In an age where data breaches and online identity theft are rampant, two-factor authentication (2FA) has emerged as a vital line of defense. Google Authenticator has been a popular choice.
But the application isn’t without its flaws. Google Authenticator’s lack of backup capabilities, limited cross-platform support, and inability to sync across multiple devices leave many users seeking more robust solutions.
Imagine the frustration of losing access to your accounts simply because you changed or lost your phone. This scenario is quite common, given Google Authenticator’s inability to back up and restore account data.
It’s a considerable inconvenience, particularly in our digital age where we’re always on the go, upgrading devices or sometimes dealing with the unexpected loss of our gadgets. The stress of being locked out, the struggle to regain control over your digital identity – it’s an ordeal you don’t want to face.
Fortunately, there are several robust Google Authenticator alternatives that not only rectify these issues but also provide additional layers of security and convenience.
This article will guide you through the best alternatives, highlighting their key features and benefits. By the end, you’ll be able to choose the most suitable two-factor authentication solution for your needs.
Understanding Google Authenticator
In today’s digital landscape, Google Authenticator is a formidable guardian of our virtual realms, ensuring a secure and robust authentication process.
As a two-factor authentication (2FA) application, Google Authenticator provides an additional defense against unauthorized access, surpassing traditional password-centric systems.
Google Authenticator operates on the principles of Time-Based One-Time Passwords (TOTP). It employs a cryptographic algorithm that continuously generates time-bound, unique codes. These codes, combined with your regular login credentials, fortify your online accounts with an added shield of protection.
The user experience with Google Authenticator is seamless yet invulnerable. A secret key is shared between the service provider and the app upon setup. Subsequently, each code the app generates validates your identity for a brief temporal window.
The synchronization between the service provider and the app is pivotal. The algorithms must be perfectly in sync to prevent authentication failures. Luckily, Google Authenticator employs Hash-based Message Authentication Codes (HMAC) to guarantee synchronization.
Furthermore, the offline nature of Google Authenticator imparts it an edge over SMS-based 2FA. Users can access codes without an internet connection, thwarting potential cyber threats.
To conclude, Understanding Google Authenticator unravels the essence of its robustness. With its adept utilization of cutting-edge cryptographic algorithms and seamless user experience, Google Authenticator remains a trailblazer in safeguarding our digital domains. Embrace this potent tool to bolster your cybersecurity and revel in the peace of mind it bestows.
Best Google Authenticator Alternatives
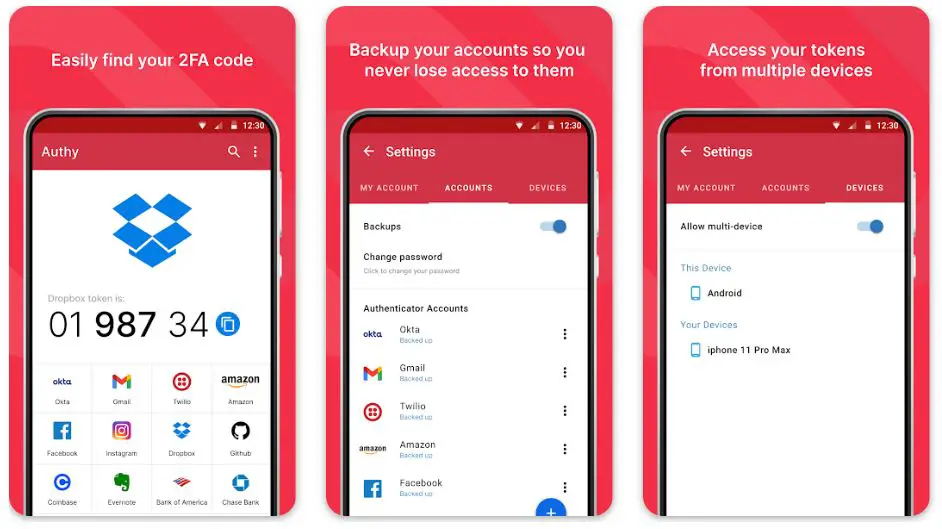
1. Authy
Authy emerges as a formidable alternative to the renowned Google Authenticator in secure digital authentication. As a trusted app designed by Twilio, Authy offers an array of unique features that set it apart from traditional 2FA applications.
Authy provides multi-device synchronization, a feature that distinguishes it from Google Authenticator. Users can seamlessly access their accounts from multiple devices, including smartphones and smartwatches.
This cross-platform functionality ensures a convenient and flexible user experience, granting access to codes regardless of the device used.
Another key advantage of Authy lies in its encrypted cloud backups. This feature enables users to safeguard their authentication tokens securely in the cloud. In contrast, Google Authenticator lacks built-in backup support, which can be a point of concern for users.
Moreover, Authy offers multi-device authentication, which allows users to approve login requests from different devices simultaneously. This adds extra convenience for those who frequently switch between multiple gadgets.
Additionally, Authy’s TOTP refresh mechanism ensures that tokens remain valid even if the device is offline for a significant period. This feature enhances usability, especially when internet connectivity is intermittent.
Lastly, Authy boasts an intuitive and user-friendly interface, making it an excellent choice for tech-savvy users and newcomers to 2FA.
In conclusion, Authy is a robust and feature-rich alternative to Google Authenticator. With its multi-device synchronization, encrypted cloud backups, multi-device authentication, and TOTP refresh mechanism, Authy sets a new standard for seamless and secure digital authentication. Embrace this powerful app to fortify your online presence and experience enhanced peace of mind.
