential tool, you can significantly enhance your user experience and solve common problems that may have previously left you scratching your head.
Welcome to the unseen world of the Desktop Window Manager.
Understanding Desktop Window Manager
Desktop Window Manager (DWM) is an integral component of the Microsoft Windows operating system that plays a crucial role in managing the visual experience of the desktop environment.
It acts as a window manager and graphical shell, responsible for handling the display and arrangement of windows and providing visual effects and transparency.
DWM separates the graphical user interface (GUI) rendering from the underlying application processes.
It utilizes a layered approach to composition, where each window is rendered independently and combined to form the final display.
This approach enables efficient utilization of system resources and enhances the overall responsiveness and fluidity of the user interface.
One of the key features of DWM is its ability to enable hardware-accelerated rendering. By leveraging the power of the computer’s graphics processing unit (GPU), DWM offloads the window rendering tasks to the GPU, resulting in smoother animations, improved responsiveness, and reduced CPU utilization.
This is particularly beneficial when dealing with resource-intensive applications or simultaneously working with multiple windows.
Another notable aspect of DWM is its support for desktop composition. Instead of relying on individual applications to draw their windows directly on the screen, DWM composes all the window contents into a unified desktop image.
This approach allows for visually appealing effects such as transparency and window animations and enables advanced features like live thumbnail previews and Aero Peek.
DWM also plays a vital role in window management. It provides essential functions such as window resizing, window snapping, and window tiling, allowing users to organize and arrange their windows on the desktop easily.
Additionally, DWM introduces the concept of Virtual Desktops, enabling users to create multiple virtual workspaces and switch between them seamlessly, thereby increasing productivity and reducing clutter.
Furthermore, DWM incorporates various visual effects that enhance the aesthetics of the desktop environment. These effects include glass-like window borders, shadow effects, and smooth window transitions, all contributing to a visually pleasing user experience.
In conclusion, understanding Desktop Window Manager is crucial for comprehending the inner workings of the Windows operating system.
Its role in managing Windows, facilitating hardware-accelerated rendering, supporting desktop composition, and providing various visual effects makes it essential for delivering a seamless and visually appealing user interface.
With efficient resource utilization and advanced window management capabilities, DWM significantly contributes to a productive and enjoyable computing experience.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Desktop Window Manager
Desktop Window Manager (DWM) offers a range of advantages and disadvantages that impact the user experience and system performance.
Understanding these factors can help users make informed decisions regarding utilizing this essential component in the Microsoft Windows operating system.
Advantages of DWM:-
1. Enhanced Visual Experience
DWM provides visually appealing effects like transparency, window animations, and smooth transitions. These features elevate the aesthetics of the desktop environment, making it more engaging and enjoyable for users.
2. Hardware Acceleration
By leveraging GPU resources, DWM offloads window rendering tasks, resulting in improved responsiveness, smoother animations, and reduced CPU load. This efficient utilization of system resources enhances overall system performance.
3. Desktop Composition
DWM’s desktop composition approach allows live thumbnail previews and features like Aero Peek, enabling users to access window content and quickly switch between applications. This enhances multitasking capabilities and improves productivity.
4. Window Management
DWM offers convenient window management features such as resizing, snapping, and tiling.
These functionalities make it easier for users to organize and arrange windows on the desktop, promoting efficient multitasking.
5. Virtual Desktops
DWM introduces the concept of Virtual Desktops, enabling users to create multiple virtual workspaces. This feature allows for better organization, reduced desktop clutter, and improved focus on specific tasks, thereby increasing productivity.
Disadvantages of DWM:-
1 . System Resource Usage
While DWM’s hardware acceleration improves performance, it may consume many system resources, especially GPU memory and processing power.
This can potentially impact the performance of resource-intensive applications or older systems with limited hardware capabilities.
2. Compatibility Issues
Some older applications or graphics drivers may not be fully compatible with DWM, leading to compatibility issues or visual artifacts. This can result in inconsistent or distorted rendering of windows and effects.
3. Increased Power Consumption
DWM’s reliance on GPU resources and constant rendering can increase power consumption, especially on laptops and portable devices. This can reduce battery life and limit the system’s usability when running on battery power.
4. Limited Customization
While DWM offers visual effects, the level of customization available to users is somewhat limited compared to third-party window managers. Users seeking extensive customization options may find DWM’s offerings relatively restricted.
5. Performance Impact on Older Systems
DWM’s resource requirements may impose a noticeable performance impact on older systems with limited hardware capabilities, resulting in slower responsiveness and reduced overall system performance.
In conclusion, Desktop Window Manager (DWM) brings several advantages, such as an enhanced visual experience, hardware acceleration, advanced window management, and virtual desktops.
However, it also presents disadvantages, including increased resource usage, potential compatibility issues, elevated power consumption, limited customization options, and performance impact on older systems.
Weighing these factors allows users to make informed decisions based on their needs and system requirements.
Troubleshooting Common DWM Issues
How To handle high resource usage by DWM
1. Update Graphics Drivers
Keeping your graphics drivers up to date is crucial for optimal DWM performance. Outdated or incompatible graphics drivers can lead to excessive resource usage.
Remember when I explained that the dwm.exe process is responsible for visual processes in your system?
Well, it works with graphics card drivers and other hardware drivers to ensure that visual processes run smoothly.
When drivers become outdated or corrupted by bugs, this can have a negative (high CPU usage) impact on the dwm.exe process due to their close relationship.
What you will need to do is locate updates for your drivers.