Pros:-
Multi-Device Synchronization: Authy’s ability to sync across multiple devices ensures a seamless user experience, allowing users to access their authentication codes from smartphones and smartwatches.
Encrypted Cloud Backups: The encrypted cloud backup feature offers an added layer of security, enabling users to store their authentication tokens securely in the cloud.
Multi-Device Authentication: Authy allows users to approve login requests from different devices simultaneously, making it convenient for those with multiple gadgets.
TOTP Refresh Mechanism: Authy’s TOTP refresh mechanism ensures that authentication tokens remain valid even when the device is offline, enhancing usability in various scenarios.
Intuitive User Interface: Authy’s user-friendly interface makes it easy for tech-savvy individuals and newcomers to navigate and use the app efficiently.
Cross-Platform Functionality: Authy’s support across different platforms, including Android and iOS devices, grants users the flexibility to choose their preferred devices.
Backup and Restore: Authy allows users to back up and restore their tokens easily, providing peace of mind in case of device loss or upgrade.
Cons:-
Third-Party Dependency: Authy is developed by Twilio, which means users must rely on the company’s servers for authentication, raising concerns about data privacy and security.
Account Registration Required: Authy requires users to create an account, adding an extra step to the setup process compared to Google Authenticator’s straightforward installation.
Centralized Storage: While encrypted, using cloud storage means users must trust Authy’s security measures and the cloud service provider for token protection.
Limited Offline Use: Authy’s TOTP refresh mechanism helps, but the app still requires an internet connection for certain operations, which might be inconvenient in offline scenarios.
Dependency on Mobile Devices: Authy’s multi-device support primarily revolves around mobile devices, potentially limiting access for users who prefer desktop-based 2FA.
In conclusion, Authy presents a compelling set of advantages as a Google Authenticator alternative, such as multi-device synchronization, encrypted cloud backups, and an intuitive user interface.
However, users should consider third-party dependency, centralized storage, and the need for an account during the decision-making process. By carefully evaluating these pros and cons, users can make an informed choice that aligns with their security and usability preferences.
Authy vs Google authenticator:-
Google Authenticator is a straightforward and widely recognized 2FA app developed by Google. It provides time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) for account verification, ensuring a simple and efficient authentication process.
As an independent app, it doesn’t rely on a centralized account, which some users may find appealing for privacy reasons. However, this also means that users are responsible for manually transferring their 2FA tokens to new devices, which can be cumbersome.
On the other hand, Authy offers a more feature-rich experience. One of its primary advantages is multi-device synchronization, allowing users to access their 2FA tokens across multiple devices seamlessly.
This feature is particularly beneficial for those who use smartphones, tablets, or computers interchangeably. Additionally, Authy provides cloud backup for easy token recovery in case of device loss or failure.
Moreover, Authy’s PIN protection and biometric authentication add an extra layer of security to the app, enhancing overall account protection. The app also offers encrypted cloud storage, which may appeal to users who prioritize data security.
While Google Authenticator is a no-frills, straightforward option, Authy’s additional features make it a compelling choice for users seeking enhanced usability and security.
However, the trade-off is that Authy’s cloud-based approach might raise concerns for some users who prioritize decentralization and privacy.
In conclusion, when deciding between Authy and Google Authenticator, it’s essential to consider individual needs and priorities. If simplicity and independence are paramount, Google Authenticator might be the ideal choice.
On the other hand, users who value multi-device synchronization, cloud backup, and additional security features may find Authy to be the better fit. Ultimately, both apps offer strong 2FA capabilities, and the decision comes down to which features align better with each user’s specific requirements.
Download The App From Google Play Store
Download The App From Apple App Store
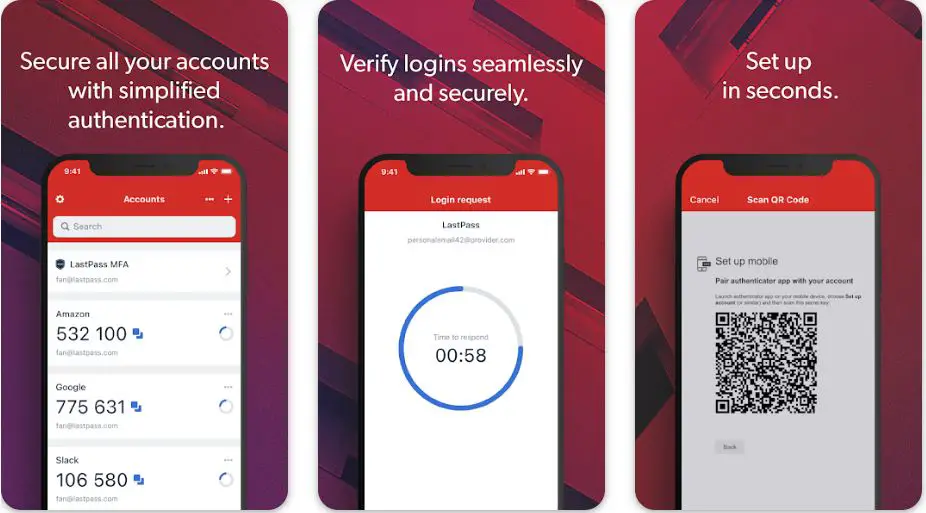
2. LastPass Authenticator
LastPass Authenticator is a powerful Google Authenticator alternative in the dynamic digital security landscape. Developed by LastPass, a renowned name in password management, this app offers many distinctive features that set it apart from traditional authentication methods.
The seamless integration of LastPass Authenticator with the LastPass password manager provides users with a convenient one-stop solution for both password and 2FA management. This unified approach streamlines the authentication process and enhances the overall user experience.
One of the standout features of LastPass Authenticator is its encrypted cloud backup, which ensures that users’ 2FA tokens are securely stored and easily accessible across multiple devices. This added layer of security eliminates the risk of losing critical access during device changes or failures.
LastPass Authenticator offers biometric authentication options to bolster security further, allowing users to employ fingerprint or face recognition technology to protect their 2FA codes. This advanced security feature enhances user confidence and safeguards sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Moreover, the app’s versatility extends to smartphones, tablets, and iPads, offering cross-device support for users seeking flexibility and convenience in accessing their 2FA codes.
Additionally, LastPass Authenticator caters to managing multiple accounts with its multi-token support feature, streamlining the process of securing access to various online services.
With its user-friendly interface and comprehensive feature set, LastPass Authenticator is an excellent Google Authenticator alternative, empowering individuals and organizations to fortify their digital security.
In conclusion, LastPass Authenticator is a robust and user-centric alternative to Google Authenticator. Its seamless integration with LastPass, encrypted cloud backup, biometric authentication, tablet support, and multi-token management make it a compelling choice for enhancing online security.
Pros:-
Seamless Integration: LastPass Authenticator’s integration with the LastPass password manager offers a unified password and 2FA management solution, streamlining the authentication process.
Encrypted Cloud Backup: The app’s encrypted cloud backup ensures secure storage of 2FA tokens, allowing easy access across multiple devices and protection against data loss.
Biometric Authentication: LastPass Authenticator’s biometric options (fingerprint or face recognition) enhance security and provide a convenient way for users to access their 2FA codes.
Tablet and iPad Support: The app’s compatibility with tablets and iPads provides flexibility and convenience for users with multiple devices.
Multi-Token Support: LastPass Authenticator allows users to manage authentication codes for multiple accounts, simplifying securing various online services.
User-Friendly Interface: The app’s intuitive interface makes it easy for tech-savvy individuals and newcomers to navigate and use efficiently.
Trusted Developer: Developed by LastPass, a reputable name in password management, users can rely on the app’s security standards and reputation.
Cons:-
Limited Ecosystem: While LastPass Authenticator supports tablets and iPads, it may not have the extensive platform coverage that other alternatives offer.
Dependency on LastPass: The app’s seamless integration with LastPass may not appeal to users who prefer other password managers.
Limited Offline Use: LastPass Authenticator, like many 2FA apps, requires an internet connection for certain operations, which might be inconvenient in offline scenarios.
Third-Party Dependency: Storing data in the cloud requires users to trust LastPass’ security measures and the cloud service provider for token protection.
Account Registration Required: Setting up an account with LastPass may add an extra step for users compared to more straightforward standalone 2FA apps.
Not Open Source: Some security-conscious users may prefer open-source alternatives, which allow code scrutiny for potential vulnerabilities.
In conclusion, LastPass Authenticator offers compelling advantages, including seamless integration, encrypted cloud backup, biometric authentication, and multi-token support.
However, users should consider factors like limited platform support, third-party dependency, and account registration while choosing their ideal 2FA app. By carefully evaluating these pros and cons, users can make informed decisions that align with their security and usability preferences.
Download The App From Google Play Store
Download The App From Apple App Store
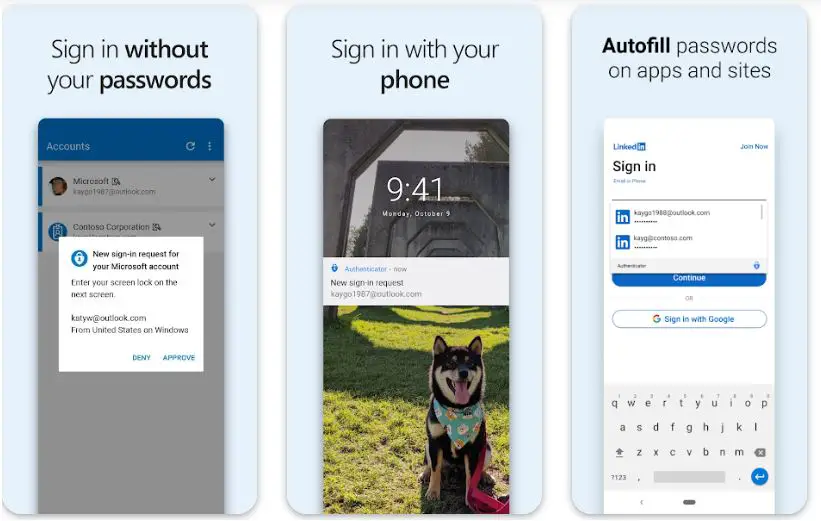
3. Microsoft Authenticator
Microsoft Authenticator stands out as a robust Google Authenticator alternative in the ever-evolving digital security landscape. Developed by Microsoft, this app offers several unique features that distinguish it from traditional authentication methods.