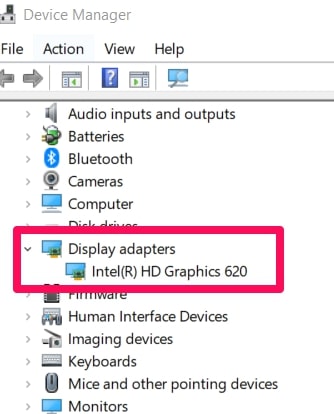
To Update Drivers, Navigate to the Device Manager by searching for it using the search box on the taskbar.
Open the Device Manager when your search results come out. It should be the first option on the list.
When the Device Manager is open, select Display Adapters.
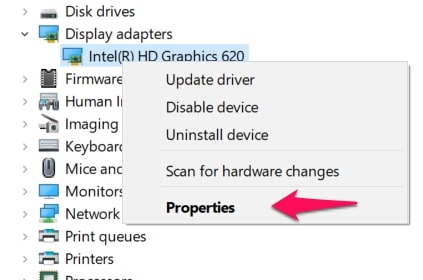
Then right-click on your Graphics card when you find it. Click on Properties in the list of options that will appear.
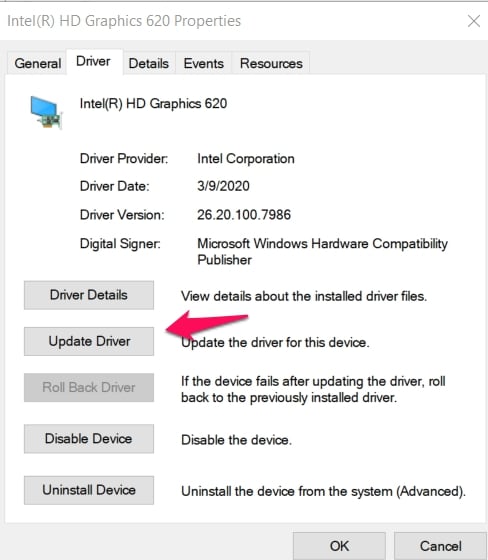
In the Properties menu, go to the Driver tab. This is where you will find the Update Driver option. Click on it.
Then click on Search Automatically For Updated Driver Software.
You can now follow the on-screen instructions to install the updates if any are found. Then afterward, check if the issue is gone.
You can also Visit the website of your graphics card manufacturer and download the latest drivers for your specific hardware model.
2. Changing Your Theme Or Your Wallpaper
This sounds easy. And it doesn’t even sound like a fix. It is something you normally do.
It works because some themes and wallpapers can cause the dwm.exe process to use more resources.
Changing these themes can easily solve your high CPU usage issue.
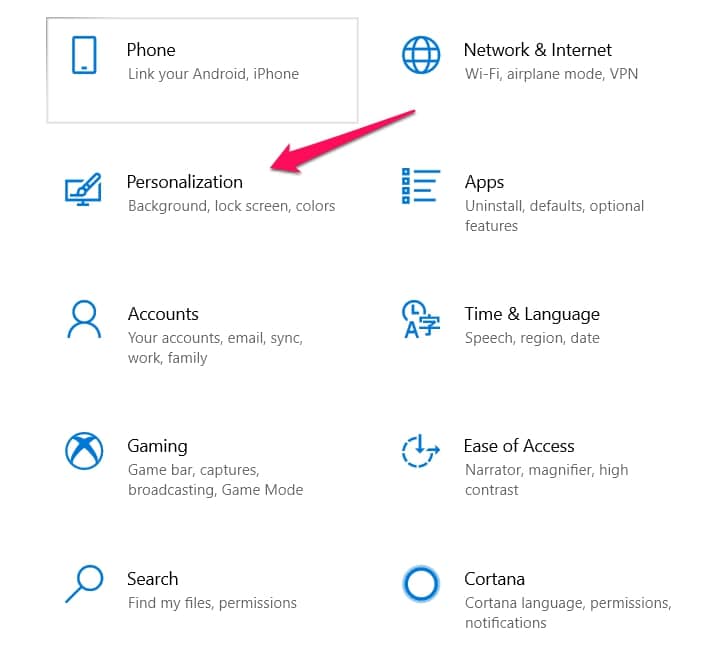
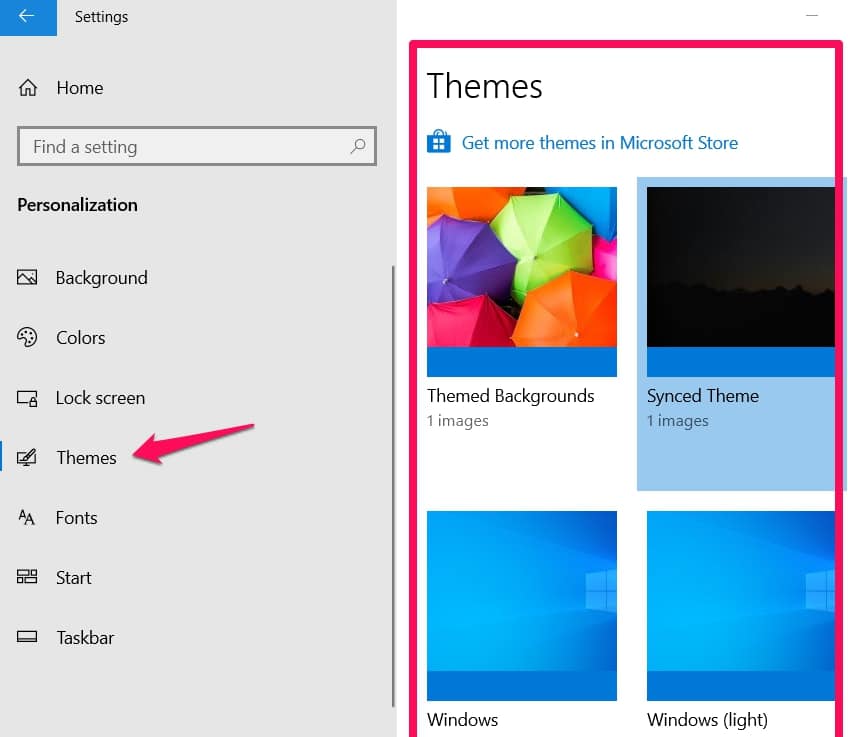
To change your theme, use the shortcut keys ( Windows + I ) to reach your Settings menu.