A key advantage of Microsoft Authenticator is its support for multi-factor authentication (MFA), adding an extra layer of security beyond the standard two-factor authentication (2FA). Users can opt for biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, for an even more secure login process.
The app’s seamless integration with Microsoft services, such as Office 365 and Azure, is a standout feature. This integration enhances user experience and allows quick and secure access to Microsoft accounts and services.
With support for time-based one-time passwords (TOTP), Microsoft Authenticator is compatible with various third-party services that utilize 2FA. This versatility makes it a reliable option for securing various online accounts beyond Microsoft’s ecosystem.
Moreover, Microsoft Authenticator extends its reach beyond smartphones, offering compatibility with tablets and iPads. This cross-device support provides users with flexibility in accessing their authentication codes.
The app’s cloud backup feature adds another convenience layer, allowing users to easily restore their 2FA tokens, ensuring continuous access even during device changes.
With its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features, Microsoft Authenticator is an excellent choice for individuals and organizations seeking a reliable and versatile authentication solution.
In conclusion, Microsoft Authenticator is a powerful and feature-rich alternative to Google Authenticator. Its multi-factor authentication, seamless integration with Microsoft services, TOTP support, tablet compatibility, and cloud backup make it an attractive option for enhancing online security.
Pros:-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Microsoft Authenticator offers support for multi-factor authentication, providing an extra layer of security beyond traditional two-factor authentication (2FA).
Biometric Authentication: The app allows users to utilize biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, for enhanced security and ease of use.Seamless Integration: Microsoft Authenticator seamlessly integrates with Microsoft services like Office 365 and Azure, facilitating quick and secure access to Microsoft accounts and services.
Time-Based One-Time Passwords (TOTP) Support: The app supports TOTP, making it compatible with various third-party services that utilize 2FA.
Cross-Device Support: Microsoft Authenticator is compatible with smartphones and tablets, offering flexibility in accessing authentication codes across multiple devices.
Cloud Backup: The app’s cloud backup feature ensures easy restoration of 2FA tokens, providing continuous access even during device changes or failures.
User-Friendly Interface: Microsoft Authenticator features an intuitive interface, making it easy for users to navigate and use effectively.
Cons:-
Platform Dependency: While Microsoft Authenticator is available for Android and iOS devices, users of other operating systems may not have access to the app.
Microsoft Ecosystem: The app’s seamless integration benefits users within the Microsoft ecosystem, but it may not appeal to those who primarily use services from other providers.
Limited Offline Use: Like many 2FA apps, Microsoft Authenticator requires an internet connection for certain operations, which might be inconvenient in offline scenarios.
Third-Party Dependency: The app relies on Microsoft’s servers for authentication, which may raise concerns about data privacy and security for some users.
Account Registration Required: Setting up a Microsoft account is necessary to use Microsoft Authenticator, adding an extra step compared to standalone 2FA apps.
Not Open Source: Some security-conscious users may prefer open-source alternatives, which allow code scrutiny for potential vulnerabilities.
In conclusion, Microsoft Authenticator presents compelling advantages, including MFA support, biometric authentication, seamless integration, TOTP compatibility, cross-device support, and cloud backup.
However, users should consider factors like platform dependency, ecosystem alignment, and offline usability while choosing their ideal 2FA app. By carefully evaluating these pros and cons, users can make informed decisions that align with their security and usability preferences.
Download The App From Google Play Store
Download The App From Apple App Store
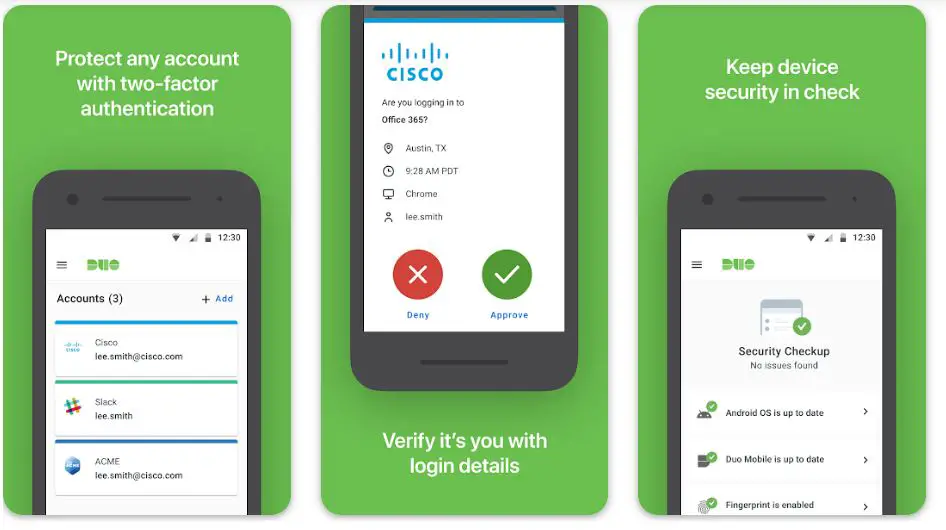
4. Duo Mobile
In robust two-factor authentication (2FA) apps, Duo Mobile emerges as a compelling Google Authenticator alternative. Developed by Duo Security, this app offers unique features that set it apart from traditional authentication methods.
Duo Mobile provides a seamless and secure 2FA experience through its push-based authentication. This innovative approach sends a push notification to the user’s device, allowing them to approve or deny login requests with a simple tap. This frictionless process enhances user convenience while maintaining strong security.
One of the standout features of Duo Mobile is its support for multiple authentication methods, including time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) and biometric authentication. This versatility allows users to choose the best method for their preferences and devices.
The app’s compatibility with various platforms, including smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches, provides users a seamless experience across different devices. This cross-platform support ensures accessibility and convenience for users on the go.
Moreover, Duo Mobile offers an additional layer of security with its self-enrollment process. Users can self-register their devices, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to their accounts.
For added protection, Duo Mobile leverages end-to-end encryption for all communication, safeguarding sensitive data from potential threats.
With its user-friendly interface and comprehensive feature set, Duo Mobile is an excellent choice for individuals and organizations seeking to fortify their digital security.
In conclusion, Duo Mobile is a powerful and versatile alternative to Google Authenticator. Its push-based authentication, support for multiple authentication methods, cross-platform compatibility, self-enrollment process, and end-to-end encryption make it a standout option for enhancing online security.
Pros:-
Push-Based Authentication: Duo Mobile’s push-based authentication offers a frictionless experience, allowing users to approve login requests with a simple tap, enhancing convenience without compromising security.
Multiple Authentication Methods: The app supports various authentication methods, including time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) and biometric authentication, providing users with flexibility and options based on their preferences and device capabilities.
Cross-Platform Compatibility: Duo Mobile is compatible with smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches, ensuring a seamless experience across different devices and platforms.
Self-Enrollment Process: The self-enrollment feature allows users to easily register their devices, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and adding an extra layer of security.
End-to-End Encryption: Duo Mobile leverages end-to-end encryption for all communication, protecting sensitive data from potential threats.
User-Friendly Interface: The app’s intuitive interface makes it easy for tech-savvy individuals and newcomers to navigate and use efficiently.
Trusted Developer: Duo Mobile is developed by Duo Security, a reputable company known for its expertise in cybersecurity and authentication solutions.
Cons:-
Dependency on Duo Security: As Duo Security develops Duo Mobile, users must rely on the company’s servers for authentication, which may raise concerns about data privacy and security.
Internet Connection Required: Like many 2FA apps, Duo Mobile requires an internet connection for certain operations, which might be inconvenient in offline scenarios.
Account Registration Required: Setting up an account with Duo Mobile is necessary to utilize its authentication services, which may add an extra step compared to more straightforward standalone 2FA apps.
Not Open Source: Some security-conscious users may prefer open-source alternatives, which allow code scrutiny for potential vulnerabilities.
Limited Offline Use: While push-based authentication offers convenience, it may require an internet connection to work effectively, limiting offline usability.
Mixed Reviews on Battery Consumption: Some users have reported that Duo Mobile’s push notifications and background activity can impact device battery life.
In conclusion, Duo Mobile offers compelling advantages, including push-based authentication, multiple authentication methods, cross-platform compatibility, a self-enrollment process, and end-to-end encryption.
However, users should consider factors like third-party dependency, internet connection requirements, account registration, and battery consumption while choosing their ideal 2FA app. By carefully evaluating these pros and cons, users can make informed decisions that align with their security and usability preferences.
Download The App From Google Play Store
Download The App From Apple App Store
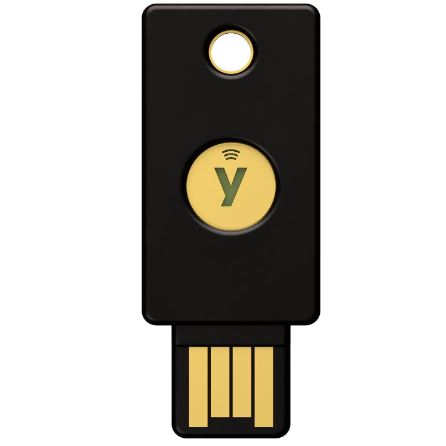
5. YubiKey
In robust authentication solutions, YubiKey shines as a compelling Google Authenticator alternative. Developed by Yubico, this versatile security key offers a range of advanced features that set it apart from traditional authentication methods.
At the heart of YubiKey lies its cutting-edge technology, including support for U2F (Universal 2nd Factor) and FIDO2 (Fast Identity Online). These open authentication standards provide a secure and phishing-resistant login experience, ensuring strong protection against unauthorized access.
One of the standout features of YubiKey is its physical form factor, which is designed to fit into standard USB-A ports. This compact design makes it convenient for users to easily carry their keys, providing hassle-free access to their accounts across various devices.
Beyond its USB connectivity, YubiKey also caters to the modern world with NFC login capabilities. Users with NFC-enabled devices can tap their YubiKey for seamless authentication, adding to the versatility of this security key.
Furthermore, YubiKey stands out for its heavy-duty build, making it shock-resistant and waterproof. This robust construction ensures the key’s durability even in challenging environments, offering peace of mind to users who value security and reliability.
With support for dual verification, YubiKey allows users to strengthen their authentication process by combining multiple factors, such as a PIN or biometric scan, along with the physical key.
In conclusion, YubiKey is a powerful and multifaceted Google Authenticator alternative. Its support for U2F and FIDO2, compatibility with USB-A and NFC, heavy-duty construction, and dual verification capabilities make it a standout choice for individuals and organizations seeking to elevate their digital security.
Pros:-
Advanced Security: YubiKey supports U2F and FIDO2, providing strong protection against phishing attacks and unauthorized access and enhancing overall security.