Then select the Personalization option in the settings menu you just opened.
I usually suggest to folks that they use a theme they have used before, a theme that didn’t cause the high CPU usage when it was used.
Click on Theme> Change theme
If the issue is resolved when you change your theme, you know what the problem is and solved it.
If the issue still continues, follow the other suggested tips below.
3. Removing Screensavers (If Active)
Many users have complained that an active screensaver caused a high CPU usage issue. When they removed the screensaver, the issue went with it.
So, the idea is to disable your screensaver if you have one active.
You should also note that you might not know you have an active screensaver because the default screensaver might show a dark screen.
So, follow the steps below and disable any screensaver found.
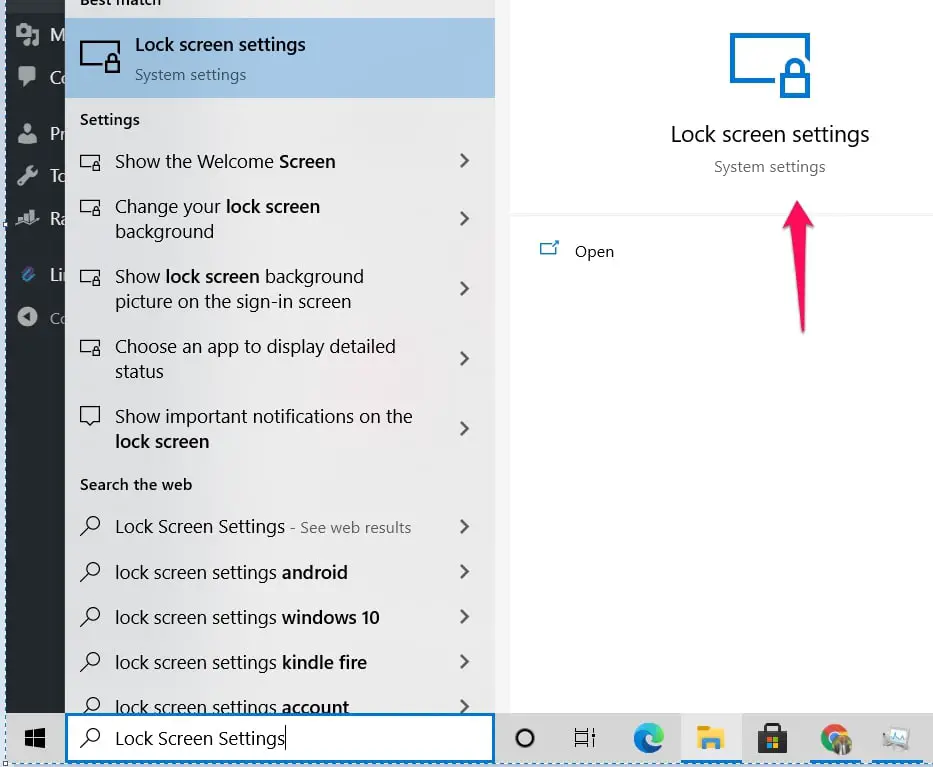
You will first have to launch the search bar. Use the shortcut keys (Windows + S) to do that.
In the bar that appears, input this text – Lock Screen Settings and then search for it.
Choose the Lock Screen Settings option that will appear first on your search results list. This will open the Lock Screen Settings menu.
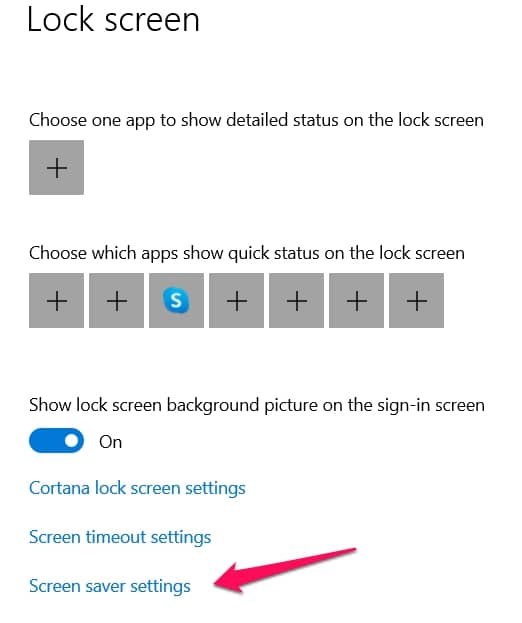
You will find the Screensaver Settings at the bottom of the menu you just opened.
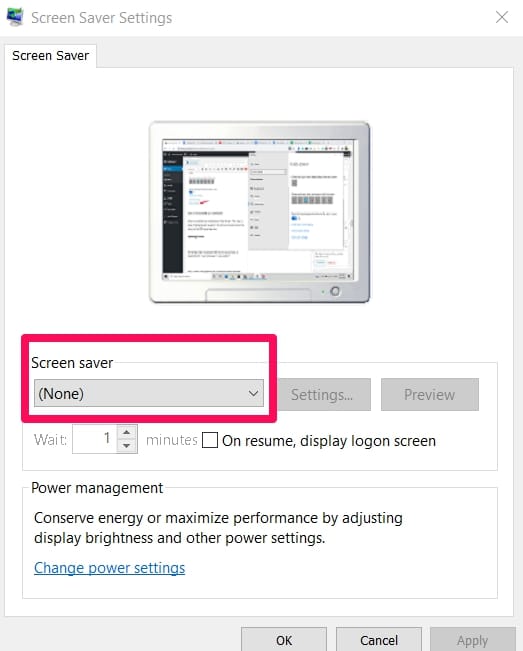
Click on it and disable your screensaver.
When you disable your screensaver, check if the issue is gone. If Screensavers caused it, the dwm.exe process should now use normal CPU resources.
4 . Adjust Visual Effects
DWM offers various visual effects to enhance the desktop experience. However, these effects can contribute to high resource consumption.
Adjusting visual effects settings can help alleviate the strain on system resources.
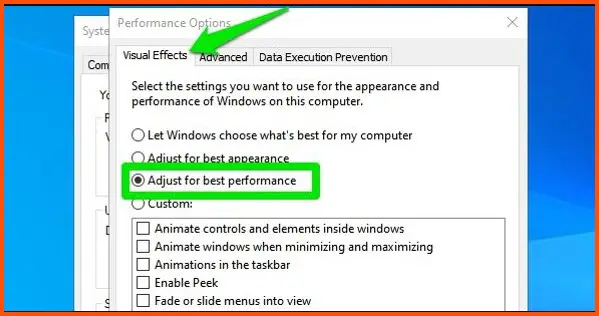
To do this, right-click on “This PC” or “My Computer” and select “Properties.” Then click on “Advanced system settings” and navigate to the “Performance” section.
Choose the “Adjust for best performance” option to disable all visual effects or manually select which effects to disable, balancing visual appeal and resource usage.
5. Reduce Transparency
Transparency effects, while visually pleasing, can consume substantial GPU resources. Reducing transparency can alleviate the resource burden on DWM.
To adjust transparency settings, right-click on the desktop, select “Personalize,” and choose “Colors.” Scroll down and toggle off the “Transparency effects” option.
This adjustment can help improve system responsiveness and reduce GPU load.
6. Limit Window Animations
Window animations, such as minimizing or maximizing effects, can contribute to high resource usage. Disabling or reducing the duration of these animations can improve system performance.
To modify animation settings, access the “Performance Options” menu as described in Step 4. Under the “Visual Effects” tab, uncheck the box for “Animate windows when minimizing and maximizing” to disable these animations.
7. Close Unnecessary Background Applications
Running numerous applications in the background can strain system resources, affecting DWM performance.
To reduce resource usage, close unnecessary applications and processes that are not essential for your current tasks.
Press “Ctrl+Shift+Esc” to open the Task Manager and navigate to the “Processes” or “Details” tab to identify resource-intensive applications. Right-click on the selected processes and choose “End Task” to terminate them.
8. Disable Startup Programs
Certain programs set to launch at startup can contribute to high resource usage by DWM. Disabling unnecessary startup programs can help alleviate the strain on system resources.
To manage startup programs, press “Ctrl+Shift+Esc” to open the Task Manager, navigate to the “Startup” tab, and disable programs you don’t need to run automatically when the system starts.
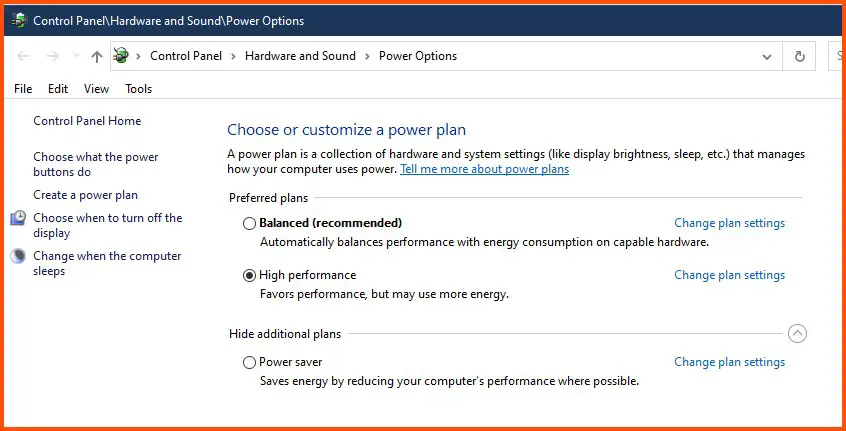
9. Optimize Power Settings
Power settings can influence the performance of DWM, especially on laptops and portable devices. Adjusting power settings to prioritize performance over power saving can help mitigate resource usage.
Access the Power Options by right-clicking on the battery icon in the taskbar and selecting “Power Options.”
Choose a power plan emphasizing performance, such as the “High performance” option.
10. Upgrade Hardware Components
If your system consistently experiences high resource usage by DWM, despite optimizing settings, it may be time to consider upgrading your hardware components.
Adding more RAM or upgrading to a more powerful GPU can significantly improve DWM’s performance. Consult a hardware professional to determine the best upgrade options for your specific system configuration.
11. Use Alternative Window Managers
In situations where high resource usage by DWM persists, exploring alternative window managers may be a viable solution.
Third-party window managers offer different resource utilization profiles and customizable features.
Examples include “Dexpot,” “DisplayFusion,” or “Actual Window Manager.” These applications provide alternative window management options and can help distribute resource usage more efficiently.
12. Seek Professional Assistance
If you have tried the steps above and are still experiencing persistent high resource usage by DWM, it may be beneficial to seek professional assistance.