Physical Form Factor: The compact design of YubiKey, with compatibility for USB-A ports and NFC login, offers convenience and ease of use for users across various devices.
Versatility: YubiKey’s support for NFC login extends its compatibility to modern devices with NFC capabilities, further enhancing its usability.
Robust Construction: YubiKey’s heavy-duty and shock-resistant build ensures durability and reliability even in challenging environments.
Dual Verification: With dual verification capabilities, YubiKey allows users to combine multiple factors for authentication, adding an extra layer of security.
Phishing Resistance: YubiKey’s hardware-based authentication significantly reduces the risk of falling victim to phishing attacks, offering increased peace of mind.
Wide Adoption: YubiKey is widely adopted and supported by various platforms and services, making it a versatile choice for securing a broad range of accounts.
Cons:-
Physical Key Required: Unlike software-based solutions, YubiKey requires users to have a physical key for authentication, which may be less convenient for some users.
Initial Setup: Setting up YubiKey with various accounts may require an initial configuration process, which could take time and effort.
Compatibility: While YubiKey is supported by many services, not all platforms may offer native support for this authentication method, potentially limiting its use on certain websites or applications.
Cost: YubiKey is a premium security product, and purchasing multiple keys for different devices or backups may involve additional expenses.
Risk of Loss or Damage: As with any physical device, there is a risk of losing or damaging the YubiKey, which could lead to potential access issues if a backup method is unavailable.
Limited Mobile Device Support: While YubiKey offers NFC support for mobile devices, not all smartphones or tablets may have NFC capabilities, reducing compatibility for some users.
In conclusion, YubiKey offers a range of advantages, including advanced security, versatile form factor, robust construction, and phishing resistance.
However, users should consider factors like needing a physical key, initial setup, compatibility, cost, and potential risks while evaluating YubiKey as their Google Authenticator alternative. By carefully weighing these pros and cons, users can decide to strengthen their digital security with YubiKey.
6. FIDO2 Security Key
In robust two-factor authentication (2FA) solutions, the FIDO2 Security Key emerges as an innovative Google Authenticator alternative. This security key is designed with a folding design and offers many advanced features that set it apart from traditional authentication methods.
The FIDO2 Security Key utilizes the latest FIDO2 standard, providing a strong foundation for multi-layered protection. Its support for HOTP (HMAC-based One-Time Password) ensures a secure and phishing-resistant login experience, safeguarding users from unauthorized access.

One of the standout features of the FIDO2 Security Key lies in its versatile compatibility. It supports various operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and Mac OS, making it suitable for various users across different platforms.
Furthermore, this security key extends its support to popular online services and platforms, such as Gmail, Facebook, Dropbox, Salesforce, and GitHub, enhancing its usability for securing multiple accounts.
The foldable design of the key offers an added layer of convenience, allowing users to protect the USB (Type A) connector when not in use. This design also ensures the key’s durability, making it resistant to physical damage.
With its focus on user privacy and security, the FIDO2 Security Key ensures that cryptographic operations are performed directly on the device without sharing sensitive information with external parties.
In conclusion, the FIDO2 Security Key is a powerful and adaptable Google Authenticator alternative. Its utilization of the FIDO2 standard, versatile platform compatibility, support for popular online services, folding design, and cryptographic privacy features make it an excellent choice for individuals and organizations seeking to bolster their digital security.
Pros:-
Strong Security: The FIDO2 Security Key utilizes the latest FIDO2 standard, offering multi-layered protection and secure login experiences, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Phishing Resistance: Support for HOTP ensures a phishing-resistant authentication process, protecting users from phishing attacks.
Versatile Compatibility: The FIDO2 Security Key is compatible with various operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and Mac OS, making it suitable for many users.
Support for Popular Services: This security key extends its support to popular online services and platforms like Gmail, Facebook, Dropbox, Salesforce, and GitHub, enhancing its usability for securing multiple accounts.
Folding Design: The foldable design protects the USB (Type A) connector when not in use, improving portability and ensuring the key’s durability against potential physical damage.
Cryptographic Privacy: Cryptographic operations are performed directly on the device, ensuring user privacy and security without sharing sensitive information with external parties.
Physical Token: The FIDO2 Security Key provides a physical token for authentication, reducing reliance on mobile devices and offering an additional layer of protection.
Cons:-
Physical Key Required: As with all hardware-based solutions, users need to have the physical FIDO2 Security Key for authentication, which may be less convenient than software-based methods.
Initial Setup: Setting up the FIDO2 Security Key with various accounts may require an initial configuration process, which could take time and effort.
Port Compatibility: As a USB (Type A) device, the key may not be compatible with devices that lack a USB-A port, potentially limiting its use on certain devices.
Risk of Loss or Damage: Similar to any physical device, there is a risk of losing or damaging the FIDO2 Security Key, which could lead to potential access issues if a backup method is unavailable.
Limited Mobile Device Support: The FIDO2 Security Key may have limited support on some mobile devices, affecting its usability for users relying heavily on smartphones or tablets.
Cost: The FIDO2 Security Key is a premium security product, and purchasing multiple keys for different devices or as backups may involve additional expenses.
In conclusion, the FIDO2 Security Key offers a range of advantages, including strong security, phishing resistance, versatile compatibility, folding design, support for popular services, and cryptographic privacy.