Reach out to computer technicians or system administrators specializing in Windows operating systems. They can analyze your system, identify underlying issues, and provide tailored solutions for high resource consumption.
In conclusion, handling high resource usage by Desktop Window Manager (DWM) involves a combination of software and hardware optimizations.
Updating graphics drivers, adjusting visual effects, reducing transparency, limiting window animations, closing unnecessary background applications, disabling startup programs, optimizing power settings, upgrading hardware components, considering alternative window managers, and seeking professional assistance are effective strategies to optimize system performance.
By implementing these measures, users can ensure a smoother and more efficient desktop experience while mitigating the strain on system resources.
Dealing with DWM crashes and instability
Desktop Window Manager (DWM) is a crucial Microsoft Windows operating system component that manages window rendering and composition.
However, users may sometimes encounter DWM crashes and instability, leading to a disruptive desktop experience.
1. Update Graphics Drivers
Outdated or incompatible graphics drivers commonly cause DWM crashes and instability. Keeping your graphics drivers up to date is essential for optimal performance.
Visit the website of your graphics card manufacturer and download the latest drivers compatible with your hardware. Regularly updating drivers can resolve compatibility issues, improve stability, and minimize the occurrence of DWM crashes.
2. Check for Windows Updates
Keeping your Windows operating system up to date is crucial for maintaining system stability. Microsoft periodically releases Windows updates that include bug fixes and performance enhancements.
These updates often address known issues related to DWM and can significantly reduce crashes and instability. Ensure you enable automatic updates or manually check for and install the latest updates.
3. Scan for Malware
Malware infections can interfere with the normal operation of DWM, leading to crashes and instability. Perform a thorough system scan using reliable antivirus software to detect and remove any malware or potentially unwanted programs.
Regularly update your antivirus software and perform scheduled scans to keep your system protected and minimize the risk of DWM-related issues.
4. Disable Unnecessary Visual Effects
Certain visual effects DWM provides can strain system resources and contribute to crashes and instability. Disabling unnecessary visual effects can help alleviate these issues.
To adjust visual effects settings, right-click on “This PC” or “My Computer,” select “Properties,” click on “Advanced system settings,” and navigate to the “Performance” section.
Choose the “Adjust for best performance” option to disable all visual effects or manually select specific effects to disable, balancing aesthetics with system stability.
5. Reduce Hardware Overclocking
Overclocking hardware components, such as the CPU or GPU, can lead to increased heat generation and instability, potentially causing DWM crashes.
If you have overclocked your system, consider reverting to the default clock speeds. This helps ensure your hardware operates within recommended specifications and reduces the likelihood of excessive heat or voltage instability.
6. Perform System File Check and Repair
Corrupted or damaged system files can contribute to DWM crashes and instability. To check for and repair system files, open the Command Prompt as an administrator and run the System File Checker (SFC) utility.
Type “sfc /scannow” and press Enter. The utility will scan your system for corrupt files and attempt to repair them automatically.
After the process completes, restart your system and check if the DWM crashes and instability persist.
7. Uninstall Problematic Applications
Certain applications may conflict with DWM, leading to crashes and instability. If you have recently installed or updated any software before experiencing DWM-related issues, consider uninstalling or rolling back those applications.
To uninstall an application, go to “Settings” > “Apps” > “Apps & features,” select the application, and click on “Uninstall.”
Restart your system after uninstalling the problematic application to see if the DWM crashes and instability have been resolved.
8. Use Compatibility Mode for Older Programs
Some older applications may not be fully compatible with DWM, resulting in crashes and instability.
To mitigate these issues, utilize the Compatibility Mode feature. Right-click on the application’s shortcut or executable file, select “Properties,” and navigate to the “Compatibility” tab.
Check the box for “Run this program in compatibility mode for” and choose the appropriate Windows version from the drop-down menu.
Applying compatibility settings can help resolve compatibility-related DWM crashes and instability.
9. Restore System to a Previous Point
If you started experiencing DWM crashes and instability recently, performing a system restore to a previous point can be helpful.
System restore allows you to revert your system settings and configurations to a state where DWM functions properly.
Access the “System Protection” settings by right-clicking on “This PC” or “My Computer,” selecting “Properties,” and clicking on “System Protection.”
Choose the “System Restore” option and follow the instructions to restore your system to a previous point.
10. Seek Technical Support
If you have exhausted all troubleshooting steps and continue to experience persistent DWM crashes and instability, it may be beneficial to seek technical support.
Reach out to Microsoft support or consult with computer technicians who specialize in Windows operating systems. They can provide advanced diagnostics, analyze system logs, and offer tailored solutions for complex DWM-related issues.
In conclusion, handling DWM crashes and instability requires a systematic approach to identifying and resolving underlying causes.
Updating graphics drivers, checking for Windows updates, scanning for malware, disabling unnecessary visual effects, reducing hardware overclocking, performing system file checks, uninstalling problematic applications, using compatibility mode, restoring the system to a previous point, and seeking technical support are effective strategies for dealing with DWM crashes and instability.
By implementing these measures, users can ensure a stable and reliable desktop environment while minimizing disruptions and improving overall system performance.
Steps to Take When DWM Is Not Enabling Certain Graphical Effects
Desktop Window Manager (DWM) is a fundamental component of the Microsoft Windows operating system that enables various graphical effects to enhance the visual experience.
However, in certain instances, users may encounter issues where DWM fails to enable specific graphical effects.
1. Check System Requirements
The first step is to verify whether your system meets the minimum requirements for enabling graphical effects.
Ensure your computer has a compatible graphics card supporting the desired effects. Check the official documentation or the manufacturer’s website for the specific requirements of the effects you are attempting to enable.
2. Update Graphics Drivers
Outdated or incompatible graphics drivers can prevent DWM from enabling certain graphical effects.
To address this, visit the website of your graphics card manufacturer and download the latest drivers for your hardware model. Updating the drivers ensures compatibility and can resolve issues that hinder DWM from enabling the desired effects.
3. Verify DWM Compatibility
Some graphical effects may require specific versions of Windows or specific editions of the operating system.
Verify whether the effects you are trying to enable are compatible with your version of Windows and edition (e.g., Home, Pro, Enterprise). This information can usually be found in the official Windows documentation or on Microsoft’s website.
4. Adjust Visual Effects Settings
If DWM is not enabling certain graphical effects, it is worth checking the visual effects settings on your system.
Right-click on “This PC” or “My Computer,” select “Properties,” click on “Advanced system settings,” and navigate to the “Performance” section.
Choose either the “Adjust for best performance” option to enable all visual effects or manually select the specific effects you want to enable. Ensure that the desired effects are selected, and click “Apply” to save the changes.
5. Enable Transparency Effects
Certain graphical effects, such as transparency, may require additional configuration to be enabled.
Right-click on the desktop, select “Personalize,” and choose “Colors.” Scroll down to find the option for transparency effects and ensure it is toggled on.
Enabling transparency can unlock various graphical effects that rely on this feature.
6. Restart Desktop Window Manager
Restarting the DWM process can sometimes resolve issues with certain graphical effects not being enabled.
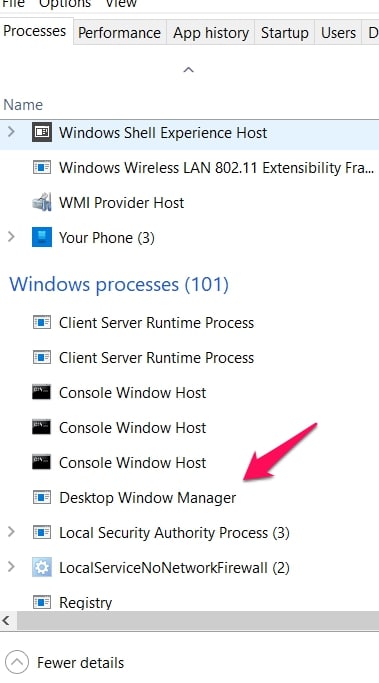
To restart DWM, open the Task Manager by pressing “Ctrl+Shift+Esc.” Navigate to the “Processes” or “Details” tab, locate the dwm.exe process, right-click on it, and select “End Task” or “End Process.”
Afterward, click “File” in the Task Manager menu and choose “Run new task.” Type “dwm” in the “Open” field and press Enter to start DWM again.
7. Perform System File Check and Repair
Corrupted or missing system files can also prevent DWM from enabling certain graphical effects. To check and repair system files, open the Command Prompt as an administrator and run the System File Checker (SFC) utility.
Type “sfc /scannow” and press Enter. The utility will scan your system for corrupt files and attempt to repair them automatically.
After the process, restart your computer and check if the desired graphical effects are enabled.
8. Use Compatibility Mode
In some cases, certain graphical effects may not be compatible with specific applications or older software.
You can try running the application or software in compatibility mode to overcome this. Right-click on the shortcut or executable file, select “Properties,” and navigate to the “Compatibility” tab.
Check the box for “Run this program in compatibility mode for” and choose a compatible Windows version from the dropdown menu. Apply the changes and launch the application to see if the graphical effects are now enabled.
9. Disable Third-Party Software
Conflicts with third-party software can sometimes interfere with DWM’s ability to enable certain graphical effects. Temporarily disable any third-party software that may interact with DWM, such as window managers or system enhancement tools.
Restart your computer and check if the desired graphical effects function properly. If so, selectively enable the third-party software to identify the specific program causing the conflict.
Tips for Resolving DWM-Related Errors During Gaming or Other Graphic-Intensive Tasks
Follow the below steps apart from the steps mentioned above.
1. Optimize Graphics Settings
Adjusting your graphics settings can help alleviate DWM-related errors. Reduce the graphics quality or adjust individual settings within your game or graphic-intensive application.
Lowering settings such as resolution, anti-aliasing, or texture quality can lessen the strain on DWM and improve stability during demanding tasks.
3. Disable Full-Screen Optimizations
Windows 10 includes Full-Screen Optimizations, which can sometimes interfere with DWM during gaming or graphic-intensive tasks. To disable this feature, right-click on the game’s executable file, select “Properties,” and navigate to the “Compatibility” tab.
Check the “Disable fullscreen optimizations” box and click “Apply.” This can help mitigate DWM-related errors by bypassing potential conflicts.
3. Disable Overclocking
If you have overclocked your graphics card or CPU, it’s worth reverting to the default clock speeds. Overclocking can push components beyond their stability limits and lead to DWM-related errors.
Resetting your hardware to its default clock speeds ensures a stable system during intense gaming or graphic-intensive tasks.
Future of Desktop Window Manager
The Future of Desktop Window Manager (DWM) holds significant promise as the Windows operating system evolves.
DWM has played a vital role in managing the visual experience and window composition, and its future developments aim to enhance user productivity, streamline workflows, and provide a visually stunning desktop environment.
With the advancement of graphics processing technology and the increasing capabilities of modern hardware, the future of DWM will likely focus on leveraging these advancements to deliver even more visually appealing and immersive experiences.
This includes further enhancements to graphical effects, such as real-time ray tracing, global illumination, and advanced shadow rendering.
These improvements will elevate the visual quality of windows, bringing them closer to photorealism and enhancing the overall user experience.
As technology progresses, the future of DWM will also see an increased emphasis on adaptive and intelligent window management.