However, users should consider factors like needing a physical key, initial setup, port compatibility, potential risks, limited mobile device support, and cost while evaluating the FIDO2 Security Key as their Google Authenticator alternative. By carefully weighing these pros and cons, users can decide to strengthen their digital security with the FIDO2 Security Key.
Check Price on Amazon7. Aegis Authenticator – Open Source Alternative
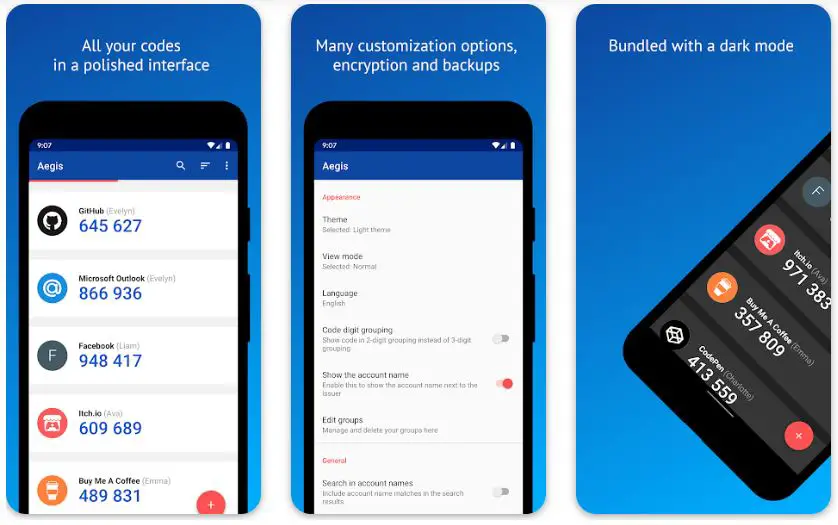
In the realm of robust two-factor authentication (2FA) solutions, Aegis Authenticator stands out as a noteworthy open-source Google Authenticator alternative. Developed by Beem Development, this app offers many unique features that set it apart from traditional authentication methods.
The distinguishing factor of Aegis Authenticator lies in its commitment to open-source principles. Being open-source means that the app’s source code is accessible to the public, enabling transparency, collaboration, and security scrutiny by the developer community.
One of the standout features of Aegis Authenticator is its ease of use. The user-friendly interface ensures a smooth and intuitive experience for setting up and managing 2FA tokens across various accounts.
The app supports both time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) and HMAC-based one-time passwords (HOTP), offering versatility in securing a wide range of online services.
For added convenience, Aegis Authenticator allows users to import and export their tokens, making migrating between devices or creating backups easier.
Regarding security, Aegis Authenticator employs strong encryption to protect user data and authentication tokens, ensuring user privacy and safeguarding against potential threats.
Moreover, as an open-source project, the app benefits from continuous community-driven development and updates, providing users with confidence in its long-term reliability.
In conclusion, Aegis Authenticator is a powerful open-source alternative to Google Authenticator. Its open-source nature, user-friendly interface, support for TOTP and HOTP, import and export functionality, and strong encryption make it an attractive choice for individuals and organizations seeking a trustworthy and customizable 2FA solution.
Pros:-
Open Source: Aegis Authenticator’s open-source nature allows for transparency, collaboration, and security scrutiny by the developer community, enhancing trust and credibility.
User-Friendly Interface: The app’s intuitive interface ensures a smooth and user-friendly experience for setting up and managing 2FA tokens.
Versatile Support: Aegis Authenticator supports both time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) and HMAC-based one-time passwords (HOTP), making it compatible with various online services.
Import and Export: The app allows users to import and export their tokens, providing convenience in migrating between devices or creating backups.
Strong Encryption: Aegis Authenticator employs robust encryption to protect user data and authentication tokens, ensuring high security.
Community-Driven Development: Being an open-source project, Aegis Authenticator benefits from continuous development and updates driven by the developer community, ensuring ongoing improvements and bug fixes.
Customizability: The open-source nature of Aegis Authenticator allows tech-savvy users to customize the app according to their specific security needs and preferences.
Cons:-
Limited Platform Support: As of the current version, Aegis Authenticator is only available for Android devices, which may restrict its usability for users on other platforms.
No Cloud Backup: Unlike some proprietary authentication apps, Aegis Authenticator does not offer built-in cloud backup functionality, requiring users to export and import tokens for device transfers manually.
Potential for Bugs: While community-driven development can lead to continuous improvements, it may also introduce occasional bugs or compatibility issues with certain devices or systems.
Less Streamlined Setup: Aegis Authenticator’s open-source nature may require more manual setup and configuration than closed-source alternatives offering guided setup processes.
Dependency on Community Support: As an open-source project, Aegis Authenticator’s long-term development and support rely on the availability and engagement of the developer community.
No Official iOS Version: Aegis Authenticator is not officially available for iOS devices, limiting its usage to users primarily using Apple products.
In conclusion, Aegis Authenticator offers a range of advantages, including its open-source nature, user-friendly interface, versatile support, import/export functionality, strong encryption, and community-driven development.
However, users should consider factors like platform support, cloud backup options, potential bugs, setup complexity, dependency on community support, and iOS availability while evaluating Aegis Authenticator as their open-source Google Authenticator alternative.
By carefully weighing these pros and cons, users can decide to strengthen their digital security with Aegis Authenticator.