DWM will likely incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to learn user preferences, automate window placement and sizing, and dynamically adjust the desktop environment based on user habits and workflows. This will allow for a more personalized and efficient desktop experience.
Moreover, the future of DWM will likely include seamless integration with emerging technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR).
DWM will be crucial in rendering and managing virtual environments, providing users with immersive experiences and intuitive interactions.
This integration will blur the boundaries between the physical and virtual worlds, enabling users to seamlessly switch between traditional desktop applications and immersive virtual or augmented experiences.
Another area of development for the future of DWM is multi-platform compatibility. As technology evolves, cross-platform compatibility becomes increasingly important.
DWM may expand its reach beyond the Windows operating system, supporting other platforms like macOS or Linux.
This would allow users to experience the benefits of DWM’s advanced window management and visual effects across different operating systems, creating a consistent and familiar user experience.
Additionally, the future of DWM will likely involve enhanced support for multi-monitor setups and ultra-wide displays.
DWM will adapt to the growing trend of using multiple monitors or high-resolution displays, offering seamless window management, improved multi-tasking capabilities, and optimal screen real estate utilization.
This will empower users to manage their workflow across multiple screens and enhance productivity efficiently.
In conclusion, the future of Desktop Window Manager (DWM) is full of exciting possibilities.
As technology advances, DWM will embrace cutting-edge graphics processing capabilities, introduce adaptive and intelligent window management, integrate with emerging technologies like VR and AR, expand its compatibility across platforms, and improve support for multi-monitor setups.
-These developments will transform the desktop experience, providing users with visually stunning environments, personalized workflows, and enhanced productivity.
The future of DWM holds great potential for a seamless and immersive computing experience.
How to disable desktop window manager on Windows 11
To disable Desktop Window Manager (DWM) on Windows 11, follow these steps:
Step 1:- Open the Task Manager by right-clicking on the taskbar and selecting “Task Manager” from the context menu.
Step 2:- In the Task Manager window, navigate to the “Processes” or “Details” tab.
Step 3:– Look for the process named “dwm.exe” in the list of running processes.
Step 4:- Right-click on “dwm.exe” and select “End task” or “End Process” from the context menu. A warning dialog may appear, informing you about the potential consequences of terminating DWM.
Step 5:– Confirm the termination of DWM by clicking on “End process” or “End now.”
Disabling DWM will result in losing visual effects, transparency, and advanced window management capabilities. It may also affect the stability and functionality of the Windows 11 desktop environment.
Disabling DWM should only be done if you have a specific need or troubleshooting requirement. It is generally recommended to keep DWM enabled to ensure a smooth and visually appealing desktop experience on Windows 11.
📗FAQ’s
Why is my desktop Windows Manager using so much memory?
The Desktop Window Manager (DWM) manages the Windows operating system’s visual effects, transparency, and window composition. However, it is common for users to notice high memory usage by DWM.
This can occur due to various factors, including:
Multiple Open Windows: If numerous applications and windows open simultaneously, DWM needs to allocate memory to handle the rendering and management of each window, resulting in increased memory usage.
Visual Effects and Transparency: DWM utilizes memory resources to support visually appealing effects like transparency, window animations, and live thumbnail previews. Enabling these effects can contribute to higher memory usage.
Graphics-Intensive Applications: Running graphics-intensive applications or games that require a significant amount of video memory can strain DWM, leading to increased memory usage.
To mitigate high memory usage by DWM, you can try reducing the number of open windows, disabling or reducing the intensity of visual effects, and closing unnecessary background applications to free up memory resources.
Why is desktop windows manager using so much CPU?
Excessive CPU usage by the Desktop Window Manager (DWM) can negatively impact system performance.
Several reasons may contribute to high CPU usage by DWM:-
Graphics Drivers: Outdated or incompatible graphics drivers can cause DWM to consume more CPU resources than necessary. Updating your graphics drivers to the latest version can help resolve this issue.
Graphics Intensive Tasks: Performing graphics-intensive tasks like video editing or playing high-resolution videos can strain DWM and increase CPU usage.
Multiple Monitors: Using multiple monitors can require additional processing power from DWM to manage and render content across different screens, resulting in higher CPU usage.
To address high CPU usage by DWM, you can try updating your graphics drivers, closing unnecessary applications or processes, reducing the number of active windows, and optimizing power settings to prioritize performance.
Is it safe to end Desktop Window Manager?
Ending the Desktop Window Manager (DWM) process is not recommended as it is a vital Windows operating system component.
Terminating DWM can result in losing visual effects, transparency, and window management capabilities. It may also lead to system instability and potential crashes.
While DWM’s resource usage can vary depending on your system configuration and the applications you are running, it is designed to optimize resource allocation and ensure a smooth desktop experience.
If you are experiencing issues related to DWM, it is advisable to troubleshoot the specific problem rather than ending the process.
Why is Desktop Window Manager taking 100% of my GPU?
Desktop Window Manager (DWM) utilizing 100% of your GPU can indicate that it struggles to render the graphical effects and window composition.
Some reasons for this high GPU usage include the following:
Graphics Driver Issues: Outdated or incompatible graphics drivers can cause DWM to consume excessive GPU resources. Updating your graphics drivers to the latest version may resolve the issue.
High Display Resolution: Running applications or games at high display resolutions can increase the workload on DWM, resulting in higher GPU usage.
Graphics Intensive Tasks: Performing tasks that require intensive graphics processing, such as rendering 3D models or playing high-definition videos, can cause DWM to utilize a significant portion of the GPU.
To address the issue of DWM taking 100% of your GPU, you can try updating your graphics drivers, reducing the display resolution, closing unnecessary applications, and adjusting the visual effects settings to reduce the strain on DWM.
How do I fix Desktop Window Manager high RAM usage?
Excessive RAM usage by the Desktop Window Manager (DWM) can impact system performance.
To resolve high RAM usage by DWM, you can try the following steps:-
Update Graphics Drivers: Outdated or incompatible graphics drivers can contribute to high RAM usage by DWM. Ensure that you have the latest drivers installed for your graphics card.
Adjust Visual Effects: Reduce or disable visual effects in the Performance Options settings to lessen the strain on DWM. Right-click on “This PC” or “My Computer,” select “Properties,” click on “Advanced system settings,” and navigate to the “Performance” section.
Close Unnecessary Background Applications: Closing unnecessary applications running in the background can free up memory resources and alleviate RAM usage by DWM.
Scan for Malware: Malware infections can affect system processes, including DWM. Perform a thorough scan using reliable antivirus software to detect and remove malicious programs.
By following these steps, you can reduce the RAM usage by DWM and improve overall system performance.
How do I reduce DWM RAM usage?
To reduce the RAM usage of the Desktop Window Manager (DWM), you can try the following measures:
Minimize Visual Effects: Disable or reduce the intensity of visual effects in the Performance Options settings. This can lower the memory requirements of DWM.
Close Unnecessary Applications: Close applications not in use to free up memory resources for DWM. This can help reduce its RAM usage.
Optimize Power Settings: Adjust the power settings to prioritize performance. This can ensure that DWM operates efficiently and minimizes unnecessary memory usage.
Update Graphics Drivers: Outdated or incompatible graphics drivers can contribute to higher RAM usage by DWM. Update your graphics drivers to the latest version to ensure optimal performance.
By implementing these measures, you can effectively reduce the RAM usage of DWM and optimize system memory usage.
How much RAM should DWM use?
The amount of RAM the Desktop Window Manager (DWM) uses can vary depending on several factors, including the number of open windows, active applications, visual effects settings, and system resources.
DWM typically consumes a modest amount of memory, usually ranging from tens to a few hundred megabytes.
It is important to note that the RAM usage of DWM can increase when running graphics-intensive applications or using visual effects like transparency or live thumbnails. However, excessive RAM usage by DWM may indicate underlying issues or conflicts.
Suppose you notice unusually high RAM usage by DWM. In that case, it is recommended to investigate potential causes, such as outdated drivers, incompatible software, or malware infections, and take appropriate steps to resolve them.
Can I uninstall Desktop Window Manager?
The Desktop Window Manager (DWM) is an integral part of the Windows operating system and cannot be uninstalled separately.
It is responsible for managing visual effects, transparency, and window composition, and its removal would significantly impact the functionality and visual experience of the desktop environment.
Attempting to uninstall or disable DWM can lead to system instability, loss of visual effects, and potential crashes.
Therefore, it is not advisable to uninstall or disable DWM as it plays a critical role in providing a smooth and visually appealing desktop experience.
What is the purpose of the window manager?
The window manager is a crucial component of an operating system that controls the appearance, placement, and behavior of windows on the screen.
It manages the windowing system, enabling users to interact with graphical user interfaces (GUI) and ensuring a seamless user experience.
The window manager is responsible for window creation, resizing, moving, minimizing, maximizing, and closing. It also facilitates window decorations, including title bars, borders, and controls.
Furthermore, the window manager may support additional features like virtual desktops, window grouping, and window stacking or tiling.
Overall, the purpose of the window manager is to provide an efficient and intuitive interface for users to interact with applications and manage multiple windows on their computer screen.
Is Desktop Windows Manager legit?
Yes, the Desktop Window Manager (DWM) is a legitimate Windows operating system component.
Microsoft developed and maintained it and manages the visual effects, transparency, and window composition in the Windows desktop environment.
DWM provides various features and capabilities, such as visual effects, live thumbnails, taskbar previews, and window management functionalities.
It ensures a smooth and visually appealing user experience by offloading window rendering tasks to the GPU and optimizing resource allocation.
As an essential part of Windows, DWM is integral to the functioning of the operating system and is considered a legitimate and necessary component.
Is disabling Desktop Window Manager safe?
Disabling the Desktop Window Manager (DWM) is not recommended unless you have a specific need or troubleshooting requirement.
DWM is vital in managing the Windows operating system’s visual experience, window composition, and graphical effects.
Disabling DWM can result in losing visual effects, transparency, and advanced window management capabilities. It may also lead to system instability, impact the functionality of other applications, and potentially cause crashes.
While there may be rare scenarios where disabling DWM is necessary for troubleshooting or compatibility purposes, it is generally advised to keep DWM enabled to ensure a smooth and visually appealing desktop experience.
Conclusion
As we’ve navigated through the integral world of the Desktop Window Manager, it’s clear that this powerful tool has a much greater impact on your computing experience than you may have thought.
From enabling smooth multitasking and visually stunning graphical effects to its crucial role in offscreen rendering and high DPI settings, DWM is the unsung hero of our day-to-day computer interactions.
However, understanding its advantages does not come without recognizing the potential hiccups – system resource usage and compatibility issues – that sometimes lead to user frustration. But with the knowledge you now possess, troubleshooting common DWM issues should be a less daunting task.
As technology advances, so will the capabilities and complexities of the Desktop Window Manager.
By exploring and understanding DWM, you can stay ahead of these changes, adapt to them, and optimize your digital experience.
In conclusion, the Desktop Window Manager is a silent yet essential player in our computing lives.
By understanding it better, we can tackle problems and appreciate the seamless user experience we often take for granted.
Remember, the more you know, the smoother your digital journey becomes.