Download The App From Google Play Store
Factors To Consider When Choosing an Alternative
In today’s digital landscape, securing online accounts has become paramount to safeguarding sensitive information and personal data. Two-factor authentication (2FA) has emerged as a popular method to enhance account security, and Google Authenticator has long been a go-to choice for many users.
However, there are various factors to consider when choosing a Google Authenticator alternative that best suits individual needs and preferences.
1. Security Features: The primary concern when selecting an authenticator app is its security level. Look for alternatives supporting robust authentication protocols, such as FIDO2 (Fast Identity Online) and U2F (Universal 2nd Factor), as they protect against phishing and account breaches.
2. Compatibility: Ensure that the chosen alternative is compatible with your frequently used platforms and services. It should work seamlessly with various operating systems and support various online accounts.
3. User-Friendly Interface: An app with an intuitive and user-friendly interface will enhance the overall experience and ease of use. Look for alternatives that make setting up and managing 2FA tokens straightforward and hassle-free.
4. Backup and Recovery: Consider whether the alternative offers token backup and recovery options. A backup ensures you can regain access to your accounts in case of device loss or failure.
5. Device Support: Check if the alternative is compatible with your devices. Some authenticator apps are available for smartphones and smartwatches, providing flexibility and convenience.
6. Biometric Authentication: Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, can add more security and convenience to the authentication process. Look for alternatives that support this feature if it aligns with your preferences.
7. Open-Source vs. Closed-Source: Decide between open-source and closed-source alternatives based on your comfort level with code transparency and community-driven development.
8. Third-Party Trust: Consider the reputation and trustworthiness of the app’s developer or company. Opt for alternatives from reputable sources with a track record of providing secure solutions.
9. Offline Access: Evaluate whether the chosen alternative requires an internet connection for generating authentication codes. Some apps offer offline access, which can be beneficial in scenarios with limited connectivity.
10. Cost: While many authenticator apps are free, some may offer premium features at a cost. Assess whether the additional features justify the expense for your specific use case.
In conclusion, selecting the right Google Authenticator alternative requires thoughtful consideration of various factors.
By focusing on security features, compatibility, user-friendliness, backup options, device support, biometric authentication, source code transparency, developer reputation, offline access, and cost, users can make an informed decision that aligns with their security needs and usability preferences.
Evaluating these factors will lead to a more robust and secure 2FA solution, ultimately enhancing online account protection.
📗FAQ’s
Is there an alternative to Google Authenticator for free?
Yes, Authy is a popular free alternative to Google Authenticator, offering additional features like multi-device synchronization and cloud backup.
If you are looking for an open-source alternative then consider Aegis Authenticator.
Is Authy better than Google Authenticator?
It depends on user preferences. Authy provides more features, while Google Authenticator offers simplicity and independence.
How do I use Google Authenticator without the app?
Google Authenticator requires the app to generate codes. Without the app, you won’t be able to use it.
Do you need Google Authenticator?
It’s optional, but using 2FA like Google Authenticator enhances account security.
Is there a better 2FA than Google Authenticator?
Authy is considered a feature-rich alternative to Google Authenticator.
What is better than Google Authenticator?
Authy is a popular choice for those seeking more features and convenience.
Why not to use Authy?
Some users prefer decentralized 2FA solutions, which Authy’s cloud-based approach might not align with.
Which is the strongest 2FA method?
Hardware tokens like YubiKey are considered among the strongest 2FA methods.
What happens if I lose my phone with Google Authenticator?
Without a backup, you may lose access to your accounts. Save backup codes or use Authy’s cloud backup.
How to do 2-step verification without a phone?
Some services offer backup options like email verification or backup codes if you lose your phone.
What happens if I lost my Google Authenticator app?
Without a backup, you may face difficulties accessing your accounts.
Why 2FA is no longer safe?
2FA can be vulnerable to SIM-swapping attacks and phishing attempts.
Is Google Authenticator safer than SMS?
Yes, Google Authenticator is safer than SMS-based 2FA, which can be susceptible to SIM swapping.
Which authentication factor is strongest?
The strongest authentication involves multiple factors, like something you know, have, and are.
What is the most secure Authenticator?
Hardware tokens like YubiKey and biometric authentication are considered highly secure.
Which is the safest authentication type?
Hardware tokens and biometric authentication are among the safest options.
What is the easiest Authenticator to use?
Google Authenticator is known for its simplicity and ease of use.
What is safer than 2FA?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) with hardware tokens is considered safer than 2FA.
Can I have Google Authenticator on two devices?
Google Authenticator is tied to one device at a time, but Authy supports multi-device synchronization.
Closing Remarks
Navigating the landscape of two-factor authentication can be daunting, given the myriad of solutions available today. However, the key to finding the best Google Authenticator alternatives lies in understanding your needs and security preferences.
Whether you value cross-platform compatibility, backup and restore functionalities, or multi-device syncing, there is a 2FA solution designed to meet your requirements.
Remember, the ultimate goal is to ensure the safety of your online identity and data, and each tool we’ve discussed offers unique features to help you achieve this.
It’s essential to explore and consider the features of Authy, LastPass Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, Duo Mobile, and YubiKey, as they each bring a unique blend of security, convenience, and usability to the table.
By evaluating these Google Authenticator alternatives, you’re making a crucial step towards enhanced digital security, granting yourself peace of mind in an increasingly interconnected world.
Rest assured, with these tools; you’re well-equipped to secure your online presence against potential threats.